
Products: ABAQUS/Standard ABAQUS/Explicit ABAQUS/CAE

A general beam section:
is used to define beam section properties that are computed once and held constant for the entire analysis;
can be used to define linear or nonlinear section behavior;
for linear section behavior can be associated only with linear material behavior; and
enables the use of meshed cross-sections (“Meshed beam cross-sections,” Section 10.4.1).

Linear section response is calculated as follows. At each point in the cross-section the axial stress, ![]() , and the shear stress,
, and the shear stress, ![]() , are given by
, are given by
![]()
![]()
is Young's modulus (which may depend on the temperature, ![]() , and field variables,
, and field variables, ![]() , at the beam axis);
, at the beam axis);
![]()
is the shear modulus (which may also depend on the temperature and field variables at the beam axis);
![]()
is the axial strain;
![]()
is the shear caused by twist; and
![]()
is the thermal expansion strain.
![]()
![]()
is the thermal expansion coefficient,
![]()
is the current temperature at a point in the beam section,
![]()
are field variables,
![]()
is the reference temperature for ![]() ,
,
![]()
is the initial temperature at this point (see “Defining initial temperatures” in “Initial conditions,” Section 27.2.1), and
![]()
are the initial values of the field variables at this point (see “Defining initial values of predefined field variables” in “Initial conditions,” Section 27.2.1).
The temperature is defined from the temperature of the beam axis and the gradients of temperature with respect to the local ![]() - and
- and ![]() -axes:
-axes:
![]()
The axial force, N; bending moments, ![]() and
and ![]() about the 1 and 2 beam section local axes; torque, T; and bimoment, W, are defined in terms of the axial stress
about the 1 and 2 beam section local axes; torque, T; and bimoment, W, are defined in terms of the axial stress ![]() and the shear stress
and the shear stress ![]() (see “Beam element formulation,” Section 3.5.2 of the ABAQUS Theory Manual). These terms are
(see “Beam element formulation,” Section 3.5.2 of the ABAQUS Theory Manual). These terms are
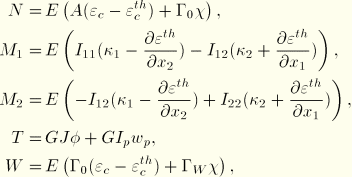
A
is the area of the section,
![]()
is the moment of inertia for bending about the 1-axis of the section,
![]()
is the moment of inertia for cross-bending,
![]()
is the moment of inertia for bending about the 2-axis of the section,
J
is the torsional rigidity,
![]()
is the sectorial moment of the section,
![]()
is the warping constant of the section,
![]()
is the axial strain measured at the centroid of the section,
![]()
is the thermal axial strain,
![]()
is the curvature change about the first beam section local axis,
![]()
is the curvature change about the second beam section local axis,
![]()
is the twist,
![]()
is the bicurvature defining the axial strain in the section due to the twist of the beam, and
![]()
is the difference between the unconstrained warping amplitude, ![]() , and the actual warping amplitude, w.
, and the actual warping amplitude, w.
Linear beam section response is defined geometrically by A, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() , J, and—if necessary—
, J, and—if necessary—![]() and
and ![]() .
.
You can input these geometric quantities directly or specify a standard library section and ABAQUS will calculate these quantities. In either case define the orientation of the beam section (see “Beam element cross-section orientation,” Section 23.3.4); give Young's modulus, the torsional shear modulus, and the coefficient of thermal expansion, as functions of temperature; and associate the section properties with a region of your model.
If the thermal expansion coefficient is temperature dependent, the reference temperature for thermal expansion must also be defined as described later in this section.
You can define “generalized” linear section behavior by specifying A, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() , J, and—if necessary—
, J, and—if necessary—![]() and
and ![]() directly. In this case you can specify the location of the centroid, thus allowing the bending axis of the beam to be offset from the line of its nodes. In addition, you can specify the location of the shear center.
directly. In this case you can specify the location of the centroid, thus allowing the bending axis of the beam to be offset from the line of its nodes. In addition, you can specify the location of the shear center.
| Input File Usage: | Use the following option to define generalized linear beam section properties: |
*BEAM GENERAL SECTION, SECTION=GENERAL, ELSET=name A, If necessary, use the following option to specify the location of the centroid: *CENTROID If necessary, use the following option to specify the location of the shear center: *SHEAR CENTER |
| ABAQUS/CAE Usage: | Property module: |
You can select one of the standard library sections (see “Beam cross-section library,” Section 23.3.9) and specify the geometric input data needed to define the shape of the cross-section. ABAQUS will then calculate the geometric quantities needed to define the section behavior automatically.
| Input File Usage: | *BEAM GENERAL SECTION, SECTION=library_section, ELSET=name |
| ABAQUS/CAE Usage: | Property module: |
Linear beam section response for a meshed section profile is obtained by numerical integration from the two-dimensional model. The numerical integration is performed once, determining the beam stiffness and inertia quantities, as well as the coordinates of the centroid and shear center, for the duration of the analysis. These beam section properties are calculated during the beam section generation and are written to the text file jobname.bsp. This text file can be included in the beam model. See “Meshed beam cross-sections,” Section 10.4.1, for a detailed description of the properties defining the linear beam section response for a meshed section, as well as for how a typical meshed section is analyzed.
| Input File Usage: | Use the following options: |
*BEAM GENERAL SECTION, SECTION=MESHED, ELSET=name *INCLUDE, INPUT=jobname.bsp |
| ABAQUS/CAE Usage: | Meshed cross-sections are not supported in ABAQUS/CAE. |

Typically nonlinear section behavior is used to include the experimentally measured nonlinear response of a beam-like component whose section distorts in its plane. When the section behaves according to beam theory (that is, the section does not distort in its plane) but the material has nonlinear response, it is usually better to use a beam section integrated during the analysis to define the section geometrically (see “Using a beam section integrated during the analysis to define the section behavior,” Section 23.3.6), in association with a material definition.
Nonlinear section behavior can also be used to model beam section collapse in an approximate sense: “Nonlinear dynamic analysis of a structure with local inelastic collapse,” Section 2.1.1 of the ABAQUS Example Problems Manual, illustrates this for the case of a pipe section that may suffer inelastic collapse due to the application of a large bending moment. In following this approach you should recognize that such unstable section collapse, like any unstable behavior, typically involves localization of the deformation: results will, therefore, be strongly mesh sensitive.
Nonlinear section response is assumed to be defined by
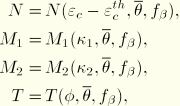
These nonlinear responses may be purely elastic (that is, fully reversible—the loading and unloading responses are the same, even though the behavior is nonlinear) or may be elastic-plastic and, therefore, irreversible.
The assumption that these nonlinear responses are uncoupled is restrictive; in general, there is some interaction between these four behaviors, and the responses are coupled. You must determine if this approximation is reasonable for a particular case. The approach works well if the response is dominated by one behavior, such as bending about one axis. However, it may introduce additional errors if the response involves combined loadings.
You can define “generalized” nonlinear section behavior by specifying the area, A; moments of inertia, ![]() for bending about the 1-axis of the section,
for bending about the 1-axis of the section, ![]() for bending about the 2-axis of the section, and
for bending about the 2-axis of the section, and ![]() for cross-bending; and torsional rigidity, J. These values are used only to calculate the transverse shear stiffness; and, if needed, A is used to compute the mass density of the element. In addition, you can define the orientation and the axial, bending, and torsional behavior of the beam section (N,
for cross-bending; and torsional rigidity, J. These values are used only to calculate the transverse shear stiffness; and, if needed, A is used to compute the mass density of the element. In addition, you can define the orientation and the axial, bending, and torsional behavior of the beam section (N, ![]() ,
, ![]() , T), as well as the thermal expansion coefficient. If the thermal expansion coefficient is temperature dependent, the reference temperature for thermal expansion must also be defined as described below.
, T), as well as the thermal expansion coefficient. If the thermal expansion coefficient is temperature dependent, the reference temperature for thermal expansion must also be defined as described below.
Nonlinear generalized beam section behavior cannot be used with beam elements with warping degrees of freedom.
The axial, bending, and torsional behavior of the beam section and the thermal expansion coefficient are defined by tables. See “Material data definition,” Section 16.1.2, for a detailed discussion of the tabular input conventions. In particular, you must ensure that the range of values given for the variables is sufficient for the application since ABAQUS assumes a constant value of the dependent variable outside this range.
| Input File Usage: | Use the following options to define generalized nonlinear beam section properties: |
*BEAM GENERAL SECTION, SECTION=NONLINEAR GENERAL, ELSET=name A, |
| ABAQUS/CAE Usage: | Nonlinear generalized cross-sections are not supported in ABAQUS/CAE. |
If the particular behavior is linear, N, ![]() ,
, ![]() , and T should be specified as functions of the temperature and predefined field variables, if appropriate.
, and T should be specified as functions of the temperature and predefined field variables, if appropriate.
As an example of axial behavior, if
![]()
| ABAQUS/CAE Usage: | Nonlinear generalized cross-sections are not supported in ABAQUS/CAE. |
If the particular behavior is nonlinear but elastic, the data should be given from the most negative value of the kinematic variable to the most positive value, always giving a point at the origin. See Figure 23.3.7–1 for an example.
| ABAQUS/CAE Usage: | Nonlinear generalized cross-sections are not supported in ABAQUS/CAE. |
By default, elastic-plastic response is assumed for N, ![]() ,
, ![]() , and T.
, and T.
The inelastic model is based on assuming linear elasticity and isotropic hardening (or softening) plasticity. The data in this case must begin with the ![]() point and proceed to give positive values of the kinematic variable at increasing positive values of the conjugate force or moment. Strain softening is allowed. The elastic modulus is defined by the slope of the initial line segment, so that straining beyond the point that terminates that initial line segment will be partially inelastic. If strain reversal occurs in that part of the response, it will be elastic initially. See Figure 23.3.7–2 for an example.
point and proceed to give positive values of the kinematic variable at increasing positive values of the conjugate force or moment. Strain softening is allowed. The elastic modulus is defined by the slope of the initial line segment, so that straining beyond the point that terminates that initial line segment will be partially inelastic. If strain reversal occurs in that part of the response, it will be elastic initially. See Figure 23.3.7–2 for an example.
| ABAQUS/CAE Usage: | Nonlinear generalized cross-sections are not supported in ABAQUS/CAE. |

The thermal expansion coefficient may be temperature dependent. In this case the reference temperature for thermal expansion, ![]() , must be defined.
, must be defined.
| Input File Usage: | *BEAM GENERAL SECTION, ZERO= |
| ABAQUS/CAE Usage: | Property module: Create Section: select Beam as the section Category and Beam as the section Type: Section integration: Before analysis: Basic: Reference temperature: |

You can define initial stresses (see “Defining initial stresses” in “Initial conditions,” Section 27.2.1) for general beam sections that will be applied as initial section forces and moments. Initial conditions can be specified only for the axial force, the bending moments, and the twisting moment. Initial conditions cannot be prescribed for the transverse shear forces.

In the shear flexible elements ABAQUS provides for a possible uniform cross-sectional area change by allowing you to specify an effective Poisson's ratio for the section. This effect is considered only in geometrically nonlinear analysis (see “Procedures: overview,” Section 6.1.1) and is provided to model the reduction or increase in the cross-sectional area for a beam subjected to large axial stretch.
The value of the effective Poisson's ratio must be between –1.0 and 0.5. By default, this effective Poisson's ratio for the section is set to 0.0 so that this effect is ignored. Setting the effective Poisson's ratio to 0.5 implies that the overall response of the section is incompressible. This behavior is appropriate if the beam is made of rubber or if it is made of a typical metal whose overall response at large deformation is essentially incompressible (because it is dominated by plasticity). Values between 0.0 and 0.5 mean that the cross-sectional area changes proportionally between no change and incompressibility, respectively. A negative value of the effective Poisson's ratio will result in an increase in the cross-sectional area in response to tensile axial strains.
This effective Poisson's ratio is not available for use with Euler-Bernoulli beam elements.
| Input File Usage: | *BEAM GENERAL SECTION, POISSON= |
| ABAQUS/CAE Usage: | Property module: Create Section: select Beam as the section Category and Beam as the section Type: Section integration: Before analysis: Basic: Section Poisson's ratio: |

When the beam section and material behavior are defined by a general beam section, you can include mass and stiffness proportional damping in the dynamic response (calculated in ABAQUS/Standard with the direct time integration procedure, “Implicit dynamic analysis using direct integration,” Section 6.3.2). Stiffness proportional damping cannot be used with nonlinear generalized sections.
See “Material damping,” Section 20.1.1, for more information about the material damping types available in ABAQUS.
| Input File Usage: | Use both of the following options: |
*BEAM GENERAL SECTION *DAMPING |
| ABAQUS/CAE Usage: | Property module: Create Section: select Beam as the section Category and Beam as the section Type: Section integration: Before analysis: Advanced: Alpha, Beta, and Composite |

Define temperatures and field variables by giving the values at the origin of the cross-section as either predefined fields or initial conditions (see “Predefined fields,” Section 27.6.1, or “Initial conditions,” Section 27.2.1). Temperature gradients can be specified in the local 1- and 2-directions; other field-variable gradients defined through the cross-section will be ignored in the response of beam elements that use a general beam section definition.

Only the section forces, moments, and transverse shear forces and section strains, curvatures, and transverse shear strains can be output (see “Element output” in “Output to the data and results files,” Section 4.1.2, and “Element output” in “Output to the output database,” Section 4.1.3).
You can output stress and strain at particular points in the section. For linear section behavior defined using a standard library section or a generalized section, only axial stress and axial strain values are available. For linear section behavior defined using a meshed section, axial and shear stress and strain are available. For nonlinear generalized section behavior, axial strain output only is provided.
To locate points in the section at which output of axial strain (and, for linear section behavior, axial stress) is required, specify the local ![]() coordinates of the point in the cross-section: ABAQUS numbers the points 1, 2, … in the order that they are given.
coordinates of the point in the cross-section: ABAQUS numbers the points 1, 2, … in the order that they are given.
The variation of ![]() over the section is given by
over the section is given by
![]()
For open-section beam element types, the variation of ![]() over the section has an additional term of the form
over the section has an additional term of the form ![]() , where
, where ![]() is the warping function. The warping function itself is undefined in the general beam section definition. Therefore, ABAQUS will not take into account the axial strain due to warping when calculating section points output. Axial strains due to warping are included in the stress/strain output if a beam section integrated during the analysis is used.
is the warping function. The warping function itself is undefined in the general beam section definition. Therefore, ABAQUS will not take into account the axial strain due to warping when calculating section points output. Axial strains due to warping are included in the stress/strain output if a beam section integrated during the analysis is used.
ABAQUS uses St. Venant torsion theory for noncircular solid sections. The torsion function and its derivatives are necessary to calculate shear stresses in the plane of the cross-section. The function and its derivatives are not stored for a general beam section. Therefore, you can request output of axial components of stress/strain only. A beam section integrated during the analysis must be used to obtain output of shear stresses.
| Input File Usage: | Use both of the following options to specify the output section points for general beam sections: |
*BEAM GENERAL SECTION *SECTION POINTS |
| ABAQUS/CAE Usage: | Property module: Create Section: select Beam as the section Category and Beam as the section Type: Section integration: Before analysis: Output Points: x1, x2, ... |
If you specify the output section points to obtain the maximum axial stress/strain (MAXSS) for a linear generalized section, the output value will be the maximum of the values at the user-specified section points. You must select enough section points to ensure that this is the true maximum. MAXSS output is not available for nonlinear generalized sections or for an ABAQUS/Explicit analysis.
For meshed cross-sections you can indicate in the two-dimensional cross-section analysis the elements and integration points where the stress and strain will be calculated during the subsequent beam analysis. ABAQUS will then add the section points specification to the resulting jobname.bsp text file. This text file is then included as the data for the general beam section definition in the subsequent beam analysis. See “Meshed beam cross-sections,” Section 10.4.1, for details.
The variation of the axial strain ![]() over the meshed section is given by
over the meshed section is given by
![]()
The variations of shear components ![]() and
and ![]() over the meshed section are given by
over the meshed section are given by
![]()
![]()
For the case of an orthotropic composite beam material, the axial stress ![]() and the two shear components
and the two shear components ![]() and
and ![]() are calculated in the beam section (1, 2) axis as follows:
are calculated in the beam section (1, 2) axis as follows:
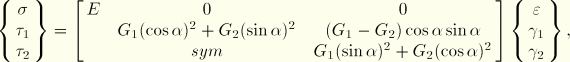
| Input File Usage: | Use both of the following options in the two-dimensional meshed cross-section analysis to specify the output section points for the subsequent beam analysis: |
*BEAM SECTION GENERATE *SECTION POINTS section_point_label, element_number, integration_point_number |
| ABAQUS/CAE Usage: | Meshed cross-sections are not supported in ABAQUS/CAE. |