LeggedRaces
Contents
Motivation
In a legged race, a group of people must try to move forward as quickly as possible with their legs tied to each other. In other words, the group can only be as quick as its slowest link and they must try to move in unison. In many ways, this concept mirrors parallel phasers. In this studio, you will use phasers and forall loops in order to simulate a legged race.
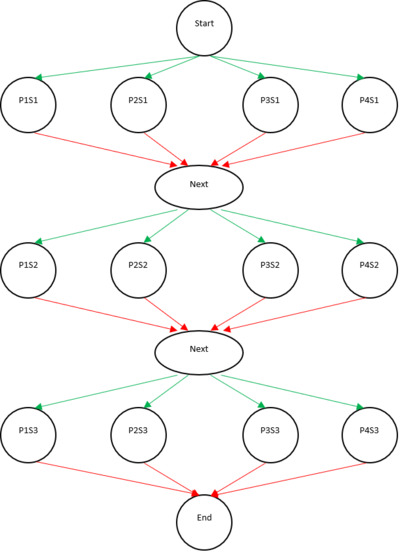
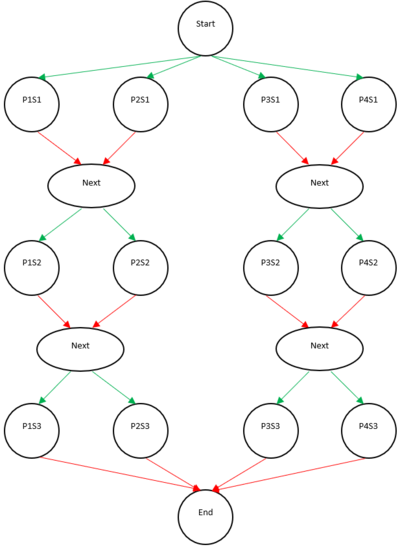
You will complete four methods that cover two different types of races. The first three versions are an "n+1 legged race". This is where all participants are a part of the same group. Each person's legs are tied to their neighbors, and thus it is impossible for one person to take a second step before everyone else has taken their first step. The final method is a "3 legged race". Participants have a partner who they are tied to and can continue to take steps as long as their partner is keeping up with them.
Background
Code To Use
Legged Races
Looping
Phasers
class Phaser (Guide to the Java Phaser)
- register
- bulkRegister
- arriveAndAwaitAdvance
- arrive
- awaitAdvance use via PhaserUtils.awaitAdvanceForPhase(phaser, phase)
If you are on or past the phase you want to await, then calling phaser.awaitAdvance() directly is fine. If you might be on a prior phase, then invoke PhaserUtils.awaitAdvanceForPhase(phaser, phase). If in doubt, invoking awaitAdvanceForPhase is safer.
public static int awaitAdvanceForPhase(Phaser phaser, int phase) {
return awaitAdvanceForPhase(phaser, phase, () -> Thread.yield());
}
public static int awaitAdvanceForPhase(Phaser phaser, int phase, Runnable runnable) {
while (true) {
int currentPhase = phaser.awaitAdvance(phase);
if (currentPhase < 0 || currentPhase > phase) {
return currentPhase;
} else {
if (runnable != null) {
runnable.run();
}
}
}
}
Questions To Ask Yourself
- What are my tasks?
- What work does each task need to do?
- Upon what does each task depend? That is: what does each task have to wait for before it may proceed?
- What could have possibly been more important than adding a random stopping to tie their shoes animation to the visualization?
Code To Implement
SequentialLeggedRace
| class: | SequentialLeggedRace.java | |
| methods: | takeSteps | |
| package: | leggedrace.studio | |
| source folder: | student/src/main/java |
method: public void takeSteps(Participant[] participants, int stepCount) ![]() (sequential implementation only)
(sequential implementation only)
In this implementation, try to solve the problem sequentially. Your method should go through the array of participants and make each one takeStep until you do this for every stepIndex up until the stepCount for every participant.
Hint: Basically, you will need two for loops. One that iterates up until the stepCount and another which goes through the array of participants.
ForallLeggedRace
| class: | ForallLeggedRace.java | |
| methods: | takeSteps | |
| package: | leggedrace.studio | |
| source folder: | student/src/main/java |
method: public void takeSteps(Participant[] participants, int stepCount) ![]() (parallel implementation required)
(parallel implementation required)
In this implementation, the participants should all take each individual step in parallel. However, the steps should be taken each in turn sequentially. Think about where to place the forall loop so that the program only progresses to the next stepIndex after every participant has performed a takeStep with the current index value.
ForallPhasedLeggedRace
| class: | ForallPhasedLeggedRace.java | |
| methods: | takeSteps | |
| package: | leggedrace.studio | |
| source folder: | student/src/main/java |
method: public void takeSteps(Participant[] participants, int stepCount) ![]() (parallel implementation required)
(parallel implementation required)
In this solution, you will flip your sequentialLoop/parallelLoop pattern into a parallelLoop/sequentialLoop pattern with a phaser.
ForallPhasedPointToPointLeggedRace
| class: | ForallPhasedPointToPointLeggedRace.java | |
| methods: | takeSteps | |
| package: | leggedrace.studio | |
| source folder: | student/src/main/java |
method: public void takeSteps(Participant[] participants, int stepCount) ![]() (parallel implementation required)
(parallel implementation required)
In this implementation, you will build on what you did with the forall implementation to incorporate an array of phasers. Start this off by instantiating an array of phasers
Use provided int getPartnerIndex(int) to find the partner for a participant.
private static int getPartnerIndex(int index) {
boolean isOddIndex = (index&0x1) == 0x1;
if( isOddIndex ) {
return index - 1;
} else {
return index + 1;
}
}
Testing Your Solution
Visualization
| class: | LeggedRaceVisualizationApp.java | VIZ |
| package: | leggedrace.viz | |
| source folder: | student/src//java |
Click on the buttons on the right to visualize your solutions when you have implemented them. Here are examples of what the correct visualization should look like for each method.
Correctness
| class: | LeggedRaceTestSuite.java | |
| package: | leggedrace.studio | |
| source folder: | testing/src/test/java |
| class: | PartialCreditLeggedRaceTestSuite.java | |
| package: | leggedrace.studio | |
| source folder: | testing/src/test/java |
When you are passing the tests and your visualization looks good, demo it to an instructor.