Difference between revisions of "Atomic Stack Assignment"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 63: | Line 63: | ||
}</nowiki> | }</nowiki> | ||
===DefaultNode=== | ===DefaultNode=== | ||
| − | [https://www.javadoc.io/static/com.google.code.findbugs/jsr305/3.0.1/javax/annotation/concurrent/Immutable.html @Immutable] class DefaultNode. | + | The mighty [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cons cons cell] goes back to the early days of computing. People have been building amazing systems with this data structure since the 1950s. |
| + | |||
| + | We will build an [https://www.javadoc.io/static/com.google.code.findbugs/jsr305/3.0.1/javax/annotation/concurrent/Immutable.html @Immutable] class DefaultNode which implements interface Node. | ||
{{CodeToImplement|DefaultNode|value<br/>nextNode|stack.node.exercise|main}} | {{CodeToImplement|DefaultNode|value<br/>nextNode|stack.node.exercise|main}} | ||
====constructor and instance variables==== | ====constructor and instance variables==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | The constructor | ||
| + | |||
| + | <nowiki>public DefaultNode(E value, Optional<Node<E>> nextNode)</node> | ||
| + | |||
| + | is passed a value and a nextNode. Hang on to this data in instance variables. As instances of DefaultNode are to be immutable, the instance variables should be marked as <code>final</code>. | ||
| + | |||
====value==== | ====value==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | return the value. | ||
| + | |||
====nextNode==== | ====nextNode==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | return the next node. | ||
==Stack== | ==Stack== | ||
Revision as of 02:33, 10 November 2022
Contents
Background
Implicit Locks
Atomics
Node and Stack Interfaces
interface Node
public interface Node<E> {
E value();
Optional<Node<E>> nextNode();
}
interface Stack
public interface Stack<E> {
void push(E value);
Optional<E> peek();
Optional<E> pop();
}
Example
empty
Stack<String> stack = new NotThreadSafeStack<>(DefaultNode::new);
In this state, stack.peek() will return Optional.empty() and stack.pop() will also return Optional.empty().
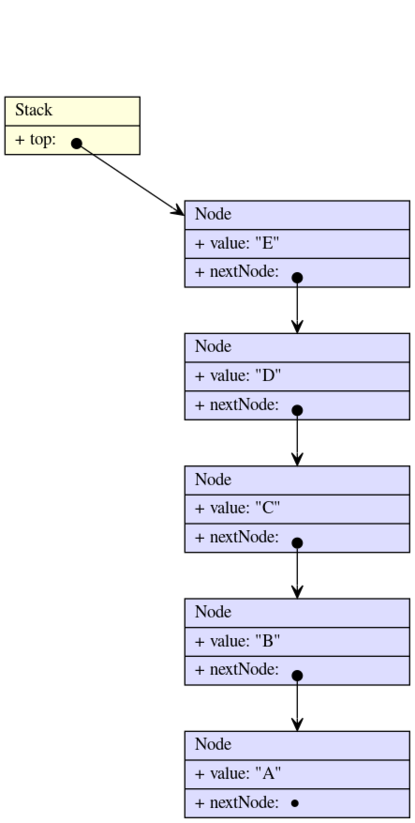
push A, B, C, D, E
Stack<String> stack = new NotThreadSafeStack<>(DefaultNode::new);
stack.push("A");
stack.push("B");
stack.push("C");
stack.push("D");
stack.push("E");
In this state, stack.peek() will return Optional.of("E").
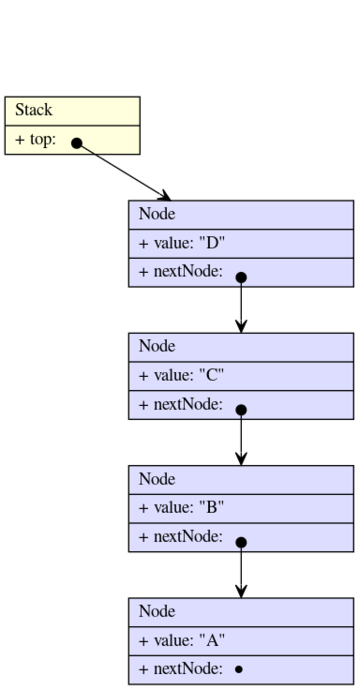
push A, B, C, D, E, pop
Stack<String> stack = new NotThreadSafeStack<>(DefaultNode::new);
stack.push("A");
stack.push("B");
stack.push("C");
stack.push("D");
stack.push("E");
Optional<String> optOfE = stack.pop();
In this state, optOfE will hold Optional.of("E") and stack.peek() will return Optional.of("D").
Code To Implement
Node
public interface Node<E> {
E value();
Optional<Node<E>> nextNode();
}
DefaultNode
The mighty cons cell goes back to the early days of computing. People have been building amazing systems with this data structure since the 1950s.
We will build an @Immutable class DefaultNode which implements interface Node.
| class: | DefaultNode.java | |
| methods: | value nextNode |
|
| package: | stack.node.exercise | |
| source folder: | main/src/main/java |
constructor and instance variables
The constructor
public DefaultNode(E value, Optional<Node<E>> nextNode)</node>
is passed a value and a nextNode. Hang on to this data in instance variables. As instances of DefaultNode are to be immutable, the instance variables should be marked as <code>final</code>.
====value====
return the value.
====nextNode====
return the next node.
==Stack==
<nowiki>public interface Stack<E> {
void push(E value);
Optional<E> peek();
Optional<E> pop();
}
NotThreadSafeStack
| class: | NotThreadSafeStack.java | |
| methods: | constructor nodeConstructor push peek pop |
|
| package: | stack.notthreadsafe.exercise | |
| source folder: | student/src/main/java |
constructor and instance variables
nodeConstructor
push
peek
pop
ConcurrentStack
| class: | ConcurrentStack.java | |
| methods: | constructor nodeConstructor push peek pop |
|
| package: | stack.concurrent.exercise | |
| source folder: | student/src/main/java |
constructor and instance variables
nodeConstructor
push
peek
pop
AtomicStack
| class: | AtomicStack.java | |
| methods: | constructor nodeConstructor push peek pop |
|
| package: | stack.atomic.exercise | |
| source folder: | student/src/main/java |
constructor and instance variables
nodeConstructor
push
peek
pop
Testing
| class: | StackTestSuite.java | |
| package: | stack.exercise | |
| source folder: | testing/src/test/java |
DefaultNode
| class: | _DefaultNodeTestSuite.java | |
| package: | stack.node.exercise | |
| source folder: | testing/src/test/java |
NotThreadSafeStack
| class: | _NotThreadSafeStackTestSuite.java | |
| package: | stack.notthreadsafe.exercise | |
| source folder: | testing/src/test/java |
ConcurrentStack
| class: | __ConcurrentStackTestSuite.java | |
| package: | stack.concurrent.exercise | |
| source folder: | testing/src/test/java |
sequential
| class: | _ConcurrentStackSequentialTestSuite.java | |
| package: | stack.concurrent.exercise | |
| source folder: | testing/src/test/java |
parallel
| class: | _ConcurrentStackParallelTestSuite.java | |
| package: | stack.concurrent.exercise | |
| source folder: | testing/src/test/java |
AtomicStack
| class: | __AtomicStackTestSuite.java | |
| package: | stack.atomic.exercise | |
| source folder: | testing/src/test/java |
sequential
| class: | _AtomicStackSequentialTestSuite.java | |
| package: | stack.atomic.exercise | |
| source folder: | testing/src/test/java |
parallel
| class: | _AtomicStackParallelTestSuite.java | |
| package: | stack.atomic.exercise | |
| source folder: | testing/src/test/java |