Difference between revisions of "N-Queens/Sudoku Assignment"
(→Solver) |
|||
| Line 52: | Line 52: | ||
Searching for solutions like n-queens can be done in parallel without the need to finish at each level. As such, <code>forasync</code> is preferable to <code>forall</code>. However: | Searching for solutions like n-queens can be done in parallel without the need to finish at each level. As such, <code>forasync</code> is preferable to <code>forall</code>. However: | ||
| − | {{Warning|Ensure that you complete all of your tasks by enclosing them all in a <code>finish</code>}} | + | {{Warning|Ensure that you complete all of your tasks by enclosing them all in a <code>finish</code>.}} |
{{CodeToImplement|ParallelNQueens|placeQueenInRow<br>countSolutions|nqueens.lab}} | {{CodeToImplement|ParallelNQueens|placeQueenInRow<br>countSolutions|nqueens.lab}} | ||
Revision as of 06:03, 4 April 2018
Motivation
Not everything in the world should be divided and conquered. Backtracking is a powerful technique which can be readily parallelized. We will gain experience with backtracking by solving the N-Queens problem and Sudoku in parallel.
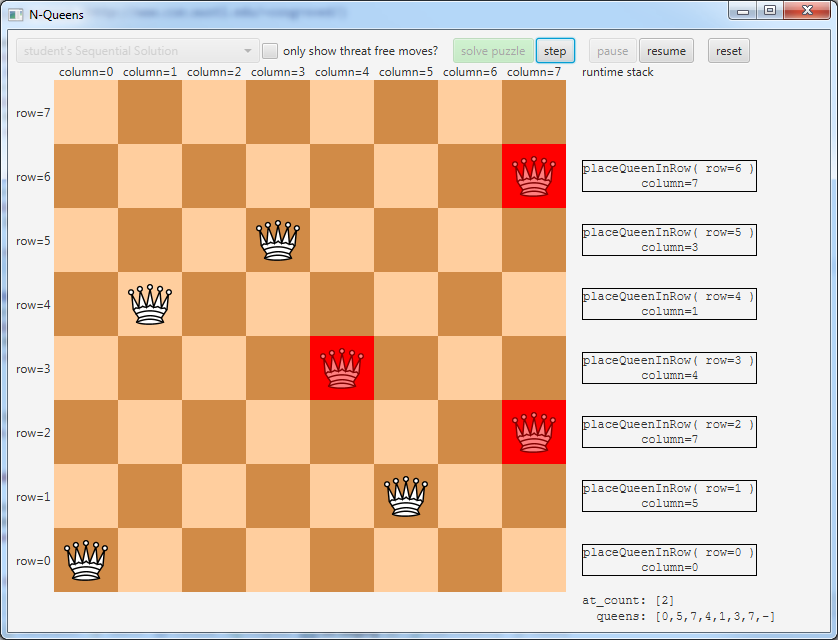
N-Queens in particular can be used to explain the call stack as the chessboard *IS* the call stack. Whoa.
Further, by employing constraint propagation and search we can dramatically improve performance for problems like Sudoku.
Background
The n-queens problem is a fundamental coding puzzle which asks: how can N queens be placed on an NxN chessboard so that they cannot attack each other? In chess, a queen can move horizontally, vertically, and diagonally across the board. Thus, to solve the n-queens problem, we must effectively figure out how to place the queens in such a way that no two of them occupy the same row, column, or diagonal.
We will be using a similar algorithm to solve a Sudoku puzzle. A Sudoku puzzle is composed of a 9-by-9 grid of squares. This grid is also divided into 9 large boxes, each of which is a 3-by-3 of the smaller squares. In a completed puzzle, each of the smaller squares contains a single number from 1 to 9 (inclusive). However, if a square contains a given number, that same number cannot be anywhere else in the same row, column, or box. Thus, for Sudoku, we are given an incomplete board and must fill in the remaining squares while meeting these requirements. For more explanation, take a look at Peter Norvig's essay about solving Sudoku.
In this assignment, you will implement solutions to both the n-queens and Sudoku problems.
Code To Implement
N-Queens
Sequential Solution
public static int countSolutions(MutableQueenLocations queenLocations) {
MutableInt count = new MutableInt(0);
placeQueenInRow(count, queenLocations, 0);
return count.intValue();
}
| class: | SequentialNQueens.java | |
| methods: | placeQueenInRow | |
| package: | nqueens.lab | |
| source folder: | student/src/main/java |
method: private static void placeQueenInRow(MutableInt count, MutableQueenLocations queenLocations, int row) ![]() (sequential implementation only)
(sequential implementation only)
Parallel Solution
Board State
Investigate DefaultMutableQueenLocations and AbstractQueenLocations for clues on how to implement DefaultImmutableQueenLocations.
| class: | DefaultImmutableQueenLocations.java | |
| methods: | createNext getColumnOfQueenInRow getRowCount getBoardSize |
|
| package: | nqueens.lab | |
| source folder: | student/src/main/java |
method: public DefaultImmutableQueenLocations createNext(int column) ![]() (sequential implementation only)
(sequential implementation only)
There are two constructors for this class. A public one which creates a fresh new board state with no queens yet placed. and a private one which creates a new board with the state of a given board which is further constrained by a new queen in the next row. You need to create a new instance using one of these two constructors. Which one is it?
method: public int getColumnOfQueenInRow(int row) ![]() (sequential implementation only)
(sequential implementation only)
method: public int getRowCount() ![]() (sequential implementation only)
(sequential implementation only)
method: public int getBoardSize() ![]() (sequential implementation only)
(sequential implementation only)
NOTE: We will refer to the standard 8x8 chessboard's size as 8 and not 64.
method: public boolean isNextRowThreatFree(int column) ![]() (sequential implementation only)
(sequential implementation only)
Do not feel compelled to build this method from scratch. Investigate your super class for a utility method that will be helpful.
ParallelNQueens
Searching for solutions like n-queens can be done in parallel without the need to finish at each level. As such, forasync is preferable to forall. However:
finish. |
| class: | ParallelNQueens.java | |
| methods: | placeQueenInRow countSolutions |
|
| package: | nqueens.lab | |
| source folder: | student/src/main/java |
method: public static int countSolutions(ImmutableQueenLocations queenLocations) ![]() (parallel implementation required)
(parallel implementation required)
method: private static void placeQueenInRow(FinishAccumulator<Integer> acc, ImmutableQueenLocations queenLocations) ![]() (parallel implementation required)
(parallel implementation required)
Tips
N-Queens
There are three classes you will need to modify: DefaultImmutableQueenLocations.java, SequentialNQueens.java, and ParallelNQueens.java. Start with QueenLocations and then we recommend moving on to the sequential solution before the parallel one. Take a look at the javadocs to see what everything does and what you will need to implement.
A couple of notes and common issues:
- As
ImmutableQueenLocationsis immutable, you will need to create a new instance of the object whenever you move on from one row to the next. This is wherecreateNextcomes in, along with the private constructor of this class. - The
isNextRowThreatFreemethod can easily be completed with a method inAbstractQueenLocations. Refer to that for help. - The sequential solution uses
MutableQueenLocationswhile the parallel solution uses your implementation ofImmutableQueenLocations. Be careful to use the correctQueenLocationsimplementation. - As the name suggests,
placeQueenInRowwill go through the columns of the given row to check if a queen can fit in that location. If it can, it will set that value inMutableQueenLocations. If the examined row is that last row of the board, you have found one valid solution to the n-queens problem. Update the correct parameter accordingly. Otherwise, recurse and keep going until you reach the last row. - For the parallel implementation of
placeQueenInRow, we are using the "one-finish" pattern. Do not callfinishin the recursive method. - The syntax for instantiating a
FinishAccumulatorofIntegeris:FinishAccumulator<Integer> acc = newIntegerFinishAccumulator(NumberReductionOperator.SUM); - The syntax for using a
FinishAccumulatoris:finish(register(acc), () -> { //body });
Sudoku
Sudoku is another problem well solved by backtracking. Check the understanding you gained of backtracking with N-Queens by challenging yourself to solve sudoku's solver without assistance.
We then add constraint propagation and search ordering to make this problem more compelling.
Background
Code To Investigate
enum Square
public Collection<Square> getPeers()- all enums have a
values()method
class Units
public static Iterable<Collection<Square>> allUnits()
Code To Implement
Feel free to tackle this problem however you choose.
Constraint Propagator
Specify which path you would like to be tested in ConstraintPropagatorSupplier.
| class: | ConstraintPropagatorSupplier.java | |
| methods: | get | |
| package: | sudoku.lab | |
| source folder: | student/src/main/java |
Your implementation should look like this:
public class ConstraintPropagatorSupplier implements Supplier<ConstraintPropagator> {
@Override
public ConstraintPropagator get() {
return new PeerRemovingConstraintPropagator();
}
}
or this:
public class ConstraintPropagatorSupplier implements Supplier<ConstraintPropagator> {
@Override
public ConstraintPropagator get() {
return new DefaultConstraintPropagator();
}
}
Path A) PeerRemovingConstraintPropagator
| class: | DefaultConstraintPropagator.java | |
| methods: | createOptionSetsFromGivens createNextOptionSets associateValueWithSquareAndRemoveFromPeers |
|
| package: | sudoku.lab | |
| source folder: | student/src/main/java |
method: public Map<Square, SortedSet<Integer>> createOptionSetsFromGivens(String givens) ![]() (sequential implementation only)
(sequential implementation only)
method: public Map<Square, SortedSet<Integer>> createNextOptionSets(Map<Square, SortedSet<Integer>> otherOptionSets, Square square, int value) ![]() (sequential implementation only)
(sequential implementation only)
method: private static void associateValueWithSquareAndRemoveFromPeers(Map<Square, SortedSet<Integer>> resultOptionSets, Square square, int value) ![]() (sequential implementation only)
(sequential implementation only)
Path B) DefaultConstraintPropagator
Peter Norvig's Essay is very helpful here. We have adopted his terms, but challenge yourself to complete this section without simply translating his pseudocode.
To simplify things a bit, we have elected to not short circuit when a 0 option square is found (relying on the search ordering to take care of that for us).
| class: | DefaultConstraintPropagator.java | |
| methods: | createOptionSetsFromGivens createNextOptionSets assign eliminate |
|
| package: | sudoku.lab | |
| source folder: | student/src/main/java |
method: public Map<Square, SortedSet<Integer>> createOptionSetsFromGivens(String givens) ![]() (sequential implementation only)
(sequential implementation only)
method: public Map<Square, SortedSet<Integer>> createNextOptionSets(Map<Square, SortedSet<Integer>> otherOptionSets, Square square, int value) ![]() (sequential implementation only)
(sequential implementation only)
method: private static void assign(Map<Square, SortedSet<Integer>> optionSets, Square square, int value) ![]() (sequential implementation only)
(sequential implementation only)
method: private static void eliminate(Map<Square, SortedSet<Integer>> optionSets, Square square, int value) ![]() (sequential implementation only)
(sequential implementation only)
Puzzle
Since we will be solving sudoku in parallel, you will create an new immutable puzzle for each task. This is analogous to the work you did for #NQueens.
| class: | DefaultImmutableSudokuPuzzle.java | |
| methods: | constructors createNext getValue getOptions |
|
| package: | sudoku.lab | |
| source folder: | student/src/main/java |
method: public DefaultImmutableSudokuPuzzle(ConstraintPropagator constraintPropagator, String givens) ![]() (sequential implementation only)
(sequential implementation only)
This constructor creates a puzzle constrained to an initial set of givens. You can think of the givens as the original values provided by the newspaper or airline magazine or puzzle book or whatever.
You will leverage the constraintPropagator to build your map of option sets.
method: private DefaultImmutableSudokuPuzzle(DefaultImmutableSudokuPuzzle other, Square square, int value) ![]() (sequential implementation only)
(sequential implementation only)
This constructor takes a given previous puzzle and a square value to create a new further constrained puzzle.
method: public ImmutableSudokuPuzzle createNext(Square square, int value) ![]() (sequential implementation only)
(sequential implementation only)
This method should create a new puzzle instance using one of the constructors. Which one is it?
method: public int getValue(Square square) ![]() (sequential implementation only)
(sequential implementation only)
Based on the state of the board, return the value of a given square if it is known. Otherwise, return 0.
How do we determine if a value for a given square is "known"?
method: public SortedSet<Integer> getOptions(Square square) ![]() (sequential implementation only)
(sequential implementation only)
Based on the state of the board, return the candidate values for a given square.
Search Order
Simply by changing the search order, a great reduction of work can be achieved. The class names sadly give away the approaches.
Ask yourself:
- Which algorithm will perform better and why?
- What properties make a square "filled"?
| class: | RowMajorSquareSearchAlgorithm.java | |
| methods: | selectNextUnfilledSquare | |
| package: | sudoku.lab | |
| source folder: | student/src/main/java |
method: public Square selectNextUnfilledSquare(SudokuPuzzle puzzle) ![]() (sequential implementation only)
(sequential implementation only)
Simply run through the Square.values() which will return you the Squares in row-major order.
| class: | FewestOptionsFirstSquareSearchAlgorithm.java | |
| methods: | selectNextUnfilledSquare | |
| package: | sudoku.lab | |
| source folder: | student/src/main/java |
method: public Square selectNextUnfilledSquare(SudokuPuzzle puzzle) ![]() (sequential implementation only)
(sequential implementation only)
Write pseudocode for finding the minimum item in a collection to get on the right track.
Solver
Searching for solutions like sudoku can be done in parallel without the need to finish at each level. As such, forasync is preferable to forall. However:
finish. |
| class: | ParallelSudoku.java | |
| methods: | solve solveKernel |
|
| package: | sudoku.lab | |
| source folder: | student/src/main/java |
method: public static ImmutableSudokuPuzzle solve(ImmutableSudokuPuzzle puzzle, SquareSearchAlgorithm squareSearchAlgorithm) ![]() (parallel implementation required)
(parallel implementation required)
method: private static void solveKernel(MutableObject<ImmutableSudokuPuzzle> solution, ImmutableSudokuPuzzle puzzle, SquareSearchAlgorithm squareSearchAlgorithm) ![]() (parallel implementation required)
(parallel implementation required)
Tips
A couple of notes and common issues:
- As the name suggests,
ImmutableSudokuPuzzleis immutable, and you will need to create a new instance of the object whenever you move on from one square to the next. This is analogous to the immutable n-queens board. - If you have two Lists,
aandb, and you seta = b, then any changes you make toawill also be made tob. Both variables reference the same objects; they are not copies. - You will need to implement
getValue. Look to the instances fields for what will be useful here. - Your solvers should be able to handle two different approaches to picking the next square in the puzzle to examine: row major and fewest options first. Row major just means going through the puzzle row by row, while fewest options first means solving the puzzle in the order of which squares has the fewest options.
- For fewest options first, go through every square (you can do this by calling
Square.values()) and see how many options are available for each square. Return the square with the minimal number of options. However, check to make sure the puzzle is not already completed or that you are returning already filled squares.
- For fewest options first, go through every square (you can do this by calling
- Just like n-queens, your
solveKernelis the recursive method that will be called in the solve method. Again, watch where you put yourfinish. - In your
solveKernelmethod, you should use the given search algorithm (row major or fewest options first) to select which square you will fill. After selecting a square, you should recursively call the kernel to check every viable option in the context of the puzzle. If there are no more unfilled squares, you should set the value of the solution to the finished puzzle and exit out of the recursion.
Testing Your Solution
Visualization
N-Queens
| class: | NQueensVizApp.java | VIZ |
| package: | nqueens.viz.solution | |
| source folder: | student/src//java |
Sudoku
| class: | SudokuSolutionApp.java | VIZ |
| package: | sudoku.viz.solution | |
| source folder: | student/src//java |
Correctness
There is a top-level test suite comprised of sub test suites which can be invoked separately when you want to focus on one part of the assignment.
top level
| class: | BacktrackTestSuite.java | |
| package: | backtrack.lab | |
| source folder: | testing/src/test/java |
sub
| class: | NQueensTestSuite.java | |
| package: | nqueens.lab | |
| source folder: | testing/src/test/java |
| class: | SudokuTestSuite.java | |
| package: | sudoku.lab | |
| source folder: | testing/src/test/java |
Rubric
As always, please make sure to cite your work appropriately.
Total points: 100
N-Queens subtotal: 35
- Correct DefaultImmutableQueenLocations (5)
- Correct SequentialNQueens (10)
- Correct ParallelNQueens (10)
- Parallel ParallelNQueens (10)
Sudoku subtotal: 55
- Correct DefaultImmutableSudokuPuzzle (5)
- Correct ContraintPropagator (15)
- Correct RowMajorSquareSearchAlgorithm (5)
- Correct FewestOtionsFirstSquareSearchAlgorithm (10)
- Correct ParallelSudoku (10)
- Parallel ParallelSudoku (10)
Whole project:
- Clarity and efficiency (10)