Objectives
The objectives of today’s Studio are:
- Meet some of your classmates. You’ll often need to work with classmates on Studios, so it’s important to meet several people today.
- Work through the Studio/Assignment distribution process.
- Get a high-level view of IoT systems.
- Work through the Studio submission process.
- Work through the Studio checkout process.
1. Find a Partner
Today’s studio will require groups of two. If you don’t already have someone to work with, introduce yourself to those near you.
2. Studio/Assignment Distribution
READ ALL OF THE FOLLOWING CAREFULLY BEFORE STARTING
Most Studios and Assignments will be distributed via GitHub classrooms. Here are the steps you’ll typically need to perform to get the Studio/Assignment:
- A repository will be needed for each group. Each group needs to make one GitHub group (link in the next step) and everyone in the group should be a member of the GitHub group!!!.
- Repository names should include all group member surnames. Other information, like the class and studio, is optional. (Ex:
Studio01_StevensXu). - One person should create the group and all other group members should join it. All members have equal access, so it doesn’t matter who creates and who joins. You must be a member of a submitted repo to resolve any disputes about missing credit, so be sure that all members of groups join the group and that the repo is committed!
- If the “creator” is logged in to GitHub on their computer, others could use the same computer and an “anonymous” browsing tab to login to GitHub and then join the group.
- Repository names should include all group member surnames. Other information, like the class and studio, is optional. (Ex:
- Each person needs to follow a link. Today (Studio 1) you should follow this one: https://classroom.github.com/g/vbWmrMMf
- The first time you follow a link for this class you may need to do either/both:
- Authorize GitHub classroom to access your GitHub account by clicking an Authorize button.
- Associate your GitHub account with your WUSTL e-mail address by selecting your WUSTL e-mail address from a list.
- Again, one person in the group needs to create the group. (See naming convention above). Everyone else needs to join it.
- The first time you follow a link for this class you may need to do either/both:
- When done, a repository will be created. The page should look something like:
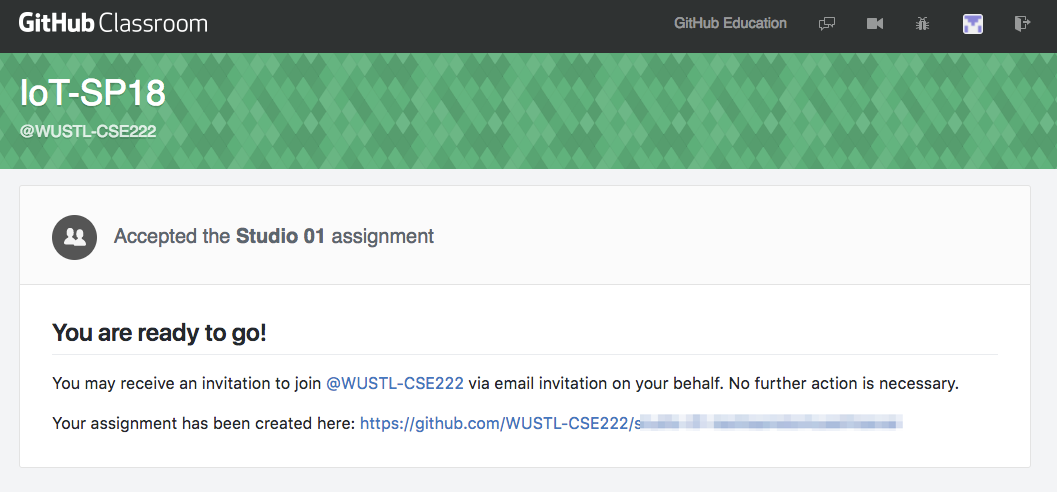
- From this point on, everyone could work from a single computer (although everyone can also follow these steps at anytime to import the repo to individual machines). Open GitHub Desktop on that computer (and login if you haven’t already).
- Select the
Clonebutton (orFile > Clone a Repository...if you have already imported other repositories).
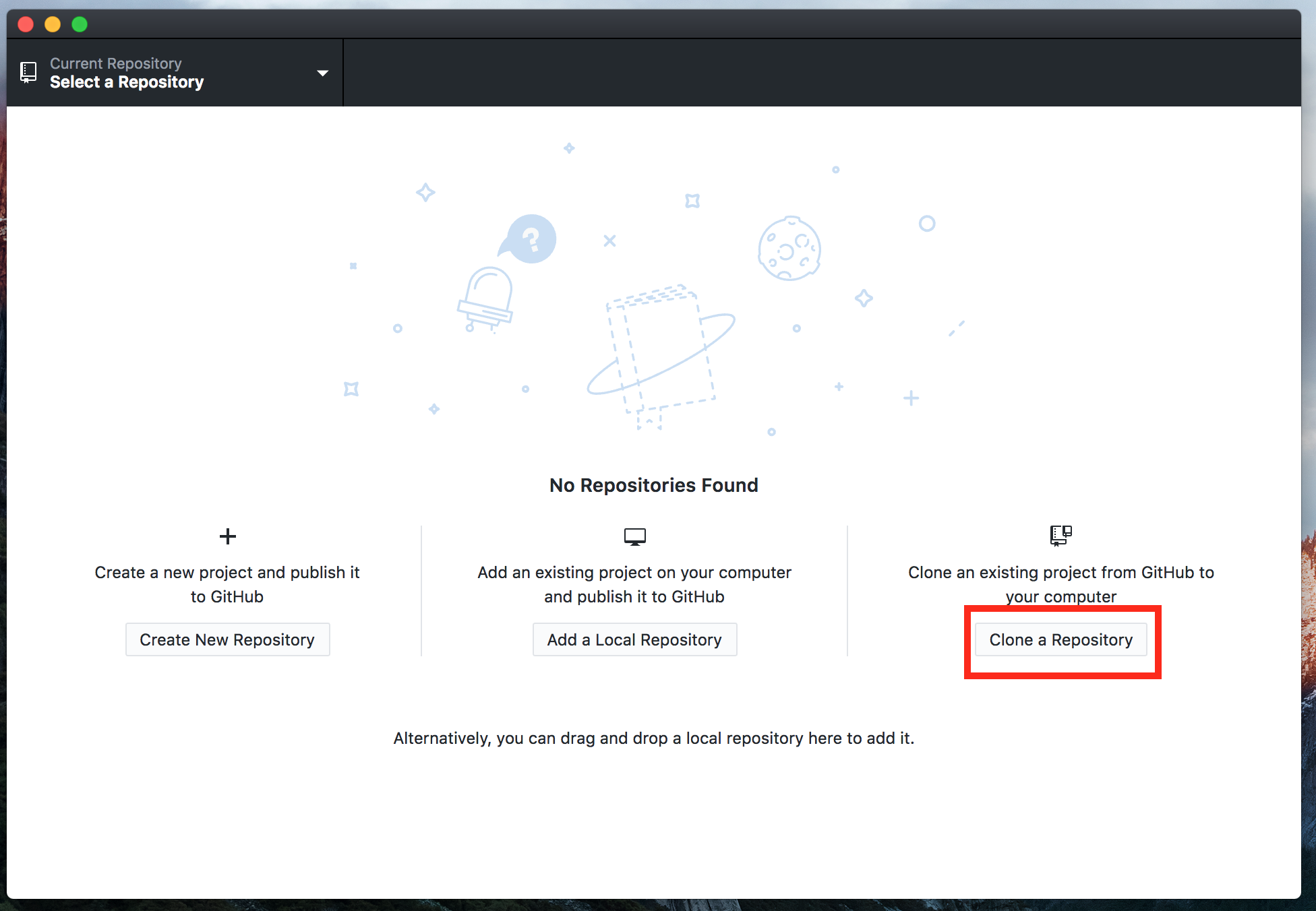
- The Note that the Clone pane should have the GitHub tab selected. The pane has four areas of interest:
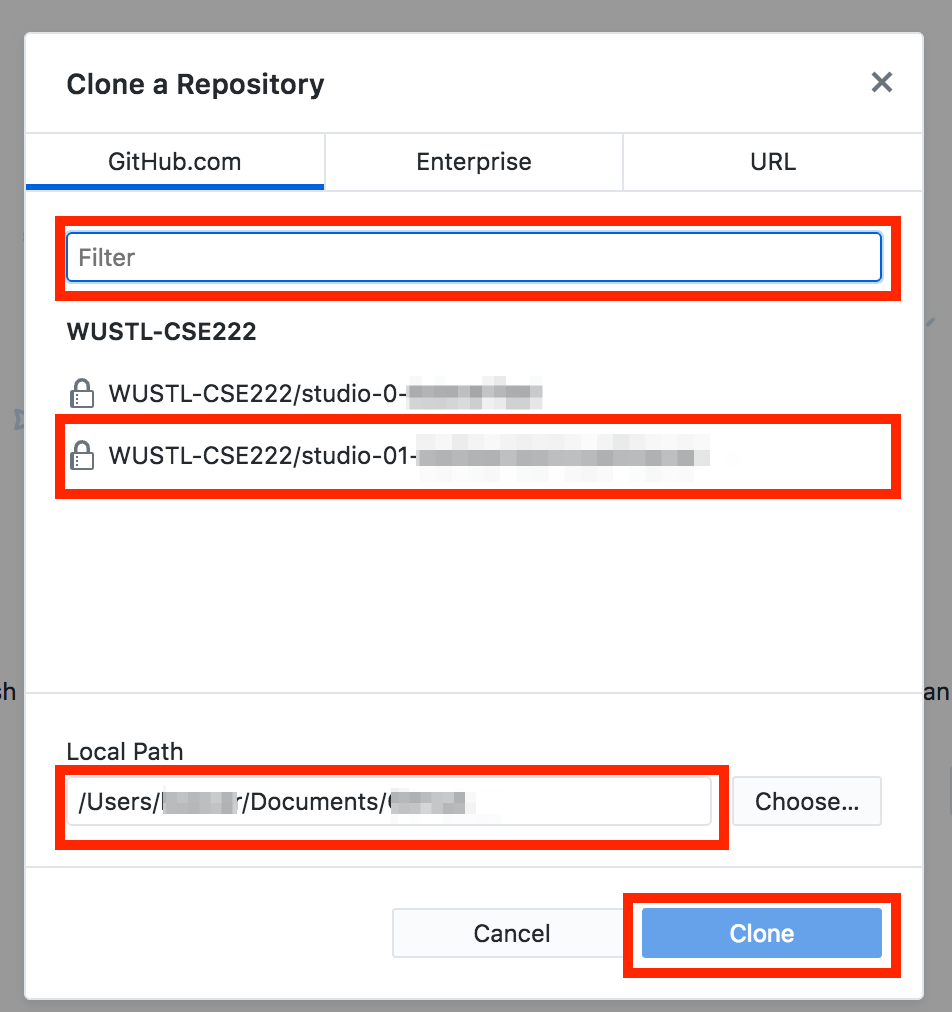
- The filter may be used if you have many repositories and want to search for just one.
- There is a list of matching repositories. Select the one you want to clone (Studio 01 today).
- The “Local Path” (Destination folder). You may want to create a folder just for 222 work and put all your 222 repos in that folder. Remember this folder because you’ll need to import the project in Particle Desktop IDE.
- The “Clone” button, which you use once you’ve selected the repository and destination.
- Clone the repository to the computer you’ll be working on (i.e., select the repo, select the path, and hit clone).
- Open Particle Desktop IDE and select
File > Add Project Folder...and select the folder for the newly cloned Repository. - In Particle Desktop, open the Project’s folder and open the
README.md, which you’ll be using in the remainder of the studio. You may also want to open the Markdown preview on theREADME(Packages > Markdown Preview > Toggle Preview).
3. IoT Games
You’ll be given a deck of cards (PDF available here). The cards are divided into five suits:
- Missions: These are tasks you’ll need complete using the other cards
- Things: The “Things” in an IoT system. These are everyday objects that could be augmented with processors, networking capabilities, and a variety of I/O.
- Services: These represent a variety of sources of data or on-line services that can be used to perform some operation.
- Human Actions: These represent ways that someone may interact with a “Thing”.
- Feedback: These represent the ways a “Thing” may provide information to a Human.
- Criteria: These represent some ways to evaluate an IoT system
The remaining steps are covered in the repository’s README.md. Be sure to fill in answers where indicated.
4. Studio Submission
Once you complete the studio:
- Be sure to save any changes to any files (only
README.mdtoday) - Return to the GitHub Desktop application and be sure that the Studio repository is selected.
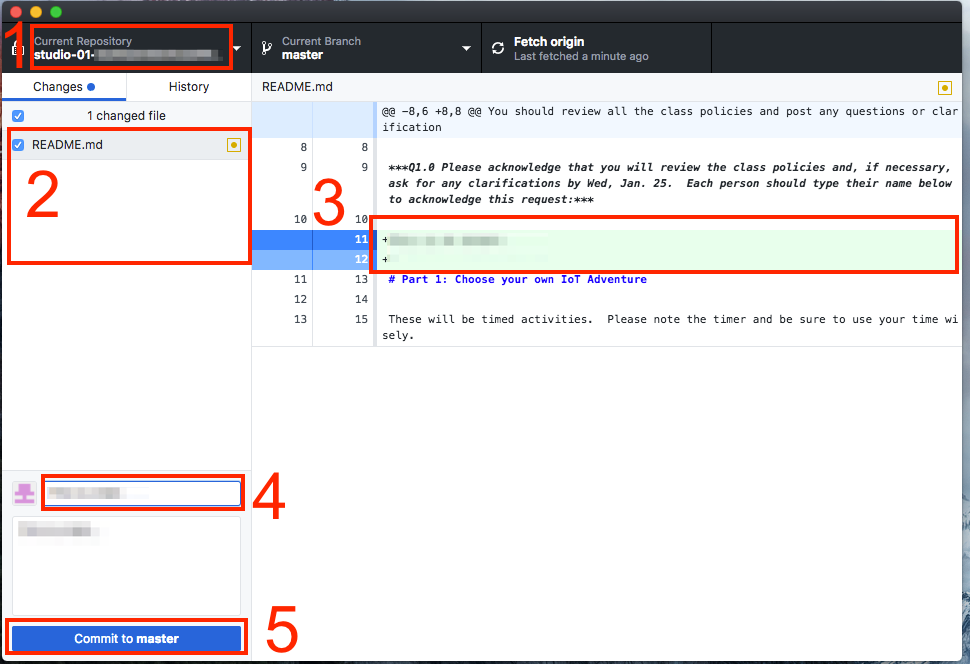
Note the areas of this window:
- You can select the repository you want to work with.
- You can see the files that have changed or been added since the last commit. You will want to be sure anything you’ve changed is selected!
- There’s a pane that will let you compare changes in files so you can see how they’ve been changed.
- There’s a box to enter the commit message. You need to enter a brief description here before you can commit.
- The
Commitbutton.
- Enter a Commit message and commit your changes. This only changes your local repository, not the one on GitHub. You must change the repository on GitHub to submit your work!!!.
- Be sure you select
Repostiroy > Pushto commit your changes to GitHub.
- Go to GitHub, select the repository, and verify that your changes have been pushed to GitHub.
5. Studio Checkout
- Open your GitHub.com page to the repository and verify that changes are posted.
- Let a TA know you are ready to check out.
- Show the TA your committed work.
- Complete the checkout process with the TA.