Product: ABAQUS/Standard

User subroutine RSURFU:
is used to define the surface of a rigid body for use in contact pairs;
can be used to define a complex rigid surface if the various capabilities provided for defining a surface in ABAQUS (see “Defining analytical rigid surfaces,” Section 2.3.4 of the ABAQUS Analysis User's Manual) are too restrictive;
will be called at points on the slave surface of a contact pair or, if contact elements are used, at each integration point of each contact element with which the rigid surface is associated; and
requires the definition of the closest point on the rigid surface, the normal and tangent directions, and the surface curvature.

This routine must determine if a point on the slave surface has penetrated the rigid surface and define the local surface geometry. If the deforming and rigid surfaces are in contact at this point, ABAQUS/Standard will impose a constraint at the point to prevent overpenetration. The local surface geometry must be defined to provide the necessary orientation for the constraint equations and friction directions and to allow ABAQUS/Standard to compute the rate of change of these equations as the point moves around on the surface—the “tangent stiffness matrix” for the surface in the Newton algorithm. For the purpose of these calculations, it is best to define a smooth surface. If the surface is defined in a discontinuous manner, convergence may be adversely affected.

Each time RSURFU is called, ABAQUS/Standard gives the current position of point A on the surface of the deforming structure, ![]() ; the current position of the rigid body reference point,
; the current position of the rigid body reference point, ![]() ; the total displacements of both of these points,
; the total displacements of both of these points, ![]() and
and ![]() ; and the total rotation of the rigid body reference point,
; and the total rotation of the rigid body reference point, ![]() .
.
The routine should perform the following calculations:
A point, ![]() , must be found on the rigid surface at which the normal to the surface passes through
, must be found on the rigid surface at which the normal to the surface passes through ![]() . If there is not a unique point
. If there is not a unique point ![]() , the routine must choose the most suitable point (usually the closest
, the routine must choose the most suitable point (usually the closest ![]() to A). The routine must pass back the coordinates of
to A). The routine must pass back the coordinates of ![]() to ABAQUS/Standard.
to ABAQUS/Standard.
RSURFU must define the distance, h, by which A has penetrated the surface below ![]() . A negative value of h means that A is outside the surface of the rigid body.
. A negative value of h means that A is outside the surface of the rigid body.
If the surfaces are in contact, which may sometimes be the case even if h is negative, RSURFU must define the local surface geometry.

There are two scenarios under which it is mandatory that the routine define the local surface geometry: if A has penetrated the surface—![]() if the surface behavior is truly rigid, or h is greater than the maximum overclosure value specified for modified surface behavior using either contact controls (see “Adjusting contact controls in ABAQUS/Standard,” Section 29.2.12 of the ABAQUS Analysis User's Manual) or a modified pressure-overclosure relationship (see “Contact pressure-overclosure relationships,” Section 30.1.2 of the ABAQUS Analysis User's Manual)—and if A was in contact at the beginning of the increment, in which case the flag LCLOSE=1 (see the variable list for the definition of LCLOSE). The variable LCLOSE is not relevant for the surface-to-surface contact formulation and is always passed in as 0. The routine can be coded so that local surface geometry definitions are always provided regardless of the scenario.
if the surface behavior is truly rigid, or h is greater than the maximum overclosure value specified for modified surface behavior using either contact controls (see “Adjusting contact controls in ABAQUS/Standard,” Section 29.2.12 of the ABAQUS Analysis User's Manual) or a modified pressure-overclosure relationship (see “Contact pressure-overclosure relationships,” Section 30.1.2 of the ABAQUS Analysis User's Manual)—and if A was in contact at the beginning of the increment, in which case the flag LCLOSE=1 (see the variable list for the definition of LCLOSE). The variable LCLOSE is not relevant for the surface-to-surface contact formulation and is always passed in as 0. The routine can be coded so that local surface geometry definitions are always provided regardless of the scenario.
The local surface geometry is specified by two orthogonal tangents to the rigid surface at ![]() , as well as the rates of change of the outward pointing normal at
, as well as the rates of change of the outward pointing normal at ![]() ,
, ![]() , with respect to local surface coordinates that are distance measuring along the tangents,
, with respect to local surface coordinates that are distance measuring along the tangents, ![]() and
and ![]() (see Figure 1–4). The tangents to the surface at
(see Figure 1–4). The tangents to the surface at ![]() must be defined so that their positive, right-handed cross product is the outward normal to the surface. For two-dimensional cases ABAQUS/Standard assumes that the second tangent is (0, 0, –1), so that when you give the direction cosines of the first tangent as (
must be defined so that their positive, right-handed cross product is the outward normal to the surface. For two-dimensional cases ABAQUS/Standard assumes that the second tangent is (0, 0, –1), so that when you give the direction cosines of the first tangent as (![]() ,
, ![]() , 0), the outward normal will be (
, 0), the outward normal will be (![]() ,
, ![]() , 0). The rates of change of the normal with respect to
, 0). The rates of change of the normal with respect to ![]() and
and ![]() are required to define the local curvature of the surface.
are required to define the local curvature of the surface.

SUBROUTINE RSURFU(H,P,TGT,DNDS,X,TIME,U,CINAME,SLNAME,
1 MSNAME,NOEL,NODE,LCLOSE)
C
INCLUDE 'ABA_PARAM.INC'
C
CHARACTER*80 CINAME,SLNAME,MSNAME
C
DIMENSION P(3),TGT(3,2),DNDS(3,2),X(3,3),TIME(2),U(6,2)
user coding to define H, P, TGT, and DNDS
RETURN
END
H
Penetration of the point A on the deforming structure into the surface of the rigid body, measured down the outward normal to the rigid surface. A negative value of H indicates that A is outside the rigid surface. Even for a completely rigid surface, A may appear to penetrate the surface during the iterations because the kinematic constraints are not fully satisfied until an increment converges.
P(3)
Position of the point ![]() on the surface of the rigid body closest to point A on the surface of the deforming structure.
on the surface of the rigid body closest to point A on the surface of the deforming structure.
TGT(3,2)
Direction cosines of the two unit tangents to the surface, ![]() and
and ![]() , at point
, at point ![]() . For two-dimensional cases only the first two components of
. For two-dimensional cases only the first two components of ![]() need be given since in this case ABAQUS/Standard assumes that
need be given since in this case ABAQUS/Standard assumes that ![]() is (0, 0, –1).
is (0, 0, –1).
DNDS(3,2)
Rates of change of the surface normal, ![]() , at
, at ![]() , with respect to distance measuring coordinates,
, with respect to distance measuring coordinates, ![]() and
and ![]() , along
, along ![]() and
and ![]() . For two-dimensional cases only the first two entries in the first column of DNDS (
. For two-dimensional cases only the first two entries in the first column of DNDS (![]() ,
, ![]() ) are required. The array DNDS is not required to be assigned for the surface-to-surface contact formulation.
) are required. The array DNDS is not required to be assigned for the surface-to-surface contact formulation.

X(K1,1)
Current coordinates of point A on the surface of the deforming structure.
X(K1,2)
Current coordinates of the rigid body reference point.
X(K1,3)
Unit normal vector for point A; relevant only for the surface-to-surface contact formulation.
TIME(1)
Value of step time at the end of the increment.
TIME(2)
Value of total time at the end of the increment.
U(K1,1)
Total displacement of point A on the surface of the deforming structure.
U(K1,2)
Total displacement and rotation of the rigid body reference point; ![]() are the displacement components,
are the displacement components, ![]() are the rotation components. For two-dimensional cases the only nonzero rotation component is
are the rotation components. For two-dimensional cases the only nonzero rotation component is ![]() : U(4,2) and U(5,2) are both zero.
: U(4,2) and U(5,2) are both zero.
CINAME
User-specified surface interaction name, left justified. For user-defined contact elements it is either the element set name given for the interface definition or the optional name assigned to the interface definition.
SLNAME
Slave surface name. Passed in as blank if RSURFU is called for contact elements.
MSNAME
Master surface name. Passed in as blank if RSURFU is called for contact elements.
NOEL
Element label for contact elements. Passed in as zero if RSURFU is called for a contact pair.
NODE
Node number for point A. For the surface-to-surface contact formulation, this quantity is passed in as 0.
LCLOSE
Flag indicating contact status at the beginning of the increment. LCLOSE=1 indicates that A is in contact (closed) at the beginning of the increment. LCLOSE=0 indicates that A is not in contact (open) at the beginning of the increment. If LCLOSE=1, P, TGT and DNDS must be defined even if A opens during this increment. LCLOSE is not used for the surface-to-surface contact formulation and is passed in as 0.

The input files for the following examples can be found in “RSURFU,” Section 4.1.9 of the ABAQUS Verification Manual. The following discussion pertains only to the node-to-surface contact formulation.
Consider the punch shown in Figure 1–5.
It consists of a spherical head of radius a, smoothly merging into a conical section with cone angleA point (slave node) on the surface of the deforming body will be associated with the spherical head or with the conical part of the punch, depending on whether it lies above or below the cone that passes through Q and the circle of intersection of the sphere and cone. Thus, define
![]()
![]()
Consider first the axisymmetric case. Then, for ![]() (the sphere) the overclosure is
(the sphere) the overclosure is
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
For ![]() (the conical surface) the clearance is
(the conical surface) the clearance is
![]()
![]()
The routine can then be coded as follows:
SUBROUTINE RSURFU(H,P,TGT,DNDS,X,TIME,U,CINAME,SLNAME,
1 MSNAME,NOEL,NODE,LCLOSE)
C
INCLUDE 'ABA_PARAM.INC'
C
CHARACTER*80 CINAME,SLNAME,MSNAME
DIMENSION P(3),TGT(3,2),DNDS(3,2),X(3,2),TIME(2),U(6,2)
C
C DEFINE THE FOLLOWING QUANTITIES:
C A = RADIUS 'A' OF THE SPHERICAL HEAD
C SINA = SINE (CONE ANGLE ALPHA)
C COSA = COSINE (CONE ANGLE ALPHA)
C Z0 = ORIGINAL 'Z' COORDINATE OF POINT 'Q'
C
A=5.0
SINA=0.5
COSA=0.86602
Z0=6.0
ZQ=Z0 + U(2,2)
C
C TEST FOR SEGMENT
C
IF(X(1,1)*SINA/COSA.LT.ZQ-X(2,1))THEN
C
C SPHERE
C
B=SQRT(X(1,1)**2 + (X(2,1)-ZQ)**2)
H=A-B
COSB=X(1,1)/B
SINB=(ZQ-X(2,1))/B
P(1)=A*COSB
P(2)=ZQ-A*SINB
TGT(1,1)=-SINB
TGT(2,1)=-COSB
DNDS(1,1)=-SINB/A
DNDS(2,1)=-COSB/A
ELSE
C CONE
H=-X(1,1)*COSA+(X(2,1)-ZQ)*SINA+A
P(1)=X(1,1) + H*COSA
P(2)=X(2,1)- H*SINA
TGT(1,1)=-SINA
TGT(2,1)=-COSA
DNDS(1,1)=0.
DNDS(2,1)=0.
END IF
RETURN
END
The above case can be directly extended to three dimensions. For this purpose we assume that the radial axis, r, is in the global (x–y) plane, so that
![]()
For ![]() (the sphere), the overclosure is
(the sphere), the overclosure is ![]() , where again
, where again
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
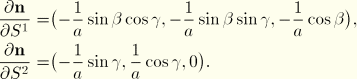
For the conical surface (![]() ), the surface separation is
), the surface separation is
![]()
![]()
There is no change of ![]() with respect to
with respect to ![]() , and, in this case
, and, in this case ![]() , where
, where ![]() , so that
, so that
![]()
The routine can then be coded as follows:
SUBROUTINE RSURFU(H,P,TGT,DNDS,X,TIME,U,CINAME,SLNAME,
1 MSNAME,NOEL,NODE,LCLOSE)
C
INCLUDE 'ABA_PARAM.INC'
C
CHARACTER*80 CINAME,SLNAME,MSNAME
DIMENSION P(3), TGT(3,2),DNDS(3,2), X(3,2), TIME(2), U(6,2)
C
C DEFINE THE FOLLOWING QUANTITIES:
C A = RADIUS 'A' OF THE SPHERICAL HEAD
C SINA = SINE (CONE ANGLE ALPHA)
C COSA = COSINE (CONE ANGLE ALPHA)
C Z0 = ORIGINAL 'Z' COORDINATE OF POINT 'Q'
C
A=5.0
SINA=0.5
COSA=0.86603
Z0=5.0
ZQ= Z0 + U(3,2)
C
C TEST FOR SEGMENT
C
R = SQRT(X(1,1)*X(1,1)+X(2,1)*X(2,1))
IF(R .GT. 0.0) THEN
COSG = X(1,1)/R
SING = X(2,1)/R
ELSE
COSG = 1.0
SING = 0.0
END IF
IF(R*SINA/COSA .LT. ZQ -X(3,1)) THEN
C
C SPHERE
C
B=SQRT(R*R+(X(3,1)-ZQ)**2)
H=A-B
COSB=R/B
SINB=(ZQ-X(3,1))/B
P(1)=A*COSB*COSG
P(2)=A*COSB*SING
P(3)=ZQ-A*SINB
TGT(1,1)=-SINB*COSG
TGT(2,1)=-SINB*SING
TGT(3,1)=-COSB
TGT(1,2)=-SING
TGT(2,2)=COSG
TGT(3,2)=0.0
DNDS(1,1)=-SINB*COSG/A
DNDS(2,1)=-SINB*SING/A
DNDS(3,1)=-COSB/A
DNDS(1,2)=-SING/A
DNDS(2,2)=COSG/A
DNDS(3,2)=0.0
ELSE
C
C CONE
C
H=-R*COSA+(X(3,1)-ZQ)*SINA+A
P(1)=(R+H*COSA)*COSG
P(2)=(R+H*COSA)*SING
P(3)=X(3,1)-H*SINA
TGT(1,1)=-SINA*COSG
TGT(2,1)=-SINA*SING
TGT(3,1)=-COSA
TGT(1,2)=-SING
TGT(2,2)=COSG
TGT(3,2)=0.0
DNDS(1,1)=0.0
DNDS(2,1)=0.0
DNDS(3,1)=0.0
C=R+H*COSA
DNDS(1,2)=-COSA*SING/C
DNDS(2,2)=COSA*COSG/C
DNDS(3,2)=0.0
END IF
C
RETURN
END