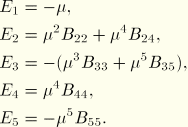6.2.3 Stokes wave theory

Assume that an infinite series of plane, uniform waves travels through the fluid in the positive S-direction. The z-coordinate is chosen to be positive in the vertical direction, so the gravity potential is 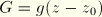 , where
, where 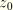 is an arbitrary datum.
is an arbitrary datum.
Assume that the fluid is inviscid and incompressible. The fluid particle velocities are derivable from a flow potential
Equilibrium is
where
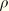
is the fluid density and
p is the pressure. Writing
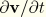
in terms of the flow potential then gives
Integrating with respect to
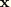
(note that
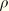
is constant since the fluid is incompressible) gives the Bernoulli equation
where
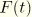
is an arbitrary function (which for convenience is set to zero) and
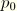
is the atmospheric pressure. Substituting in the gravity potential, this is
where
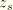
is the undisturbed surface level. From this equation the total pressure at a point below the instantaneous fluid surface is
Hence, the total pressure is the air pressure plus the hydrostatic pressure plus the dynamic pressure,
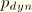
, where
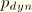
is given by
Let  be the elevation of the free surface above this level. At the free surface the Bernoulli equation is
be the elevation of the free surface above this level. At the free surface the Bernoulli equation is
assuming the pressure at the surface is negligible.
Assuming the waves are uniform, of wavelength 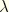 and period
and period  , and that they travel in the positive S-direction means that the solution as a function of S and t must appear in terms of a phase angle
, and that they travel in the positive S-direction means that the solution as a function of S and t must appear in terms of a phase angle
where
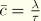
is the wave celerity. This means that, for any function in the solution,
Thus, at the free surface boundary
and the Bernoulli equation at the free surface is
or
A further boundary condition at the free surface is that the fluid particle velocity relative to the wave celerity must be tangential to the slope of the wave:
At the seabed
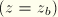
, there is no fluid motion in the vertical direction:
The problem now consists of finding a potential function,
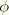
, that satisfies
Equation 6.2.3–1—the boundary condition at the seabed—as well as the boundary conditions at the surface—
Equation 6.2.3–2 and
Equation 6.2.3–3.
Stokes proposed a power series solution to this problem, and Skjelbreia and Hendrickson (1960) have obtained that solution to fifth-order. The potential function is assumed to be
where
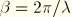
, the
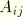
are constants that depend on the ratio of water depth to wavelength
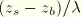
, and

is a parameter. The wave profile,
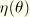
, is assumed to be
where the
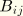
are constants for a given water depth and wavelength. Finally, it is assumed that
and that
Skjelbreia and Hendrickson obtain the 18 constants 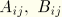 ,
, 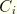 , and
, and 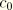 from matching terms in equal powers of
from matching terms in equal powers of  and
and 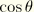 in the free surface boundary conditions, Equation 6.2.3–2 and Equation 6.2.3–3. They give the constants as functions of
in the free surface boundary conditions, Equation 6.2.3–2 and Equation 6.2.3–3. They give the constants as functions of 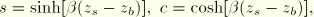 as
as
Skjelbreia and Hendrickson (1960) have a factor +2592 multiplying 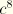 in the equation for
in the equation for 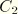 . This was corrected to –2592 by Nishimura et al. (1970).
. This was corrected to –2592 by Nishimura et al. (1970).
They then obtain equations for 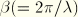 and
and  . The wave height is
. The wave height is
so
Equation 6.2.3–5 gives
Also, the form assumed for the wave celerity gives
Given the wave period, wave height, and water depth,
Equation 6.2.3–7 and
Equation 6.2.3–8 must be solved simultaneously for the wavelength,
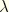
, and the parameter

. This is done with a Newton method, using the Airy (linear) wave solution as an initial guess.
Fluid particle velocities and accelerations for Stokes 5th order wave

The flow potential has been approximated as
where
The fluid particle velocities are
and the fluid particle accelerations are
Since the solution appears in terms of the phase angle
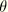
, it follows that
This allows the acceleration components to be written as
Recall the expression for the dynamic pressure:
Substitution of the expression for
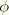
yields:
where
Finally, the surface position is given as
where
The Stokes wave field is a spatial description of the wave field. All wave field quantities are calculated up to the instantaneous fluid level. The wave field defines velocity, acceleration, and dynamic pressure at spatial locations for all values of time. Hence, the velocity, acceleration, and dynamic pressure are determined by using the current (for geometrically nonlinear analysis) or reference (for geometrically linear analysis) location of the structure at the current time in the appropriate equations. The time used in the wave field equations is the total time for the analysis, which accumulates over all steps in the analysis (static, dynamic, etc.).

![]() , where
, where ![]() is an arbitrary datum.
is an arbitrary datum.![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() be the elevation of the free surface above this level. At the free surface the Bernoulli equation is
be the elevation of the free surface above this level. At the free surface the Bernoulli equation is ![]()
![]() and period
and period ![]() , and that they travel in the positive S-direction means that the solution as a function of S and t must appear in terms of a phase angle
, and that they travel in the positive S-direction means that the solution as a function of S and t must appear in terms of a phase angle ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() from matching terms in equal powers of
from matching terms in equal powers of ![]() and
and ![]() in the free surface boundary conditions, Equation 6.2.3–2 and Equation 6.2.3–3. They give the constants as functions of
in the free surface boundary conditions, Equation 6.2.3–2 and Equation 6.2.3–3. They give the constants as functions of ![]() as
as 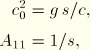

![]() in the equation for
in the equation for ![]() . This was corrected to –2592 by Nishimura et al. (1970).
. This was corrected to –2592 by Nishimura et al. (1970).![]() and
and ![]() . The wave height is
. The wave height is ![]()

![]()
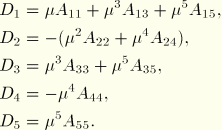
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
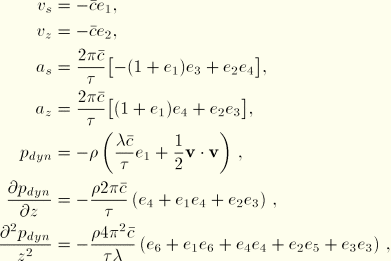
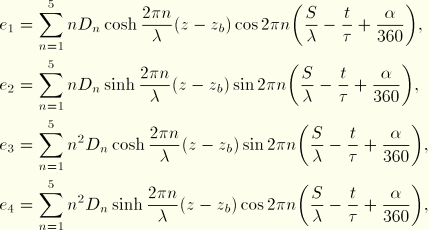
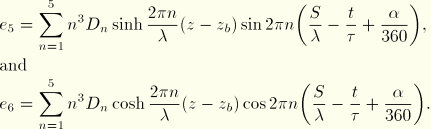
![]()