
Products: ABAQUS/Standard ABAQUS/Explicit

Mesh:
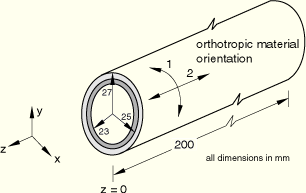
One-quarter of the cylinder cross-section and half of the length is modeled. The same problem is analyzed with different meshes. Meshes using linear solids and shells consist of eight elements along the radial and axial directions. Meshes using quadratic solids and doubly curved shells consist of four elements along the radial and axial directions. The models using continuum elements are stacked with two single-layer elements through the thickness in ABAQUS/Standard and with four single-layer elements in ABAQUS/Explicit. The models using the S4R and S8R elements use a composite section definition. The continuum shell models use two modeling techniques to model the cylinder in the thickness direction: (1) a single element with a composite section and (2) four single-layer elements stacked through the thickness.
Material:Inner isotropic cylinder: E = 2.1E5 MPa, ![]() = 0.3,
= 0.3, ![]() = 2.0 × 10–5/°C.
= 2.0 × 10–5/°C.
Outer circumferentially wound cylinder: ![]() = 130 GPa,
= 130 GPa, ![]() = 5 GPa,
= 5 GPa, ![]() = 5 GPa,
= 5 GPa, ![]() = 0.25,
= 0.25, ![]() = 0.25,
= 0.25, ![]() = 0,
= 0, ![]() = 10 GPa,
= 10 GPa, ![]() = 10 GPa,
= 10 GPa, ![]() = 5 GPa,
= 5 GPa, ![]() = 3.0 × 10–6/°C,
= 3.0 × 10–6/°C, ![]() = 2.0 × 10–5/°C,
= 2.0 × 10–5/°C, ![]() = 2.0 × 10–5/°C.
= 2.0 × 10–5/°C.
Boundary conditions:
![]() = 0 at z = 0.
= 0 at z = 0.
Loading:
Case 1: Internal pressure of 200 MPa.
Case 2 (ABAQUS/Standard only): Internal pressure of 200 MPa + temperature rise of 130°C.
This is a test recommended by the National Agency for Finite Element Methods and Standards (U.K.): Test R0031/2 from NAFEMS publication R0031, “Composites Benchmarks,” Issue 2, February 5, 2001.
The results are given in Table 4.9.2–1 and Table 4.9.2–2. All results at ![]() . The values enclosed in parentheses are percentage differences with respect to the reference solution.
. The values enclosed in parentheses are percentage differences with respect to the reference solution.
Table 4.9.2–1 ABAQUS/Standard analysis.
| Analysis | Case 1 | Case 2 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| inner cylinder | outer cylinder | inner cylinder | outer cylinder | |||||
| Composite S8R | 1421 (–9.2%) | 1421 (–0.6%) | 878 (0.4%) | 878 (15.7%) | 1241 (–10.1%) | 1241 (–1.5%) | 1056 (–3.7%) | 1056 (12.8%) |
| Stacked C3D20 | 1567 (0.1%) | 1432 (0.2%) | 880 (0.6%) | 756 (–0.4%) | 1382 (0.1%) | 1262 (0.2%) | 1062 (–3.1%) | 933 (–0.3%) |
| Composite SC8R | 1477 (–5.6%) | 1477 (3.3%) | 900 (2.9%) | 900 (18.6%) | 1299 (–5.9%) | 1299 (3.1%) | 1078 (-1.6%) | 1078 (15.2%) |
| Stacked SC8R | 1552 (–0.9 %) | 1470 (2.8%) | 849 (–2.9%) | 787 (3.7%) | 1450 (5.0%) | 1319 (4.7%) | 1011 (–7.8%) | 935 (–0.1%) |
| Composite SC8R* | 1477 (–5.6%) | 1477 (3.3%) | 900 (2.9%) | 900 (18.6%) | 1299 (–5.9%) | 1299 (3.1%) | 1078 (–1.6%) | 1078 (15.2%) |
| Stacked SC8R* | 1587 (1.4%) | 1491 (4.3%) | 848 (–3.1%) | 785 (3.4%) | 1452 (5.1%) | 1318 (4.6%) | 1011 (–7.8%) | 935 (–0.1%) |
| Reference solution | 1565 | 1430 | 875 | 759 | 1381 | 1260 | 1096 | 936 |

Composite S8R model.
Stacked C3D20 model.
Composite SC8R model.
Stacked SC8R model.
Composite SC8R model with enhanced hourglass control.
Stacked SC8R model with enhanced hourglass control.