
Products: ABAQUS/Standard ABAQUS/CAE

The frequency domain viscoelastic material model:
describes frequency-dependent material behavior in small steady-state harmonic oscillations for those materials in which dissipative losses caused by “viscous” (internal damping) effects must be modeled in the frequency domain;
assumes that the shear (deviatoric) and volumetric behaviors are independent in multiaxial stress states;
can be used in large-strain problems;
is isotropic and linear;
can be used only in conjunction with either “Linear elastic behavior,” Section 10.2.1, or “Hyperelastic behavior,” Section 10.5.1, to define the long-term elastic material properties; and
is active only during the direct-solution steady-state dynamic procedure (“Direct-solution steady-state dynamic analysis,” Section 6.3.4).

Consider a shear test at small strain, in which a harmonically varying shear strain ![]() is applied:
is applied:
![]()
![]()
![]()
The above equation states that the material responds to steady-state harmonic strain with a stress of magnitude ![]() that is in phase with the strain and a stress of magnitude
that is in phase with the strain and a stress of magnitude ![]() that lags the excitation by
that lags the excitation by ![]() . Hence, we can regard the factor
. Hence, we can regard the factor
![]()
![]()
![]()
Measurements of ![]() and
and ![]() as functions of frequency in an experiment can, thus, be used to define
as functions of frequency in an experiment can, thus, be used to define ![]() and
and ![]() and, thus,
and, thus, ![]() and
and ![]() as functions of frequency.
as functions of frequency.

In multiaxial stress states ABAQUS/Standard assumes that the frequency dependence of the shear (deviatoric) and volumetric behaviors are independent. The volumetric behavior is defined by the bulk storage and loss moduli ![]() and
and ![]() . Similar to the shear moduli, these moduli can also be expressed in terms of the (complex) Fourier transform
. Similar to the shear moduli, these moduli can also be expressed in terms of the (complex) Fourier transform ![]() of the nondimensional bulk relaxation function
of the nondimensional bulk relaxation function ![]() :
:
![]()

The linearized vibrations can also be associated with an elastomeric material whose long-term (elastic) response is nonlinear and involves finite strains (a hyperelastic material). We can retain the simplicity of the steady-state small-amplitude vibration response analysis in this case by assuming that the linear expression for the shear stress still governs the system, except that now the long-term shear modulus ![]() can vary with the amount of static prestrain
can vary with the amount of static prestrain ![]() :
:
![]()
The generalization of these concepts to arbitrary three-dimensional deformations is provided in ABAQUS/Standard by assuming that the frequency-dependent material behavior has two independent components: one associated with shear (deviatoric) straining and the other associated with volumetric straining. In the general case of a compressible material, the model is, therefore, defined for kinematically small perturbations about a predeformed state as
![]()
![]()
![]()
is the deviatoric stress, ![]() ;
;
![]()
is the equivalent pressure stress, ![]() ;
;
![]()
is the part of the stress increment caused by incremental straining (as distinct from the part of the stress increment caused by incremental rotation of the preexisting stress with respect to the coordinate system);
![]()
is the ratio of current to original volume;
![]()
is the (small) incremental deviatoric strain, ![]() ;
;
![]()
is the deviatoric strain rate, ![]() ;
;
![]()
is the (small) incremental volumetric strain, ![]() ;
;
![]()
is the rate of volumetric strain, ![]() ;
;
![]()
is the deviatoric tangent elasticity matrix of the material in its predeformed state (for example, ![]() is the tangent shear modulus of the prestrained material);
is the tangent shear modulus of the prestrained material);
![]()
is the volumetric strain-rate/deviatoric stress-rate tangent elasticity matrix of the material in its predeformed state; and
![]()
is the tangent bulk modulus of the predeformed material.
For a fully incompressible material only the deviatoric terms in the first constitutive equation above remain and the viscoelastic behavior is completely defined by ![]() .
.

The dissipative part of the material behavior is defined by giving the real and imaginary parts of ![]() and
and ![]() (for compressible materials) as functions of frequency. The moduli can be defined as functions of the frequency in one of three ways: by a power law, by tabular input, or by a Prony series expression for the shear and bulk relaxation moduli.
(for compressible materials) as functions of frequency. The moduli can be defined as functions of the frequency in one of three ways: by a power law, by tabular input, or by a Prony series expression for the shear and bulk relaxation moduli.
The frequency dependence can be defined by the power law formulŠ
![]()
| Input File Usage: | *VISCOELASTIC, FREQUENCY=FORMULA |
| ABAQUS/CAE Usage: | Property module: material editor: Mechanical |
The frequency domain response can alternatively be defined in tabular form by giving the real and imaginary parts of ![]() and
and ![]() —where
—where ![]() is the circular frequency—as functions of frequency in cycles per time. Given the frequency-dependent storage and loss moduli
is the circular frequency—as functions of frequency in cycles per time. Given the frequency-dependent storage and loss moduli ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() , the real and imaginary parts of
, the real and imaginary parts of ![]() and
and ![]() are then given as
are then given as
![]()
| Input File Usage: | *VISCOELASTIC, FREQUENCY=TABULAR |
| ABAQUS/CAE Usage: | Property module: material editor: Mechanical |
The frequency dependence can also be obtained from a time domain Prony series description of the dimensionless shear and bulk relaxation moduli:
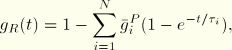
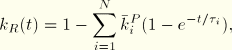
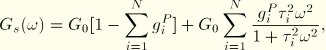
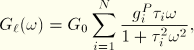
For the test data you can specify the normalized shear and bulk data separately as functions of time or specify the normalized shear and bulk data simultaneously. A nonlinear least-squares fit is performed to determine the Prony series parameters, ![]() .
.
| Input File Usage: | Use one of the following options to specify Prony data, creep test data, or relaxation test data: |
*VISCOELASTIC, FREQUENCY=PRONY *VISCOELASTIC, FREQUENCY=CREEP TEST DATA *VISCOELASTIC, FREQUENCY=RELAXATION TEST DATA Use one or both of the following options to specify the normalized shear and bulk data separately as functions of time: *SHEAR TEST DATA *VOLUMETRIC TEST DATA Use the following option to specify the normalized shear and bulk data simultaneously: *COMBINED TEST DATA |
| ABAQUS/CAE Usage: | Property module: material editor: Mechanical |
| Use one or both of the following options to specify the normalized shear and bulk data separately as functions of time: Test Data Use the following option to specify the normalized shear and bulk data simultaneously: Test Data |

For some cases of small straining of isotropic viscoelastic materials, the material data are provided as frequency-dependent uniaxial storage and loss moduli, ![]() and
and ![]() , and bulk moduli,
, and bulk moduli, ![]() and
and ![]() . In that case the data must be converted to obtain the frequency-dependent shear storage and loss moduli
. In that case the data must be converted to obtain the frequency-dependent shear storage and loss moduli ![]() and
and ![]() .
.
The complex shear modulus is obtained as a function of the complex uniaxial and bulk moduli with the expression
![]()
![]()
![]()

In all cases elastic moduli must be specified to define the rate-independent part of the material behavior. The elastic behavior is defined by an elastic, hyperelastic, or hyperfoam material model. Since the frequency domain viscoelastic material model is developed around the long-term elastic moduli, the rate-independent elasticity must be defined in terms of long-term elastic moduli. This implies that the response in any analysis procedure other than a direct-solution steady-state dynamic analysis (such as a static preloading analysis) corresponds to the fully relaxed long-term elastic solution.

The viscoelastic material model must be combined with the isotropic linear elasticity model to define classical, linear, small-strain, viscoelastic behavior. It is combined with the hyperelastic or hyperfoam model to define large-deformation, nonlinear, viscoelastic behavior. The long-term elastic properties defined for these models can be temperature dependent.
Viscoelasticity cannot be combined with any of the plasticity models. See “Combining material behaviors,” Section 9.1.3, for more details.