4.2.1 ABAQUS/Standard output variable identifiers

References
Overview

The tables in this section list all of the output variables that are available in ABAQUS/Standard. These output variables can be requested for output to the data (.dat) and results (.fil) files (see “Output to the data and results files,” Section 4.1.2) or as either field- or history-type output to the output database (.odb) file (see “Output to the output database,” Section 4.1.3). As noted specifically in the tables, a few of the output variables are written only to the output database and restart (.res) files (they are not available for output to the data or results files). These variables can be accessed only in the Visualization module of ABAQUS/CAE (ABAQUS/Viewer). Each table contains one variable type:
Element integration point variables
Element section variables
Whole element variables
Whole element energy density variables
Nodal variables
Modal variables
Surface variables
Cavity radiation variables
Section variables
Fastener interaction variables
Whole and partial model variables
Solution-dependent amplitude variables
Notation used in the output variable descriptions

The words .dat, .fil, .odb Field, and .odb History following the variable's description indicate the availability of the output variable. .dat refers to a data file output selection, .fil refers to a results file output selection, .odb "Field" refers to a field-type output selection to the output database, and .odb "History" refers to a history-type output selection to the output database. The output variable can be written to the respective file if the word "yes" appears after the category name; "no" means that the variable is not available to that file.
If the word "automatic" appears after a category name, the variable cannot be requested by name; it will be written to the respective files according to the conditions specified in the text.
Direction definitions

The direction definitions depend on the variable type.
Direction definitions for element variables
For components of stress, strain, and other tensor quantities 1, 2, and 3 refer to the directions in an orthogonal coordinate system. These directions are global directions for solid elements, surface directions for shell and membrane elements, and axial and transverse directions for beam elements. For finite-membrane-strain shell elements, membrane elements, and continuum elements associated with a local orientation (see “Orientations,” Section 2.2.5), the local output directions rotate with the average rotation of the element (integral with respect to time of the spin—see “Stress rates,” Section 1.5.3 of the ABAQUS Theory Manual). Tensor components in these cases are output in the rotating local directions.
In some cases the local output directions may differ from one integration point to the next within an element. ABAQUS/Standard does not take this variation into account when extrapolating output variables to the nodes, which affects output such as element quantities averaged at the nodes or contour plots of individual tensor components. Invariant quantities at the integration points will not be influenced by the local output directions.
You can control writing the local directions to the output database file or to the results file (see “Specifying the directions for element output” in “Output to the output database,” Section 4.1.3, and “Output of local directions to the results file” in “Output to the data and results files,” Section 4.1.2). By default, the local directions are written to the output database for all frames that include element field output. The local (material) directions (averaged at the nodes) can be visualized in ABAQUS/CAE by selecting  in the Visualization module. The directions can be printed to the data file by using user subroutine UVARM (see “UVARM,” Section 25.2.43).
in the Visualization module. The directions can be printed to the data file by using user subroutine UVARM (see “UVARM,” Section 25.2.43).
Direction definitions for equivalent rigid body variables
For all equivalent rigid body variables 1, 2, and 3 refer to global directions.
Direction definitions for nodal variables
For nodal variables 1, 2, and 3 are global directions (1=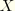 , 2=
, 2=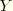 , and 3=
, and 3=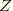 ; or for axisymmetric elements, 1=
; or for axisymmetric elements, 1= and 2=
and 2= ). If a local coordinate system is defined at a node (see “Transformed coordinate systems,” Section 2.1.5), you can specify whether output to the data or results file of vector-valued quantities at these nodes is in the local or global system (see “Specifying the directions for nodal output” in “Output to the data and results files,” Section 4.1.2). By default, nodal output is written to the data file in the local system, whereas it is written to the results file in the global system (since this is more convenient for postprocessing).
). If a local coordinate system is defined at a node (see “Transformed coordinate systems,” Section 2.1.5), you can specify whether output to the data or results file of vector-valued quantities at these nodes is in the local or global system (see “Specifying the directions for nodal output” in “Output to the data and results files,” Section 4.1.2). By default, nodal output is written to the data file in the local system, whereas it is written to the results file in the global system (since this is more convenient for postprocessing).
If nodal field output is requested for a node that has a local coordinate system defined, a quaternion representing the rotation from the global directions is written to the output database. ABAQUS/CAE automatically uses this quaternion to transform the nodal results into the local directions. Nodal history data written to the output database are always stored in the global directions.
Strain output

The total strain E is composed of the elastic strain EE, the inelastic strain IE, and the thermal strain THE. The inelastic strain IE consists of the plastic strain PE and the creep strain CE.
For geometrically nonlinear analysis ABAQUS/Standard makes it possible to output different strain measures as well as elastic and various inelastic strains. The various total strain measures (integrated strain measure E, nominal strain measure NE, and logarithmic strain measure LE) are described in “Conventions,” Section 1.2.2. The default strain measure for output to the data (.dat) and results (.fil) files is E. However, for geometrically nonlinear analysis E is not available for output to the output database (.odb) file, and LE is the default strain measure.
Temperature output

In ABAQUS temperature can either be a field variable (stress analysis, mass diffusion, …) or a degree of freedom (heat transfer analysis, fully coupled temperature-displacement analysis, …). For any analysis that involves temperature, you can request the temperature either at nodes (variable NT) or in elements (variable TEMP). If element temperature output is requested at the nodes, the integration point values are extrapolated and, if requested, averaged. These extrapolated values are generally not as accurate as the nodal temperatures themselves. An exception to this is adiabatic analysis, in which the element temperatures change due to plastic heat generation but the nodal temperatures are not updated. In that case the current nodal temperatures are obtained only if element temperature output is requested at the nodes.
For continuum elements there is only one temperature value per node (NT11). For shells and beams more than one temperature is available for each node (NT11, NT12, …) since a temperature gradient can exist through the thickness of a shell or across the cross-section of a beam. In general, variables NT12, NT13, etc. contain temperature values. However, when temperature is defined by specifying temperature gradients, nodal temperatures for a given section point can be obtained only by using the variable TEMP. See “Specifying temperature and field variables” in “Using a beam section integrated during the analysis to define the section behavior,” Section 15.3.6, and “Specifying temperature and field variables” in “Using a shell section integrated during the analysis to define the section behavior,” Section 15.6.5, for discussions on specifying temperatures in beams and shells.
Principal value output

Output of the principal values can be requested for stresses, strains, and other material tensors. Either all principal values or the minimum, maximum, or intermediate values can be obtained. All principal values of tensor ABC are obtained with the request ABCP. The minimum, intermediate, and maximum principal values are obtained with the requests ABCP1, ABCP2, and ABCP3.
For three-dimensional, (generalized) plane strain, and axisymmetric elements all three principal values are obtained. For plane stress, membrane, and shell elements, the out-of-plane principal value cannot be requested for history-type output. For field-type output, ABAQUS/CAE always reports the out-of-plane principal value as zero. Principal values cannot be obtained for truss elements or for any beam elements other than the three-dimensional beam elements with torsional shear stresses.
If a principal value or an invariant is requested for field-type output, the output request is replaced with an output request for the components of the corresponding tensor. ABAQUS/CAE calculates all principal values and invariants from these components. If a principal value is desired as history-type output, it must be explicitly requested since ABAQUS/CAE does no calculations on history data.
Tensor output

Tensor variables that are written to the output database as field-type output are written as components in either the default directions defined by the convention given in “Orientations,” Section 2.2.5 (global directions for solid elements, surface directions for shell and membrane elements, and axial and transverse directions for beam elements), or the user-defined local system. ABAQUS/CAE calculates all principal values and invariants from these components. See “Writing field output data,” Section 8.6.4 of the ABAQUS Scripting User's Manual, for a description of the different types of tensor variables.
For plane stress, membrane, and shell elements, only the in-plane tensor components (11, 22, and 12 components) are stored by ABAQUS/Standard. The out-of-plane direct component for stress (S33) is reported as zero to the output database as expected, and the out-of-plane component of strain (E33) is reported as zero even though it is not. This is because the thickness direction is computed based on section properties rather than at the material level. The out-of-plane components can be requested for field-type output and cannot be requested for history-type output. The out-of-plane stress components are not reported to the data (.dat) file or to the results (.fil) file.
For three-dimensional beam elements with torsional shear stresses, only the axial and the torsional components (the 11 and 12 components) are stored by ABAQUS/Standard. The other direct component (the 22 component) is reported as zero for field-type output and cannot be requested for history-type output.
The components for tensor variables are written to the output database in single precision. Therefore, a small amount of precision roundoff error may occur when calculating the variables' principal values. Such roundoff error may be observed, for example, when analytically zero values are calculated as relatively small nonzero values.
Element integration point variables

You can request element integration point variable output to the data, results, or output database file (see
“Element output” in “Output to the data and results files,” Section 4.1.2, and
“Element output” in “Output to the output database,” Section 4.1.3).
Tensors and associated principal values and invariants
SAll stress components.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
Sij
-component of stress (
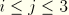
).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes All principal stresses.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
SPnMinimum, intermediate, and maximum principal stresses (
SP1  SP2
SP2  SP3
SP3).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes All stress invariants (MISES, TRESC, PRESS, INV3).
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
MISESMises equivalent stress, defined as
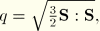
where 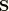 is the deviatoric stress tensor, defined as
is the deviatoric stress tensor, defined as 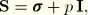 where
where 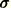 is the stress,
is the stress, 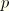 is the equivalent pressure stress (defined below), and
is the equivalent pressure stress (defined below), and 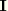 is a unit matrix. In index notation
is a unit matrix. In index notation
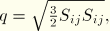
where
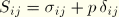
,
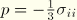
, and
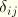
is the Kronecker delta.
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Tresca equivalent stress, defined as the maximum difference between principal stresses.
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
PRESSEquivalent pressure stress, defined as
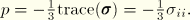 .dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Third stress invariant, defined as
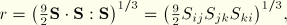
where
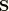
is the deviatoric stress defined in the context of Mises equivalent stress, above.
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes All kinematic hardening shift tensor components.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
ALPHAij
-component of the shift tensor (
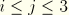
).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes All principal values of the shift tensor.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
ALPHAPnMinimum, intermediate, and maximum principal values of the shift tensor (
ALPHA1  ALPHA2
ALPHA2  ALPHA3
ALPHA3).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes All strain components. For geometrically nonlinear analysis E is not available for output to the output database (.odb) file.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
Eij
-component of strain (
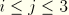
).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes All principal strains.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
EPnMinimum, intermediate, and maximum principal strains (
EP1  EP2
EP2  EP3
EP3).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes All nominal strain components.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
NEij
-component of nominal strain (
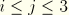
).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes All principal nominal strains.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
NEPnMinimum, intermediate, and maximum principal nominal strains (
NEP1  NEP2
NEP2  NEP3
NEP3).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes All logarithmic strain components. For geometrically nonlinear analysis LE is the default strain measure for output to the output database (.odb) file.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
LEij
-component of logarithmic strain (
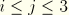
).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes All principal logarithmic strains.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
LEPnMinimum, intermediate, and maximum principal logarithmic strains (
LEP1  LEP2
LEP2  LEP3
LEP3).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes All mechanical strain rate components.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
ERij
-component of strain rate (
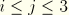
).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes All principal mechanical strain rates.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
ERPnMinimum, intermediate, and maximum principal mechanical strain rates (
ERP1  ERP2
ERP2  ERP3
ERP3).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes All components of the total deformation gradient. Available only for hyperelasticity, hyperfoam, and material models defined in user subroutine UMAT. For fully integrated first-order quadrilaterals and hexahedra, the selectively reduced integration technique is used. A modified deformation gradient is output for these elements.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: no
DGij
-component of the total deformation gradient (
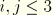
).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: no Principal stretches.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: no
DGPnMinimum, intermediate, and maximum values of principal stretches (
DGP1  DGP2
DGP2  DGP3
DGP3).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: no All elastic strain components.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
EEij
-component of elastic strain (
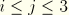
).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes All principal elastic strains.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
EEPnMinimum, intermediate, and maximum principal elastic strains (
EEP1  EEP2
EEP2  EEP3
EEP3).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes All inelastic strain components.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
IEij
-component of inelastic strain (
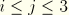
).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes All principal inelastic strains.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
IEPnMinimum, intermediate, and maximum principal inelastic strains (
IEP1  IEP2
IEP2  IEP3
IEP3).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes All thermal strain components.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
THEij
-component of thermal strain (
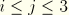
).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes All principal thermal strains.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
THEPnMinimum, intermediate, and maximum principal thermal strains (
THEP1  THEP2
THEP2  THEP3
THEP3).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes All plastic strain components. This identifier also provides PEEQ, a yes/no flag telling if the material is currently yielding or not (AC YIELD: “actively yielding”), and PEMAG when PE is requested for the data or results files. When PE is requested for field output to the output database, PEEQ is also provided.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
PEij
-component of plastic strain (
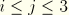
).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Equivalent plastic strain. This identifier also provides a yes/no flag (1/0 on the output database) telling if the material is currently yielding or not (AC YIELD: “actively yielding”).
The equivalent plastic strain is defined as 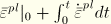 , where
, where 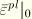 is the initial equivalent plastic strain.
is the initial equivalent plastic strain.
The definition of 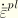 depends on the material model. For classical metal (Mises) plasticity
depends on the material model. For classical metal (Mises) plasticity 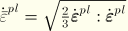 . For other plasticity models, see the appropriate section in Part IV, “Materials.”
. For other plasticity models, see the appropriate section in Part IV, “Materials.”
When plasticity occurs in the thickness direction to a gasket element whose plastic behavior is specified as part of a gasket behavior definition,
PEEQ is
PE11.
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes Equivalent plastic strain in uniaxial tension for cast iron plasticity, which is defined as
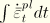
. This identifier also provides a yes/no flag (1/0 on the output database) telling if the material is currently yielding or not (AC YIELDT: “actively yielding”).
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes Plastic strain magnitude, defined as

.
For most materials,
PEEQ and
PEMAG are equal only for proportional loading. When plasticity occurs in the thickness direction to a gasket element whose plastic behavior is specified as part of a gasket behavior definition,
PEMAG is
PE11.
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes All principal plastic strains.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
PEPnMinimum, intermediate, and maximum principal plastic strains (
PEP1  PEP2
PEP2  PEP3
PEP3).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes All creep strain components. This identifier also provides CEEQ, CESW, and CEMAG when CE is requested for the data or results files.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
CEij
-component of creep strain (
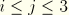
).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Equivalent creep strain, defined as
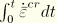
.
The definition of 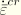 depends on the material model. For classical metal (Mises) creep
depends on the material model. For classical metal (Mises) creep 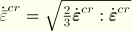 . For other creep models, see the appropriate section in Part IV, “Materials.”
. For other creep models, see the appropriate section in Part IV, “Materials.”
When creep occurs in the thickness direction to a gasket element whose creep behavior is specified as part of a gasket behavior definition,
CEEQ is
CE11.
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes Magnitude of swelling strain.
For cap creep
CESW gives the equivalent creep strain produced by the consolidation creep mechanism, defined as
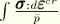
, where
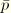
is the equivalent creep pressure,
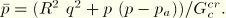 .dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes Magnitude of creep strain (defined by the same formula given above for PEMAG, applied to the creep strains).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
CEPAll principal creep strains.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
CEPnMinimum, intermediate, and maximum principal creep strains (
CEP1  CEP2
CEP2  CEP3
CEP3).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
Additional element stresses
CS11TSHRAll transverse shear stress components. Available only for thick shell elements such as S3R, S4R, S8R, and S8RT. Contouring of this variable is supported in the Visualization module of ABAQUS/CAE.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
TSHRi3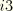
-component of transverse shear stress (
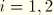
). Available only for thick shell elements such as S3R, S4R, S8R, and S8RT.
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes All substresses. Available only for ITS elements.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: no
SSnnth substress (
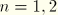
). Available only for ITS elements.
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: no
Vibration and acoustic quantities
INTENVibration intensity. Available only for the steady-state dynamics procedure. For real-only steady-state dynamics analyses, the intensity is a pure imaginary vector, but it is stored as real on the output database. Available for structural, solid, and acoustic elements and for rebar.
.dat: no .fil: no .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
ACVAcoustic particle velocity. Available only if the steady-state dynamic procedure is used, and available only for acoustic finite elements.
.dat: no .fil: no .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
ACVnComponent n of the acoustic particle velocity vector (n = 1, 2, 3). Available only if the steady-state dynamic procedure is used, and available only for acoustic finite elements.
.dat: no .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
GRADPAcoustic pressure gradient. Available only if the steady-state dynamic procedure is used, and available only for acoustic finite elements.
.dat: no .fil: no .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
Energy densities
ENERAll energy densities. None of the energy densities are available in mode-based procedures; a limited number of them are available for direct-solution steady-state dynamic and subspace-based steady-state dynamic analyses. In steady-state dynamics all energy quantities are net per-cycle values, unless otherwise noted (see
“Energy balance,” Section 1.5.5 of the ABAQUS Theory Manual).
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes Elastic strain energy density (with respect to current volume). When the Mullins effect is modeled with hyperelastic materials, this quantity represents only the recoverable part of energy per unit volume. This is the only energy density available in the data file for eigenvalue extraction procedures; to obtain this quantity for eigenvalue extraction procedures in the results file or as field output in the output database, request ENER. In steady-state dynamic analysis this is the cyclic mean value.
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
PENEREnergy dissipated by rate-independent and rate-dependent plasticity, per unit volume. Not available for steady-state dynamic analysis.
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
CENEREnergy dissipated by creep, swelling, and viscoelasticity, per unit volume. Not available for steady-state dynamic analysis.
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
VENEREnergy dissipated by viscous effects (except those from viscoelasticity and static dissipation), per unit volume.
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
EENERElectrostatic energy density. Not available for steady-state dynamic analysis.
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
JENERElectrical energy dissipated as a result of the flow of current, per unit volume. Not available for steady-state dynamic analysis.
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
DMENEREnergy dissipated by damage, per unit volume. Not available for steady-state dynamic analysis.
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
State, field, and user-defined output variables
SDVSolution-dependent state variables.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
SDVnSolution-dependent state variable n.
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
TEMPTemperature.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
FVPredefined field variables.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
FVnPredefined field variable n.
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
MFRPredefined mass flow rates.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
MFRnComponent
n of predefined mass flow rate (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes User-defined output variables.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
UVARMnUser-defined output variable n.
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
Composite failure measures
CFAILUREAll failure measure components.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
MSTRSMaximum stress theory failure measure.
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
TSAIHTsai-Hill theory failure measure.
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
TSAIWTsai-Wu theory failure measure.
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
AZZITAzzi-Tsai-Hill theory failure measure.
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
MSTRNMaximum strain theory failure measure.
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
Fluid link quantities
MFLCurrent value of the mass flow rate.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
MFLTCurrent value of the total mass flow.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
Fracture mechanics quantities
JK 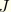
-integral, stress intensity factors. Available only for line spring elements. Output is in the following order for LS3S elements:
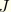
,
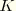
,
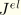
, and
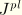
. Output is in the following order for LS6 elements:
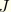
,
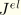
,
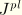
,
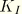
,
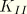
, and
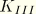
.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
Concrete cracking and additional plasticity
CRACKUnit normal to cracks in concrete.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: no
CONFNumber of cracks at a concrete material point.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: no
PEQCAll equivalent plastic strains when the model has more than one yield/failure surface.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
PEQCnnth equivalent plastic strain (
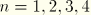
).
For jointed materials: PEQC provides equivalent plastic strains for all four possible systems (three joints - PEQC1, PEQC2, PEQC3, and bulk material - PEQC4). This identifier also provides a yes/no flag (1/0 on the output database) telling if each individual system is currently yielding or not (AC YIELD: “actively yielding”).
For cap plasticity: PEQC provides equivalent plastic strains for all three possible yield/failure surfaces (Drucker-Prager failure surface - PEQC1, cap surface - PEQC2, and transition surface - PEQC3) and the total volumetric inelastic strain (PEQC4). All identifiers also provide a yes/no flag (1/0 on the output database) telling whether the yield surface is currently active or not (AC YIELD: “actively yielding”).
When
PEQC is requested as output to the output database, the active yield flags for each component are named AC YIELD1, AC YIELD2, etc. and take the value 1 or 0.
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
Concrete damaged plasticity
DAMAGECCompressive damage variable,
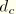
.
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes Tensile damage variable,
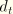
.
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes Scalar stiffness degradation variable,
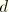
.
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes Equivalent plastic strain in uniaxial compression, which is defined as
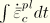
. This identifier also provides a yes/no flag (1/0 on the output database) telling if the material is currently undergoing compressive failure or not (AC YIELD: “actively yielding”).
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes Equivalent plastic strain in uniaxial tension, which is defined as
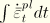
. This identifier also provides a yes/no flag (1/0 on the output database) telling if the material is currently undergoing tensile failure or not (AC YIELDT: “actively yielding”).
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
Rebar quantities
RBFORForce in rebar.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
RBANGAngle in degrees between rebar and the user-specified isoparametric direction. Available only for shell, membrane, and surface elements.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
RBROTChange in angle in degrees between rebar and the user-specified isoparametric direction. Available only for shell, membrane, and surface elements.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
Heat transfer analysis
HFLCurrent magnitude and components of the heat flux vector. The integration points for these values are located at the Gauss points.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
HFLMCurrent magnitude of heat flux vector.
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
HFLnComponent
n of the heat flux vector (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
Mass diffusion analysis
CONCMass concentration.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
ISOLAmount of solute at an integration point, calculated as the product of the mass concentration (CONC) and the integration point volume (IVOL).
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
MFLCurrent magnitude and components of the concentration flux vector.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
MFLMCurrent magnitude of the concentration flux vector.
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
MFLnComponent
n of the concentration flux vector (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
Elements with electrical potential degrees of freedom
EPGCurrent magnitude and components of the electrical potential gradient vector.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
EPGMCurrent magnitude of the electrical potential gradient vector.
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
EPGnComponent
n of the electrical potential gradient vector (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
Piezoelectric analysis
EFLXCurrent magnitude and components of the electrical flux vector.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
EFLXMCurrent magnitude of the electrical flux vector.
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
EFLXnComponent
n of the electrical flux vector (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
Coupled thermal-electrical elements
ECDCurrent magnitude and components of the electrical current density.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
ECDMCurrent magnitude of the electrical current density.
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
ECDnComponent
n of the electrical current density vector (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
Cohesive elements
MAXSCRTMaximum nominal stress damage initiation criterion.
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
MAXECRTMaximum nominal strain damage initiation criterion.
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
QUADSCRTQuadratic nominal stress damage initiation criterion.
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
QUADECRTQuadratic nominal strain damage initiation criterion.
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
DMICRTAll active components of the damage initiation criteria.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
SDEGOverall scalar stiffness degradation.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
STATUSStatus of the element (the status of an element is 1.0 if the element is active, 0.0 if the element is not).
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
Pore pressure analysis
VOIDRVoid ratio.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
PORPore pressure.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
SATSaturation.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
GELVRGel volume ratio.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
FLUVRTotal fluid volume ratio.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
FLVELCurrent magnitude and components of the pore fluid effective velocity vector.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
FLVELMCurrent magnitude of the pore fluid effective velocity vector.
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
FLVELnComponent
n of the pore fluid effective velocity vector (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
Porous metal plasticity quantities
RDRelative density.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
VVFVoid volume fraction.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
VVFGVoid volume fraction due to void growth.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
VVFNVoid volume fraction due to void nucleation.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
Two-layer viscoplasticity quantities
VSStress in the elastic-viscous network.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
VSij
-component of stress in the elastic-viscous network (
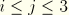
).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Stress in the elastic-plastic network.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
PSij
-component of stress in the elastic-plastic network (
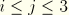
).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Viscous strain in the elastic-viscous network.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
VEij
-component of viscous strain in the elastic-viscous network (
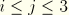
).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Plastic strain in the elastic-plastic network.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
PEij
-component of plastic strain in the elastic-plastic network (
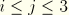
).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Equivalent viscous strain in the elastic-viscous network, defined as
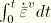
.
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes Equivalent plastic strain in the elastic-plastic network, defined as
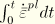
.
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
Geometric quantities
COORDCoordinates of the integration point for solid elements and rebar. These are the current coordinates if the large-displacement formulation is being used.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
IVOLIntegration point volume. Section point volume in the case of beams and shells. (Not available for eigenfrequency extraction, eigenvalue buckling prediction, complex eigenfrequency extraction, or linear dynamics procedures. Available only for continuum and structural elements not using general beam or shell section definitions.)
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
Accuracy indicators
SJPStrain jumps at nodes.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: no
Random response analysis
The following variables (beginning with R) are available only for random response dynamic analysis:
RSRoot mean square of all stress components.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
RSijRoot mean square of

-component of stress (
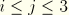
).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Root mean square of all strain components.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
REijRoot mean square of

-component of strain (
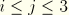
).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes RMS values of all components of connector total forces and moments.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
RCTFnRMS value of connector total force component
n (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes RMS value of connector total moment component
n (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes RMS values of all components of connector elastic forces and moments.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
RCEFnRMS value of connector elastic force component
n (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes RMS value of connector elastic moment component
n (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes RMS values of all components of connector viscous forces and moments.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
RCVFnRMS value of connector viscous force component
n (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes RMS value of connector viscous moment component
n (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes RMS values of all components of connector reaction forces and moments.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
RCRFnRMS value of connector reaction force component
n (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes RMS value of connector reaction moment component
n (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes RMS values of all components of connector friction forces and moments.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
RCSFnRMS value of connector friction force component
n (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes RMS value of connector friction moment component
n (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes RMS value of connector friction force in the direction of the instantaneous slip direction. Available only if friction is defined in the slip direction.
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
RCURMS values of all components of connector relative displacements and rotations.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
RCUnRMS value of connector relative displacement in the
n-direction (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes RMS value of connector relative rotation in the
n-direction (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes RMS values of all components of connector constitutive displacements and rotations.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
RCCUnRMS value of connector constitutive displacement in the
n-direction (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes RMS value of connector constitutive rotation in the
n-direction (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes RMS values of all components of connector friction-generating contact forces and moments.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
RCNFnRMS value of connector friction-generating contact force component
n (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes RMS value of connector friction-generating contact moment component
n (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes RMS values of connector friction-generating contact force components in the instantaneous slip direction. Available only if friction is defined in the slip direction.
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
Steady-state dynamic analysis
The following variables (beginning with P) are available only for steady-state (frequency domain) dynamic analysis. These variables include both the magnitude and phase angle for all components. Phase angles are given in degrees. In the data file there are two lines of output for each request. The first line contains the magnitude, and the second line (indicated by the SSD footnote) contains the phase angle. In the results file the magnitudes of all components are first, followed by the phase angles of all components.
PHSMagnitude and phase angle of all stress components.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: no
PHSijMagnitude and phase angle of

-component of stress (
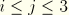
).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: no Magnitude and phase angle of all strain components.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: no
PHEijMagnitude and phase angle of

-component of strain (
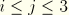
).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: no Magnitude and phase angles of the electrical potential gradient vector.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: no
PHEPGnMagnitude and phase angle of component
n of the electrical potential gradient (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: no Magnitude and phase angles of the electrical flux vector.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: no
PHEFLnMagnitude and phase angle of component
n of the electrical flux vector (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: no Magnitude and phase angle of mass flow rate. Available only for fluid link elements.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: no
PHMFTMagnitude and phase angle of total mass flow. Available only for fluid link elements.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: no
PHCTFMagnitude and phase of all components of connector total forces and moments.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: no
PHCTFnMagnitude and phase of connector total force component
n (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: no Magnitude and phase of connector total moment component
n (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: no Magnitude and phase of all components of connector elastic forces and moments.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: no
PHCEFnMagnitude and phase of connector elastic force component
n (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: no Magnitude and phase of connector elastic moment component
n (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: no Magnitude and phase of all components of connector viscous forces and moments.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: no
PHCVFnMagnitude and phase of connector viscous force component
n (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: no Magnitude and phase of connector viscous moment component
n (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: no Magnitude and phase of all components of connector reaction forces and moments.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: no
PHCRFnMagnitude and phase of connector reaction force component
n (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: no Magnitude and phase of connector reaction moment component
n (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: no Magnitude and phase of all components of connector friction forces and moments.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: no
PHCSFnMagnitude and phase of connector friction force component
n (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: no Magnitude and phase of connector friction moment component
n (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: no Magnitude and phase of connector friction force in the direction of the instantaneous slip direction. Available only if friction is defined in the slip direction.
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: no
PHCUMagnitude and phase of all components of connector relative displacements and rotations.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: no
PHCUnMagnitude and phase of connector relative displacement in the
n-direction (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: no Magnitude and phase of connector relative rotation in the
n-direction (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: no Magnitude and phase of all components of connector constitutive displacements and rotations.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: no
PHCCUnMagnitude and phase of connector constitutive displacement in the
n-direction (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: no Magnitude and phase of connector constitutive rotation in the
n-direction (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: no Magnitude and phase of all components of connector relative velocities.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: no
PHCVnMagnitude and phase of connector relative velocity in the
n-direction (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: no Magnitude and phase of connector relative angular velocity in the
n-direction (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: no Magnitude and phase of all components of connector relative accelerations.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: no
PHCAnMagnitude and phase of connector relative acceleration in the
n-direction (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: no Magnitude and phase of connector relative angular acceleration in the
n-direction (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: no Magnitude and phase of all components of connector friction-generating contact forces and moments.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: no
PHCNFnMagnitude and phase of connector friction-generating contact force component
n (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: no Magnitude and phase of connector friction-generating contact moment component
n (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: no Magnitude and phase of connector friction-generating contact force in the instantaneous slip direction. Available only if friction is defined in the slip direction.
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: no
PHCIVSLMagnitude and phase of connector instantaneous velocity in the slip direction. Available only if friction is defined in the slip direction.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: no
Element section variables

You can request element section variable output to the data, results, or output database file (see
“Element output” in “Output to the data and results files,” Section 4.1.2, and
“Element output” in “Output to the output database,” Section 4.1.3). These variables are available only for beam and shell elements with the exception of
STH, which is also available for membrane elements. They are defined for particular elements in the element descriptions in
Part V, “Elements.”
SFAll section force and moment components.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
SFnSection force component
n (
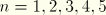
for shells;

for beams).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Section moment component
n (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Bimoment of beam cross-section. Available only for open-section beam elements.
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
ESF1Effective axial force for beams and pipes subjected to pressure loading. Available for all stress/displacement procedure types except response spectrum and random response.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
SSAVGAll average shell section stress components.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: no
SSAVGnAverage shell section stress component
n (
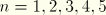
).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: no All section strain, curvature change, and twist components.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
SEnSection strain component
n (
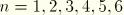
for shells;

for beams).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Section curvature change or twist
n (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Bicurvature of beam cross-section. Available only for open-section beam elements.
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
MAXSSMaximum axial stress on the section. (This variable can be used with the following types of general beam section definitions: standard library cross-sections, linear generalized cross-sections, or meshed cross-sections with specified output section points. If the output section points are specified, the MAXSS output will be the maximum of the stresses at the user-specified points.)
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: no
COORDCoordinates of the section point. These are the current coordinates if the large-displacement formulation is being used.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
STHSection thickness (current thickness for SAX1, SAX2, SAX2T, S3/S3R, S4, S4R, SAXA1
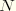
, SAXA2
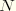
, and all membrane elements if the large-displacement formulation is used; initial thickness for all other cases).
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes Integrated section volume. (Not available for eigenfrequency extraction, eigenvalue buckling prediction, complex eigenfrequency extraction, or linear dynamics procedures. Available only for continuum and structural elements not using general beam or shell section definitions.)
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
SPEAll generalized plastic strain components. Available only for inelastic nonlinear response in a general beam section.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
SPEnGeneralized plastic strain component
n (
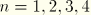
). Representing axial plastic strain, curvature change about the local 1-axis, curvature change about the local 2-axis, and twist of the beam. Available only for inelastic nonlinear response in a general beam section.
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes All equivalent plastic strains. Available only for inelastic nonlinear response in a general beam section.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
SEPEnEquivalent plastic strain component
n (
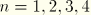
). Representing axial plastic strain, curvature change about the local 1-axis, curvature change about the local 2-axis, and twist of the beam. Available only for inelastic nonlinear response in a general beam section.
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
Frame elements
SEEAll elastic section axial, curvature, and twist strain components.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
SEE1Elastic axial strain component.
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
SKEnElastic section curvature or twist strain component (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes All plastic axial displacements and rotations at the element's ends. This identifier also provides a yes/no flag telling if the frame element's end section is currently yielding or not (AC YIELD: “actively yielding”) and a yes/no/na flag telling if buckling occurred in the strut response (AC BUCKL) or is not applicable. AC YIELD and AC BUCKL are not available in the output database.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
SEP1Plastic axial displacement at the element's ends.
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
SKPnPlastic rotations, either bending or twisting, at the element's ends (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes All generalized backstress components at the element's ends.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
SALPHAnGeneralized backstress at the element's ends (
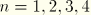
). The first component is the axial section backstress, followed by two bending backstress components and the twist backstress component.
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
Whole element variables

You can request whole element variable output to the data, results, or output database file (see
“Element output” in “Output to the data and results files,” Section 4.1.2, and
“Element output” in “Output to the output database,” Section 4.1.3).
LOADSCurrent values of distributed loads (not available for nonuniform loads).
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: no
FOUNDCurrent values of foundation pressures.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: no
FLUXSCurrent values of distributed (heat or concentration) fluxes (not available for nonuniform fluxes).
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: no
CHRGSCurrent values of distributed electrical charges.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: no
ECURSCurrent values of distributed electrical currents.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: no
ELENAll energy magnitudes in the element. None of the energies are available in mode-based procedures; a limited number of them are available for direct-solution steady-state dynamic and subspace-based steady-state dynamic analyses. In steady-state dynamics all energy quantities are net per-cycle values, unless otherwise noted.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
ELKETotal kinetic energy in the element. In steady-state dynamic analysis this is the cyclic mean value.
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
ELSETotal elastic strain energy in the element. When the Mullins effect is modeled with hyperelastic materials, this quantity represents only the recoverable part of energy in the element. This is the only energy request available in the data file for eigenvalue extraction procedures; to obtain this quantity for eigenvalue extraction procedures in the results file or as field output in the output database, request ELEN. In steady-state dynamic analysis this is the cyclic mean value.
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
ELPDTotal energy dissipated in the element by rate-independent and rate-dependent plastic deformation. Not available for steady-state dynamic analysis.
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
ELCDTotal energy dissipated in the element by creep, swelling, and viscoelasticity. Not available for steady-state dynamic analysis.
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
ELVDTotal energy dissipated in the element by viscous effects, not including energy dissipated by static stabilization or viscoelasticity.
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
ELSDTotal energy dissipated in the element resulting from automatic static stabilization. Not available for steady-state dynamic analysis.
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
ELCTETotal electrostatic energy in the element. Not available for steady-state dynamic analysis.
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
ELJDTotal electrical energy dissipated due to flow of current. Not available for steady-state dynamic analysis.
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
ELASETotal “artificial” strain energy in the element (energy associated with constraints used to remove singular modes, such as hourglass control). Not available for steady-state dynamic analysis.
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
ELDMDTotal energy dissipated in the element by damage. Not available for steady-state dynamic analysis.
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
NFORCForces at the nodes of the element caused by the stress in the element (internal forces). (Not available for eigenfrequency extraction, eigenvalue buckling prediction, complex eigenfrequency extraction, or linear dynamics procedures. The specified position for data and output database file requests is ignored.)
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
NFLUXFluxes at the nodes of the element caused by the heat conduction or mass diffusion in the element (internal fluxes). (The specified position for data and output database file requests is ignored.)
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
NCURSElectrical current at the nodes due to electrical conduction in the element.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
FILMCurrent values of film conditions (not available for nonuniform films).
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: no
RADCurrent values of radiation conditions.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: no
EVOLCurrent element volume. (Not available for eigenfrequency extraction, eigenvalue buckling prediction, complex eigenfrequency extraction, or linear dynamics procedures. Available only for continuum and structural elements not using general beam or shell section definitions.)
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
ESOLAmount of solute in an element, calculated as the sum of ISOL (amount of solute at an integration point) over all the integration points in the element.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
Connector elements
CTFAll components of connector total forces and moments.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
CTFnConnector total force component
n (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Connector total moment component
n (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes All components of connector elastic forces and moments.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
CEFnConnector elastic force component
n (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Connector elastic moment component
n (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Elastic displacements and rotations in all directions.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
CUEnElastic displacement in the
n-direction (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Elastic rotation in the
n-direction (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Plastic relative displacements and rotations in all directions.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
CUPnPlastic relative displacement in the
n-direction (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Plastic relative rotation in the
n-direction (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Equivalent plastic relative displacements and rotations in all directions.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
CUPEQnEquivalent plastic relative displacement in the
n-direction (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Equivalent plastic relative rotation in the
n-direction (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Equivalent plastic relative motion for a coupled plasticity definition.
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
CALPHAFAll components of connector kinematic hardening shift forces and moments.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
CALPHAFnConnector kinematic hardening shift force component
n (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Connector kinematic hardening shift moment component
n (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes All components of connector viscous forces and moments.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
CVFnConnector viscous force component
n (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Connector viscous moment component
n (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes All components of connector friction forces and moments.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
CSFnConnector friction force component
n (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Connector friction moment component
n (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Connector friction force in the instantaneous slip direction. Available only if friction is defined in the slip direction.
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
CNFAll components of connector friction-generating contact forces and moments.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
CNFnConnector friction-generating contact force component
n (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Connector friction-generating contact moment component
n (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Connector friction-generating contact force in the instantaneous slip direction. Available only if friction is defined in the slip direction.
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
CSLSTAll flags for connector stop and connector lock status.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
CSLSTiFlag for connector stop and connector lock status in the
i-direction (
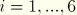
).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Components of accumulated slip in all directions.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
CASUnConnector accumulated slip in the
n-direction (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Connector angular accumulated slip in the
n-direction (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Connector accumulated slip in the instantaneous slip direction. Available only if friction is defined in the slip direction.
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
CIVCConnector instantaneous velocity in the slip direction. Available only if friction is defined in the slip direction.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
CRFAll components of connector reaction forces and moments.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
CRFnConnector reaction force component
n (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Connector reaction moment component
n (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes All components of connector concentrated forces and moments.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
CCFnConnector concentrated force component
n (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Connector concentrated moment component
n (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Relative positions in all directions.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
CPnRelative position in the
n-direction (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Relative angular position in the
n-direction (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Relative displacements and rotations in all directions.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
CUnRelative displacement in the
n-direction (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Relative rotation in the
n-direction (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Constitutive displacements and rotations in all directions.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
CCUnConstitutive displacement in the
n-direction (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Constitutive rotation in the
n-direction (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Relative velocities in all directions.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
CVnRelative velocity in the
n-direction (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Relative angular velocity in the
n-direction (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Relative accelerations in all directions.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
CAnRelative acceleration in the
n-direction (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Relative angular acceleration in the
n-direction (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
Whole element energy density variables

The following energy density output variables are written to the restart (
.res) file and the output database (
.odb) file (see
“Energy balance,” Section 1.5.5 of the ABAQUS Theory Manual):
ELEDENAll energy density components. None of the energies are available in mode-based procedures; a limited number of them are available for direct-solution steady-state dynamic and subspace-based steady-state dynamic analyses. In steady-state dynamics all energy quantities are net per-cycle values, unless otherwise noted.
.dat: no .fil: no .odb Field: yes .odb History: no
EKEDENKinetic energy density in the element. In steady-state dynamic analysis this is the cyclic mean value.
.dat: no .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
ESEDENTotal elastic strain energy density in the element. When the Mullins effect is modeled with hyperelastic materials, this quantity represents only the recoverable part of energy density in the element. This variable is not available in eigenvalue extraction procedures. In steady-state dynamic analysis this is the cyclic mean value.
.dat: no .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
EPDDENTotal energy dissipated per unit volume in the element by rate-independent and rate-dependent plastic deformation. Not available for steady-state dynamic analysis.
.dat: no .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
ECDDENTotal energy dissipated per unit volume in the element by creep, swelling, and viscoelasticity. Not available for steady-state dynamic analysis.
.dat: no .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
EVDDENTotal energy dissipated per unit volume in the element by viscous effects, not inclusive of energy dissipated through static stabilization or viscoelasticity.
.dat: no .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
ESDDENTotal energy dissipated per unit volume in the element resulting from static stabilization. Not available for steady-state dynamic analysis.
.dat: no .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
ECTEDENTotal electrostatic energy density in the element. Not available for steady-state dynamic analysis.
.dat: no .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
EASEDENTotal “artificial” strain energy density in the element (energy associated with constraints used to remove singular modes, such as hourglass control). Not available for steady-state dynamic analysis.
.dat: no .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
EDMDDENTotal energy dissipated per unit volume in the element by damage. Not available for steady-state dynamic analysis.
.dat: no .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
Nodal variables

You can request nodal variable output to the data, results, or output database file (see
“Node output” in “Output to the data and results files,” Section 4.1.2, and
“Node output” in “Output to the output database,” Section 4.1.3).
UAll physical displacement components, including rotations at nodes with rotational degrees of freedom (for output to the output database, only field-type output includes the rotations).
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
UTAll translational displacement components.
.dat: no .fil: no .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
URAll rotational displacement components.
.dat: no .fil: no .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
Un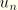
displacement component (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes 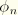
rotation component (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Warping magnitude. Available only for open-section beam elements.
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
VAll velocity components, including rotational velocities at nodes with rotational degrees of freedom (for output to the output database, only field-type output includes the rotational velocities).
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
VTAll translational velocity components.
.dat: no .fil: no .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
VRAll rotational velocity components.
.dat: no .fil: no .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
Vn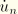
velocity component (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes 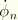
rotational velocity component (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes All acceleration components, including rotational accelerations at nodes with rotational degrees of freedom (for output to the output database, only field-type output includes the rotational accelerations).
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
ATAll translational acceleration components.
.dat: no .fil: no .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
ARAll rotational acceleration components.
.dat: no .fil: no .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
An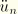
acceleration component (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes 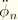
rotational acceleration component (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Pore or acoustic pressure at a node.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
CFFConcentrated fluid flow at a node.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
NTAll temperature values at a node. These will be the temperatures defined as degrees of freedom if heat transfer elements are connected to the node, or predefined temperatures if the node is connected only to stress or mass diffusion elements without temperature degrees of freedom.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
NTnTemperature degree of freedom
n at a node (
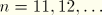
).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes All electrical potential degrees of freedom at a node.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
NNCAll normalized concentration values at a node.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
NNCnNormalized concentration degree of freedom
n at a node (
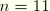
).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes All components of reaction forces, including components of reaction moments at nodes with rotational degrees of freedom (conjugate to prescribed displacements and rotations). For output to the output database, only the field-type output includes the components of reaction moments at nodes with rotational degrees of freedom.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
RTAll reaction force components.
.dat: no .fil: no .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
RMAll reaction moment components.
.dat: no .fil: no .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
RFnReaction force component
n (

) (conjugate to prescribed displacement
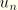
).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Reaction moment component
n (

) (conjugate to prescribed rotation
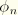
).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Reaction bimoment in degree of freedom 7, conjugate to prescribed warping amplitude. Available only for open-section beam elements.
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
CFAll components of point loads and concentrated moments.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
CFnPoint load component
n (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Point moment component
n (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Load component in degree of freedom 7. Available only for open-section beam elements.
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
TFAll components of total forces, including components of total moments at nodes with rotational degrees of freedom. Total force is the sum of the reaction force and point loads. For output to the output database, only the field-type output includes the components of total moments at nodes with rotational degrees of freedom.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
TFnTotal force component
n (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Total moment component
n (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes All components of viscous forces and moments due to static stabilization.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
VFn Stabilization viscous force component
n (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Stabilization viscous moment component
n (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Coordinates of the node. These are the current coordinates if the large-displacement formulation is being used.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
COORnCoordinate
n (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Reactive electrical nodal charge (conjugate to prescribed electrical potential).
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
CECHGConcentrated electrical nodal charge.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
RECURReactive electrical nodal current (conjugate to prescribed electrical potential).
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
CECURConcentrated electrical nodal current.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
PCAVHydrostatic fluid gauge pressure (total pressure = ambient pressure + gauge pressure).
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
CVOLHydrostatic fluid cavity volume.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
MOTAll components of motion in cavity radiation heat transfer analysis.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
MOTn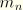
motion component (

) in cavity radiation heat transfer analysis.
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
Acoustic quantities
PORAcoustic pressure.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
INFRAcoustic infinite element “radius,” used in the coordinate map for these elements. Available only if the steady-state dynamic procedure is used, and available only for nodes attached to acoustic infinite elements.
.dat: no .fil: no .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
INFCAcoustic infinite element “cosine,” used in the coordinate map for these elements. Available only if the steady-state dynamic procedure is used, and available only for nodes attached to acoustic infinite elements.
.dat: no .fil: no .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
INFNAcoustic infinite element normal vector. Available only if the steady-state dynamic procedure is used, and available only for nodes attached to acoustic infinite elements.
.dat: no .fil: no .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
PINFAcoustic pressure coefficients for the higher-order basis functions in acoustic infinite elements. Available only if the steady-state dynamic procedure is used, and available only for acoustic infinite elements.
.dat: no .fil: no .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
Heat or mass flux
The following variables correspond to heat flux in temperature analyses or concentration volumetric flux in mass diffusion analysis:
RFLAll reaction flux values (conjugate to prescribed temperature or normalized concentration).
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
RFLnReaction flux value
n at a node (
) (conjugate to prescribed temperature or normalized concentration).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes All concentrated flux values.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
CFLnConcentrated flux values
n at a node (
).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes The total flux at the node (including flux convected through the node in convection elements), excluding external fluxes (due to concentrated fluxes, distributed fluxes, film conditions, radiation conditions, and radiation viewfactors). The value of RFLE is, thus, equal and opposite to the sum of all applied fluxes.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
RFLEnFlux value
n excluding externally applied flux loads at a node (
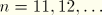
).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
Steady-state dynamic analysis
The following variables are available only for steady-state (frequency domain) dynamic analyses (modal and direct). These variables include both magnitude and phase angle for all components. Phase angles are given in degrees. In the data file there are two lines of output for each request. The first line contains the magnitude, and the second line (indicated by the SSD footnote) contains the phase angle. In the results file, the magnitudes of all components are first, followed by the phase angles of all components.
PUMagnitude and phase angle of all displacement components at the node and magnitude and phase angle of the rotations at nodes with rotational degrees of freedom.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: no
PUnMagnitude and phase angle of component
n of the displacement (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: no Magnitude and phase angle of component
n of the rotation (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: no Magnitude and phase angle of the fluid, pore, or acoustic pressure at the node.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: no
PHPOTMagnitude and phase angle of the electrical potential at the node.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: no
PRFMagnitude and phase angle of the reaction forces at the node and of the reaction moments at nodes with rotational degrees of freedom.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: no
PRFnMagnitude and phase angle of component
n of the reaction force (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: no Magnitude and phase angle of component
n of the reaction moment (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: no Magnitude and phase angle of the reactive charge at the node.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: no
Modal dynamic, steady-state, and random response analysis
The following variables are available only for modal dynamic, steady-state (frequency domain), and random response analyses. “Relative” values are measured relative to the motion of the primary base and are obtained with the identifiers
,
, and
; “Total” values include the motion of the primary base.
TUAll components of the total displacements at the node and of the total rotations at nodes with rotational degrees of freedom.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
TUnComponent
n of the total displacement (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Component
n of the total rotation (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes All components of the total velocity at the node, including rotational velocities at nodes with rotational degrees of freedom.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
TVnComponent
n of the total velocity (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Component
n of the total rate of rotation (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes All components of the total acceleration at the node, including rotational accelerations at nodes with rotational degrees of freedom.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
TAnComponent
n of the total acceleration (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Component
n of the total rotational acceleration (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
Mode-based steady-state dynamic analysis
The following variables are available only for steady-state (frequency domain) dynamic analysis based on modal superposition. “Total” values include the base motion.
PTUMagnitude and phase angle of the total displacement components at the node and magnitude and phase angle of the total rotations at nodes with rotational degrees of freedom.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: no
PTUnMagnitude and phase angle of component
n of the total displacement (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: no Magnitude and phase angle of component
n of the total rotation (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: no
Pore pressure analysis
The following variables correspond to fluid volume flux in pore pressure analyses.
RVFReaction fluid volume flux due to prescribed pressure. This flux is the rate at which fluid volume is entering or leaving the model through the node to maintain the prescribed pressure boundary condition. A positive value of RVF indicates fluid is entering the model.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
RVTReaction total fluid volume (computed only in a transient coupled pore fluid diffusion/stress analysis). This value is the time integrated value of RVF.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
Random response analysis
The following variables are available only for random response dynamic analysis. “Relative” values are measured relative to the base motion; “Total” values include the base motion.
RURoot mean square values of all components of the relative displacement at the node and of the components of rotation at nodes with rotational degrees of freedom.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
RUnRoot mean square value of component
n of the relative displacement (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Root mean square value of component
n of the relative rotation (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Root mean square values of all components of the total displacement at the node and of the components of total rotation at nodes with rotational degrees of freedom.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
RTUnRoot mean square value of component
n of the total displacement (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Root mean square value of component
n of the total rotation (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Root mean square values of all components of the relative velocity at the node and of the components of the rate of rotation at nodes with rotational degrees of freedom.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
RVnRoot mean square value of component
n of the relative velocity (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Root mean square value of component
n of the relative rate of rotation (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Root mean square values of all components of the total velocity at the node and of the components of total rotation at nodes with rotational degrees of freedom.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
RTVnRoot mean square value of component
n of the total velocity (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Root mean square value of component
n of the total rate of rotation (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Root mean square values of all components of the relative acceleration at the node and of the components of rotational acceleration at nodes with rotational degrees of freedom.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
RAnRoot mean square value of component
n of the relative acceleration (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Root mean square value of component
n of the relative rotational acceleration (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Root mean square values of all components of the total acceleration at the node and of the components of rotational acceleration at nodes with rotational degrees of freedom.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
RTAnRoot mean square value of component
n of the total value of acceleration (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Root mean square value of component
n of the total rotational acceleration (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Root mean square values of all components of the reaction forces and of reaction moments at nodes with rotational degrees of freedom.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
RRFnRoot mean square value of component
n of the reaction force (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Root mean square value of component
n of the reaction moment (

).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
Modal variables

You can request modal variable output to the data, results, or output database file (see
“Modal output from ABAQUS/Standard” in “Output to the data and results files,” Section 4.1.2, and
“Modal output from ABAQUS/Standard” in “Output to the output database,” Section 4.1.3). In steady-state dynamics
GU, etc. provide the amplitude of the mode.
GUGeneralized displacements for all modes.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
GUnGeneralized displacement for mode n.
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
GVGeneralized velocities for all modes.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
GVnGeneralized velocity for mode n.
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
GAGeneralized acceleration for all modes.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
GAnGeneralized acceleration for mode n.
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
GPUPhase angle of generalized displacements for all modes.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: no
GPUnPhase angle of generalized displacement for mode n.
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: no
GPVPhase angle of generalized velocities for all modes.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: no
GPVnPhase angle of generalized velocity for mode n.
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: no
GPAPhase angle of generalized acceleration for all modes.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: no
GPAnPhase angle of generalized acceleration for mode n.
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: no
SNEElastic strain energy for the entire model per each mode (not available for random response analysis).
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
SNEnElastic strain energy for the entire model for mode n (not available for random response analysis).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
KEKinetic energy for the entire model per each mode (not available for random response analysis).
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
KEnKinetic energy for the entire model for mode n (not available for random response analysis).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
TExternal work for the entire model per each mode (not available for random response analysis).
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
TnExternal work for the entire model for mode n (not available for random response analysis).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
BMBase motion (not available for random response or response spectrum analyses).
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
Surface variables

You can request surface variable output to the data, results, or output database file (see
“Surface output from ABAQUS/Standard” in “Output to the data and results files,” Section 4.1.2, and
“Surface output” in “Output to the output database,” Section 4.1.3). Additional information on these variables is provided in
“Defining contact pairs in ABAQUS/Standard,” Section 21.2.1, and
Chapter 22, “Contact Property Models.” The letter “M” at the end of an output variable identifier designates the magnitude of the variable.
Mechanical analysis–nodal quantities
CSTRESSContact pressure (CPRESS) and frictional shear stresses (CSHEAR).
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
CDSTRESSViscous pressure (CDPRESS) and viscous shear stresses (CDSHEAR).
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
CDISPContact opening (COPEN) and relative tangential motions (CSLIP).
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
PPRESSFluid pressure for pressure penetration analysis.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
SDVSolution-dependent state variables.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
Mechanical analysis–whole surface quantities
CFNTotal force due to contact pressure (CFNM, CFNn, n = 1, 2, 3).
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
CFSTotal force due to frictional stress (CFSM, CFSn, n = 1, 2, 3).
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
CFTTotal force due to contact pressure and frictional stress (CFTM, CFTn, n = 1, 2, 3).
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
CMNTotal moment about the origin due to contact pressure (CMNM, CMNn, n = 1, 2, 3).
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
CMSTotal moment about the origin due to frictional stress (CMSM, CMSn, n = 1, 2, 3).
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
CMTTotal moment about the origin due to contact pressure and frictional stress (CMTM, CMTn, n = 1, 2, 3).
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
CAREATotal area in contact.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
CTRQMaximum torque that can be transmitted about the z-axis by a contact surface in an axisymmetric analysis with a friction coefficient of unity.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
XNCenter of the total force due to contact pressure (XNn, n = 1, 2, 3).
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
XSCenter of the total force due to frictional stress (XSn, n = 1, 2, 3).
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
XTCenter of the total force due to contact pressure and frictional stress (XTn, n = 1, 2, 3).
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
Heat transfer analysis
HFLHeat flux per unit area leaving the slave surface.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
HFLAHFL multiplied by the area.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
HTLTime integrated HFL.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
HTLATime integrated HFLA.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
Coupled thermal-electrical analysis
ECDElectrical current per unit area.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
ECDAECD multiplied by the area.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
ECDTTime integrated ECD.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
ECDTATime integrated ECDA.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
HFLHeat flux per unit area leaving the slave surface.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
HFLAHFL multiplied by the area.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
HTLTime integrated HFL.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
HTLATime integrated HFLA.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
SJDHeat flux per unit area due to electrical current.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
SJDASJD multiplied by the area.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
SJDTTime integrated SJD.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
SJDTATime integrated SJDA.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
WEIGHTWeighting factor for heat distribution between the interface surfaces.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
Fully coupled temperature-displacement analysis
HFLHeat flux per unit area leaving the slave surface.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
HFLAHFL multiplied by the area.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
HTLTime integrated HFL.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
HTLATime integrated HFLA.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
SFDRHeat flux per unit area due to frictional dissipation.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
SFDRASFDR multiplied by the area.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
SFDRTTime integrated SFDR.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
SFDRTATime integrated SFDRA.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
WEIGHTWeighting factor for heat distribution between the interface surfaces.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
Coupled pore fluid-mechanical analysis–nodal quantities
PFLPore fluid volume flux per unit area leaving the slave surface.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
PFLAPFL multiplied by the area.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
PTLTime integrated PFL.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
PTLATime integrated PFLA.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
Coupled pore fluid-mechanical analysis–whole surface quantities
TPFLTotal pore fluid volume flux leaving the slave surface.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: no
TPTLTime integrated TPFL.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: no
Bond failure quantities
DBTTime when bond failure occurs.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
DBSAll components of remaining stress in the failed bond.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
DBSFFraction of stress that remains at bond failure.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
Cavity radiation variables

The following variables are associated with facets (sides of elements) composing cavities in radiation heat transfer and include contributions due to exchanges with the ambient. You can request cavity radiation variable output to the data, results, or output database file (see
“Requesting surface variable output” in “Cavity radiation,” Section 24.1.1, and
“Cavity radiation output in ABAQUS/Standard” in “Output to the output database,” Section 4.1.3).
RADFLRadiation flux per unit area.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
RADFLARadiation flux over the facet.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
RADTLTime integrated radiation per unit area.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
RADTLATime integrated radiation over the facet.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
VFTOTTotal viewfactor for the facet (sum of viewfactor values in the row of viewfactor matrix corresponding to the facet).
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
FTEMPFacet temperature.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: yes .odb History: yes
Section variables

You can request section variable output to the data or results file (see
“Section output from ABAQUS/Standard” in “Output to the data and results files,” Section 4.1.2). By default, all components of forces and moments are given with respect to the global system. If a local coordinate system is defined for the section output request, all components are given with respect to the local system.
Different output variables are available depending on the type of analysis. For coupled analyses the appropriate combination of variables can be requested. For example, in a coupled thermal-electrical analysis both SOH and SOE are valid output requests. Section output variables are not available for random response analysis.
All analysis types
SOAREAArea of the defined section.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: no
Stress/displacement analysis
SOFTotal force in the section.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: no
SOMTotal moment in the section.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: no
SOCFCenter of the total force in the section.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: no
Heat transfer analysis
SOHTotal heat flux across the section.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: no
Electrical analysis
SOETotal current across the section.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: no
Mass diffusion analysis
SODTotal mass flow across the section.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: no
Coupled pore fluid diffusion-stress analysis
SOPTotal pore fluid volume flux across the section.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: no
Whole and partial model variables

The output variables listed below are available for part of the model as well as the whole model.
Equivalent rigid body motion variables
You can request equivalent rigid body motion whole element set variable output to the data, results, or output database file (see
“Element output” in “Output to the data and results files,” Section 4.1.2, and
“Element output” in “Output to the output database,” Section 4.1.3). The variables listed are available only for dynamic analyses except where indicated.
XCCurrent coordinates of the center of mass for the entire set or the entire model. Available also for static analyses but only from the output database.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
XCnCoordinate
n of the center of mass for the entire set or the entire model (
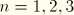
).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Current displacement of the center of mass for the entire set or the entire model. Available also for static analyses but only from the output database.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
UCnDisplacement component
n of the center of mass for the entire set or the entire model (
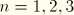
).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Rotation component
n of the center of mass for the entire set or the entire model (
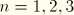
).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Equivalent rigid body velocity components summed over the entire set or the entire model.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
VCnComponent
n of the equivalent rigid body velocity summed over the entire set or the entire model (
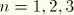
).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Component
n of the equivalent rigid body angular velocity summed over the entire set or the entire model (
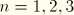
).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Current angular momentum about the center of mass for the entire set or the entire model.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
HCnComponent
n of the angular momentum about the center of mass for the entire set or the entire model (
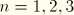
).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Current angular momentum about the origin for the entire set or the entire model.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
HOnComponent
n of the angular momentum about the origin for the entire set or the entire model (
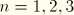
).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Current rotary inertia about the origin of the entire set or the entire model. Available also for static analyses but only from the output database.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
RIij
-component of the rotary inertia about the origin of the entire set or the entire model (
).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Current mass of the entire set or the entire model. Available also for static analyses but only from the output database.
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
VOLCurrent volume of the entire set or the entire model. Available also for static analyses but only from the output database. (Available only for continuum and structural elements that do not use general beam or shell section definitions.)
.dat: yes .fil: yes .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
Inertia relief output variables
You can request inertia relief whole model variable output to the data or output database file (see
“Element output” in “Output to the data and results files,” Section 4.1.2, and
“Element output” in “Output to the output database,” Section 4.1.3). Since these variables have unique values for the entire model, the variable output is independent of the specified region. The variables listed are available only for those analyses that include inertia relief loading (see
“Inertia relief,” Section 7.4.1).
IRXCurrent coordinates of the reference point.
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
IRXnCoordinate
n of the reference point (
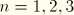
).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Equivalent rigid body acceleration components.
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
IRAnComponent
n of the equivalent rigid body acceleration (
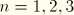
).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Component
n of the equivalent rigid body angular acceleration with respect to the reference point (
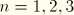
).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Inertia relief load corresponding to the equivalent rigid body acceleration.
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
IRFnComponent
n of the inertia relief load corresponding to the equivalent rigid body acceleration (
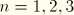
).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Component
n of the inertia relief moment corresponding to the equivalent rigid body angular acceleration with respect to the reference point (
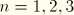
).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Rotary inertia about the reference point.
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
IRRIij
-component of the rotary inertia about the reference point (
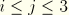
).
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes Whole model mass.
.dat: yes .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
Eigenvalue extraction
The following variables are output automatically during a frequency extraction analysis (
“Natural frequency extraction,” Section 6.3.5).
EIGVALEigenvalues.
.dat: automatic .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: automatic
EIGFREQEigenfrequencies.
.dat: automatic .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: automatic
GMGeneralized masses.
.dat: automatic .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: automatic
CDComposite damping factors.
.dat: automatic .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: automatic
PFnModal participation factors for degrees of freedom 1–6 (
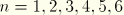
).
.dat: automatic .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: automatic Modal effective masses for degrees of freedom 1–6 (
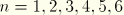
).
.dat: automatic .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: automatic
Complex eigenvalue extraction
The following variables are output automatically during a complex frequency extraction analysis (
“Complex eigenvalue extraction,” Section 6.3.6).
EIGREALReal parts of the eigenvalues.
.dat: automatic .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: automatic
EIGIMAGImaginary parts of the eigenvalues.
.dat: automatic .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: automatic
EIGFREQEigenfrequencies.
.dat: automatic .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: automatic
DAMPRATIODamping ratios.
.dat: automatic .fil: no .odb Field: no .odb History: automatic
Total energy output quantities
If the following whole model variables are relevant for a particular analysis, you can request them as output to the data, results, or output database file (see
“Total energy output” in “Output to the data and results files,” Section 4.1.2, and
“Total energy output” in “Output to the output database,” Section 4.1.3). If you do not specify an output region, whole model variables are calculated. When you specify an output region, the relevant energy totals are calculated over the user-specified region.
These variables are not available for eigenvalue buckling prediction, eigenfrequency extraction, or complex frequency extraction analysis. You cannot specify an output region for modal dynamic, random response, response spectrum, or steady-state dynamic analysis.
See
“Energy balance,” Section 1.5.5 of the ABAQUS Theory Manual, for details of the energy definitions.
ALLAE“Artificial” strain energy associated with constraints used to remove singular modes (such as hourglass control).
.dat: automatic .fil: automatic .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
ALLCDEnergy dissipated by creep, swelling, and viscoelasticity.
.dat: automatic .fil: automatic .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
ALLEEElectrostatic energy.
.dat: automatic .fil: automatic .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
ALLFDTotal energy dissipated through frictional effects. (Available only for the whole model.)
.dat: automatic .fil: automatic .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
ALLIETotal strain energy. (ALLIE = ALLSE + ALLPD + ALLCD + ALLAE + ALLQB + ALLEE + ALLDMD.)
.dat: automatic .fil: automatic .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
ALLJDElectrical energy dissipated due to flow of electrical current.
.dat: automatic .fil: automatic .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
ALLKEKinetic energy.
.dat: automatic .fil: automatic .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
ALLKLLoss of kinetic energy at impact. (Available only for the whole model.)
.dat: automatic .fil: automatic .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
ALLPDEnergy dissipated by rate-independent and rate-dependent plastic deformation.
.dat: automatic .fil: automatic .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
ALLQBEnergy dissipated through quiet boundaries (infinite elements). (Available only for the whole model.)
.dat: automatic .fil: automatic .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
ALLSDEnergy dissipated by automatic stabilization. This includes both volumetric static stabilization and automatic approach of contact pairs (the latter part included only for the whole model).
.dat: automatic .fil: automatic .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
ALLSERecoverable strain energy.
.dat: automatic .fil: automatic .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
ALLVDEnergy dissipated by viscous effects, not inclusive of energy dissipated by automatic stabilization and viscoelasticity.
.dat: automatic .fil: automatic .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
ALLDMDEnergy dissipated by damage.
.dat: automatic .fil: automatic .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
ALLWKExternal work. (Available only for the whole model.)
.dat: automatic .fil: automatic .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
ETOTALTotal energy balance (available only for the whole model). (ETOTAL = ALLKE + ALLIE + ALLVD + ALLSD + ALLKL + ALLFD + ALLJD – ALLWK.)
.dat: automatic .fil: automatic .odb Field: no .odb History: yes
Solution-dependent amplitude variables

Solution-dependent amplitude variables are given automatically with any file output or output database request.
LPFLoad proportionality factor in a static Riks analysis.
.dat: no .fil: automatic .odb Field: no .odb History: automatic
AMPCUCurrent value of the solution-dependent amplitude.
.dat: no .fil: automatic .odb Field: no .odb History: automatic
RATIOCurrent maximum ratio of creep strain rate and target creep strain rate.
.dat: no .fil: automatic .odb Field: no .odb History: automatic




![]() (ABC1, ABC2, …), where the highest value of n is determined by the type of variable. Similarly, variable identifiers of the form DEF
(ABC1, ABC2, …), where the highest value of n is determined by the type of variable. Similarly, variable identifiers of the form DEF![]() can be used for the ranges of i and
can be used for the ranges of i and ![]() indicated (DEF11, DEF12,
indicated (DEF11, DEF12, ![]() ).
).
 Material Orientations in the Visualization module. The directions can be printed to the data file by using user subroutine UVARM (see “UVARM,” Section 25.2.43).
Material Orientations in the Visualization module. The directions can be printed to the data file by using user subroutine UVARM (see “UVARM,” Section 25.2.43).![]() , 2=
, 2=![]() , and 3=
, and 3=![]() ; or for axisymmetric elements, 1=
; or for axisymmetric elements, 1=![]() and 2=
and 2=![]() ). If a local coordinate system is defined at a node (see “Transformed coordinate systems,” Section 2.1.5), you can specify whether output to the data or results file of vector-valued quantities at these nodes is in the local or global system (see “Specifying the directions for nodal output” in “Output to the data and results files,” Section 4.1.2). By default, nodal output is written to the data file in the local system, whereas it is written to the results file in the global system (since this is more convenient for postprocessing).
). If a local coordinate system is defined at a node (see “Transformed coordinate systems,” Section 2.1.5), you can specify whether output to the data or results file of vector-valued quantities at these nodes is in the local or global system (see “Specifying the directions for nodal output” in “Output to the data and results files,” Section 4.1.2). By default, nodal output is written to the data file in the local system, whereas it is written to the results file in the global system (since this is more convenient for postprocessing).




![]()
![]() is the deviatoric stress tensor, defined as
is the deviatoric stress tensor, defined as ![]() where
where ![]() is the stress,
is the stress, ![]() is the equivalent pressure stress (defined below), and
is the equivalent pressure stress (defined below), and ![]() is a unit matrix. In index notation
is a unit matrix. In index notation![]()
![]()
![]() , where
, where ![]() is the initial equivalent plastic strain.
is the initial equivalent plastic strain.![]() depends on the material model. For classical metal (Mises) plasticity
depends on the material model. For classical metal (Mises) plasticity ![]() . For other plasticity models, see the appropriate section in Part IV, “Materials.”
. For other plasticity models, see the appropriate section in Part IV, “Materials.”![]() depends on the material model. For classical metal (Mises) creep
depends on the material model. For classical metal (Mises) creep ![]() . For other creep models, see the appropriate section in Part IV, “Materials.”
. For other creep models, see the appropriate section in Part IV, “Materials.”









