Electric Longboard
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Project Overview
In this electric longboard project we want to enhance the longboard riding experience by adding automatic headlights, a way to measure the speed of the rider, and the distance rode. Riding at night can often be dangerous, these headlights will help to improve safety for the rider (along with their helmet). Typically a rider has no sense of how far or how fast they have traveled, we hope these capabilities will lend a quantitative aspect to daily usage.
Team Members
- Max Cetta
- Jacob Frank
- Alden Welsch (TA)
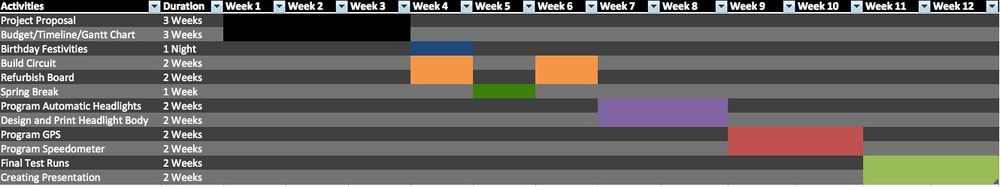
Objectives
These three aspects will be the focus of our project:
- Distance By adding a GPS chip to the board we can collect coordinate data at 1 Hz, which we can then filter and use to calculate distance travelled on a raspberry pi board.
- Speed Using a reed switch on the truck of the longboard, and a magnet attached to a wheel of the longboard we want to collect data on a second time-scale interval, which we can then convert to speed travelled based on the circumference of the wheel.
- Headlights We want to create automatic headlights that will come on when it becomes dark outside. By having a light sensor attached to our raspberry pi we can tell when it becomes dark and turn on the LED's. By interpreting the data from our reed switch circuit we also hope to be able to tell which way the board is rolling so the front of the board has headlights on, as to not blind cars or riders behind. In the process we want to add blinking safety lights in the back of the board, whichever way it may be facing.
Challenges
- Setting Up Reed Circuit Building and programming the reed circuit so it can reliably tell us how fast the board is traveling, especially at high speeds when the wheel may spin many times a second. Also figuring out how to distinguish which direction the longboard wheel is spinning.
- GPS Chip We aren not currently familiar with how to interpret GPS chip data. We will need to familiarize ourselves with GPS chip programming, and calculating distance using coordinates.
- Relay In order to maximize the brightness of the headlights we need to directly hook the LED's up to whatever battery we have. Using a solid state relay we want to maintain control of whether the lights are on or off, while maintaining maximum brightness.
- Mounting Taking all of our components and putting them in a compact container which can be secured to the longboard. We need to maintain as light a design as possible considering the board is being manually powered, while still keeping all the components safe and dry.
- Automation Ideally this circuit would be able start and stop on its own based on whether it is being ridden. Because we are using a Raspberry Pi we will be able to extract the data we want later eliminating the need for real time remote display or control. The difficulty will be figuring out how to kick start the circuit.
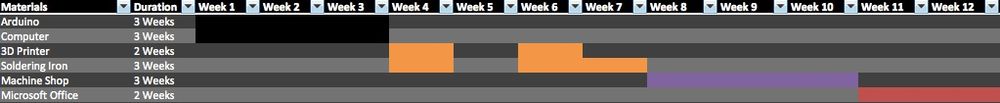
Budget
| Item | Quantity | Price | Vendor | Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12-Channel 16-bit PWM LED Driver | 2 | $7.50 | Adafruit | https://www.adafruit.com/products/1455 |
| Super Bright LED - White 10mm | 20 | $1.50 | Karlsson Robotics | |
| Super Bright LED - Red 10mm | 10 | $1.50 | Karlsson Robotics | |
| GPS Receiver - GP-20U7 (56 Channel) | 1 | $15.95 | Sparkfun | TBD |
| Reed Switch - Insulated | 10 | $1.95 | Sparkfun | |
| Magnet Square - 0.125" | 1 | $0.95 | Sparkfun | |
| Magnet Square - 0.25" | 1 | $1.50 | Sparkfun | |
| Mini Photocell | 1 | $1.50 | Sparkfun | |
| Voltage Regulator - 5V | 1 | $0.95 | Sparkfun | |
| Raspberry Pi 2 - Model B (8GB Bundle) | 1 | $49.95 | Sparkfun | |
| Resistor Kit - 1/4W (500 total) | 1 | $7.95 | Sparkfun | |
| Solder-able Breadboard - Mini | 1 | $2.95 | Sparkfun | |
| Total | $161.20 |