Smarter Door
Contents
Links
Smarter_Door_Log
Amazon Reckognition Tutorial
GitHub
Team Members
- Jonathan Strek
- Katie Cardwell
- Andrew Koltz
- Ethan Shry (TA)
- Professor Feher
Overview
We are building a door security system that sends the user a picture when an unknown person tries to open the door. The user will receive a text and be able to interact with the door by responding over text. Our security system includes a red light that illuminates when the user says the visitor is not welcome, or when the user has not authorized entry after a set period of time.
Goals
- Photograph anyone who tries to open door
- Recognize owner from an uploaded photo collection
- Text owner if unrecognized face is seen
- Respond to owner's text with security light
- Design plastic housing to make unit presentable
The goal of this project is to build a facial recognition security system for a door. The system will increase security by taking a picture of anyone who tries to open the door. If the person is not recognized by the system, a text will be sent to the user informing him/her that someone has tried to open the door. If the user does not recognize the person in the picture, they can respond via text and a security light will go on. This light should discourage people from trying to open a random door, and it also indicates to law enforcement that someone unknown has tried to enter the door.
Gantt Chart
Challenges
- Learning Python
- Gaining familiarization with Twilio
- Security of user interface
- Building a 3D casing for raspberry pi detector
- Ensuring motion detector only signals to camera to take a picture when there is truly someone in front of the door rather than when people walk by or there is motion in the background
Security Concerns
- Who can upload a picture to be recognized
- Who receives the text from the Raspberry Pi
- Who can text the Raspberry Pi
Budget
- Raspberry Pi: provided ($35)
- Raspberry Pi Camera: provided ($12)
- Infrared PIR motion Sensor: ($12) (https://www.adafruit.com/product/189?gclid=CjwKCAiAqaTjBRAdEiwAOdx9xo34FxU9DTSkwjdc8BoTUGuFJe6SMUgkO7Ussy_YMhy5Z-2xehN72xoCVYsQAvD_BwE)
- Twilio Messaging ($10)
- Amazon Web Services Recognition: ($5)
- 3D Printing software and materials: ($10)
- Small breadboard ($6)
- a LED
- a 330 ohm resistor
Total: $90
Why this project?
Security in dorms or houses is always a concern, and we hope to alleviate such worries. The increase in dependence on online retailing means more strangers than ever are using your address to find your place of residence. With Smarter Door you will not have to worry about who is at the door. Dorms can also be safer as a red light outside of a dorm will be a sign that an RA or even WUPD should be called.
Design and Solutions
General Overview and Setup:
- Download development environment (we used Visual Studio and Atom)
- Download Python, Node, CSS, and HTML extensions
- Download MySQL
- Create AWS instance
- Create AWS S3 bucket
- Connect to raspberry pi
- Create AWS database instance
- Connect to MySQL
- Purchase Twilio number that can send and receive messages
How Our Product Runs
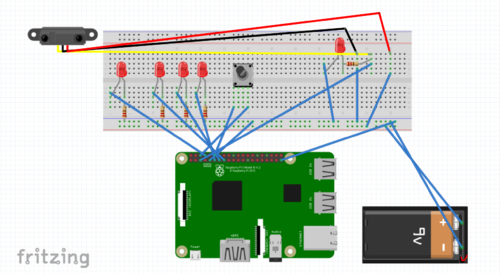
Door:
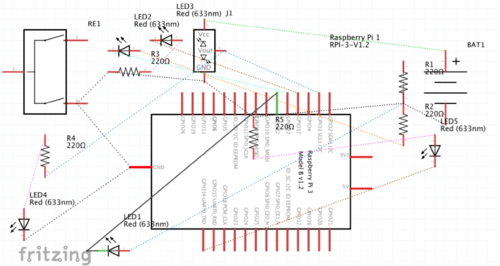
Our project uses a raspberry pi to combine the inputs and outputs of a PIR motion sensor, a Raspberry Pi Camera and various colored LEDs. If motion is detected (one of the blue LEDs light up), the camera takes a picture (while the other blue LED is on) and sends the picture to S3 to undergo facial recognition (a yellow light is shown to indicate the picture being processed). If Amazon Rekognition recognizes the user, a green light is displayed for 7 seconds before running again. If the user is not recognized, the picture is sent to the owner of the door asking for approval. If the owner texts back a positive response, a green light is displayed. If they text back a negative response, the blue, yellow and green light all go on, indicating that this person is an intruder. A button is placed into our system for demoing purposes, acting as a backup for the motion sensor. Below is the circuit schematic for our physical system and a flowchart to display the process of recognition at the door.
Server:
- AWS Lightsail Server alerts the door owner that there is someone at the door, sends picture to user, and receives reply
- These objectives are achieved by utilizing routes and Twilio. The server is continuously listening on an open port, when the Pi sends a picture to the bucket it gives the server the name of the photo. The server then uses the name along with a static ip for the public s3 bucket to send the picture using the Twilio number. The user is prompted to reply to the photo, and the text is sent back to Twilio, which uses a webhook to send the content of the reply back to the server. The server can send that information to the Pi, which changes lights based on the reply.
Database:
- Stores information and pictures of who tried to enter
Database:
S3:
S3 is a storage "bucket" run by Amazon Web Services. In this project we created a file within our S3 bucket. In this one file we saved the images of our 3 faces which we pulled from in our code to be the owners of the door. This bucket also holds all of the pictures of those who tried to enter (when motion was detected) with a filename indicative of the time of the occurrence. In the AmazonRekognition tutorial linked to this project page, one can learn how to send images to the S3 bucket and pull pictures from the S3 bucket using your Amazon Web Services credentials and python.
Web UI:
- Allows the user to access the information from the database
- Currently includes a landing page (buttons are for learning HTML, will be removed), and a link to a page which displays the visitors to the door.
- Allows the user to access the information from the database
- New picture
AWS rekognition:
AWS Rekognition is the program we used to detect and compare faces. It determines a similarity confidence number based on the location and prevalence of facial landmarks. We can compare this confidence number to a chosen threshold to choose to identify them as an owner or not. In this project we used Rekognition to detect a face in the taken picture and compare it to a list of faces that we had uploaded to our S3 bucket as the "owners". A detailed tutorial of how to create an AWS account, how to use S3 buckets and Rekognition and how to utilize the Raspberry Pi Camera in this process is uploaded and linked to this page.
API
- Communicates with the door owner using Twilio
Features & Design Choices
We used Visual Studio to code in HTML, CSS, Node, and Python to run our server, and our Raspberry Pi. The Amazon Web Service Lightsail server allowed us to communicate between the door, the facial recognition, and the end user. The Raspberry Pi controls the motion sensing and picture taking, and uploads the pictures to AWS to be used in facial recognition.
The majority of the project is comprised of the Raspberry Pi, AWS server, facial recognition, bucket, and Twilio. We chose the Pi because it is easy to use, yet complex enough to handle communications with the server. Amazon Web Service was chosen because it provided us with an affordable and easy to use suite of web services to handle communications. The Lightsail server listens to the pi, contacts the user, receives the decision, and sends the decision back to the Pi. The amazon facial Rekognition was chosen because it made it really easy to utilize our s3 bucket and aws server. It also printed out facial recognition results in a very tangible "confidence level" number which made it easy to analyze. The S3 bucket allowed us to store the new images from the Pi and send them with the server to the user. The S3 bucket was also very easy to upload pictures directly to for the purposes of uploading owners and also is a relatively cheap storage mechanism even for the large amount of pictures that we are storing in it. We chose Twilio because it was a simple way to communicate from a third party to the user. For a small amount anyone can purchase a Twilio number with the ability to send texts, and with minimal console work can write a script to send anything from that message to any number in the United States or Canada.
References
- Twilio set up PI https://www.twilio.com/docs/sms/quickstart/node#send-an-outbound-sms-message-with-nodejs
- Proposal presentation Proposal Presentation
- Twilio add on installation [1]