Difference between revisions of "Library Chair"
| Line 45: | Line 45: | ||
(Found on Amazon, but Wiki won't let me post the link to the page because of a spam filter) | (Found on Amazon, but Wiki won't let me post the link to the page because of a spam filter) | ||
| − | * Resistors/ | + | * Resistors/Capacitors/Diodes: ~$5.00 |
* Wire: $2.50 | * Wire: $2.50 | ||
Revision as of 23:10, 16 November 2017
Contents
Overview
It's a Wednesday night. You're sitting in your room watching Netflix, putting off studying for your exam next week. You're cozy in bed, and it's cold and dark outside, plus your suite-mate just said he's ordering Domino's and there might be a slice or two left over for you. Every fiber of your being is willing you to stay home, eat, and watch TV, but that nagging voice in the back of your head tells you that you're a Wash U student damnit, and you'd better take this exam seriously! So you muster up some energy and get the kid on your floor who is in the class with you to walk to the library and study for a bit. When you guys get there, though, you see that every seat in the library is taken! ARGH!!
Few things are more annoying than when you decide to actually go study but then can't because there isn't an open spot for you in the library. Enter the Library Chair. In simple terms the Library Chair system consists of an interactive chair and a web interface. The chair can detect when someone is sitting in it, and this information is then relayed (via a few arduinos and a raspberry pi) to a website which displays a map of all the chairs in the library and which ones are occupied. You can check this website from the safety and comfort of your own room; no more cold walks to the library that end up being futile!
For more specific information on how the system operates, please look at the "Objectives" section of this wiki.
Team Members
Josh Zucker
Nick Blenko
Tom Howe
Our wonderful TA, Mo
And Professor Morley, adviser
Objectives
Our project's main objective is to create an interface that library goers can use to see which seats in the library are available, and which are occupied. This interface will be dependent on data obtained from a pressure detecting circuit hooked up to an arduino and affixed to the bottom of a library chair. This circuit will then communicate occupancy and location data to another arduino connected to a raspberry pi. The raspberry pi will in turn communicate this data to a web server. We are aiming for the circuit/arduino device to be accurate, low energy, and completely powered by solar panels.
As a group we are simultaneously working on a few different smaller goals. These include: finalizing the circuit that will detect when someone is sitting in the chair, figuring out how to communicate effectively between the arduinos and how to generate the wave function necessary for the circuit to operate from an arduino, integrating a solar power source into the circuit, communicating data from the raspberry pi to a web server, and designing and implementing an aesthetically pleasing web interface.
Challenges
- Finding the best way to communicate information at a low energy level from our circuit in the chair to a processor
- Integrating a pressure detecting circuit with an arduino serving as a function generator and RF communicator
- Learning to use a Raspberry Pi to communicate information to a server
- Setting up a server
- Creating a user interface
Gantt Chart
Budget
- Chair: Cost Varies - (donated by Professor Morley)
- Raspberry Pi: $35.00
- Solar cells: $9.50
(Found on Amazon, but Wiki won't let me post the link to the page because of a spam filter)
- Resistors/Capacitors/Diodes: ~$5.00
- Wire: $2.50
- Web Server: $12/Year
- Bluehost Account $3.99/Month
- RF Link Receiver (433 MHz) $4.95
https://www.sparkfun.com/products/10532
- RF Link Transmitter (433 MHz) $3.95
https://www.sparkfun.com/products/10534
- 2x Arduino Uno - one provided by school, one bought at link below for $27.95
https://www.amazon.com/gp/product/B008GRTSV6/ref=oh_aui_detailpage_o03_s00?ie=UTF8&psc=1
Total: $104.84
Building the Circuit
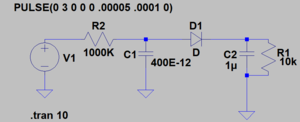
Our circuit is composed of two main parts, an RC circuit and a peak detector. The RC circuit does the actual people detecting. The circuit detects a person because it is fed a square wave with a period roughly equal to four time constants, when someone sits in the circuit they effect the capacitance of it, as the human body has a capacitance of 100-200 pF, and increases the capacitance in the RC circuit, increasing the time constant as well. When the time constant is increased the period of the square wave is not long enough for the capacitor to charge to its peak and so the peak voltage of the circuit is lower when the chair is occupied. The peak detector comes in here to make the measuring the voltage easier. The first part of the peak detector is a diode, which will only let through voltage that is higher than the voltage on the other side of the circuit, therefore if the voltage of the RC circuit is less than the peak voltage it will not be let through. The next element in the peak detector is a parallel RC circuit. In this circuit the capacitor maintains the voltage on the other side of the diode, at the peak voltage, while the resistor slowly drains it, so that when the peak voltage is lowered it is noticed on the other side of the peak detector. Voltage is measured across the parallel RC circuit.
Group Presentation
Communicating Chair to Processor
Solar Power
Server
Interface
To create the interface, we first bought the domain www.librarychair205.com. We then got a third party account at BlueHost, where we could manage our domain. In order to upload code to the domain, it involves creating an FTP account, using Filezilla to upload to that FTP account, using Atom to write code in html so it is compatible with the FTP account, and being able to grab the data from the RaspberryPi server.
Our steps:
- Generate functional HTML code in Atom
- Save the HTML code in index form to be compatible with Firezilla
- Set up the connection between the Firezilla account and the online server's account and IP address
- Upload the FTP file to Bluehost