Difference between revisions of "Render Part A Assignment"
(→Text) |
|||
| Line 101: | Line 101: | ||
==Text== | ==Text== | ||
{{RubyToImplement|text|drawings/core|Text|Object|initialize(text, font)<br/>render()}} | {{RubyToImplement|text|drawings/core|Text|Object|initialize(text, font)<br/>render()}} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
{{RubyToRun|text|drawings/core|main}} | {{RubyToRun|text|drawings/core|main}} | ||
Revision as of 03:27, 9 August 2023
Contents
Diagram
Graphics
Code to Implement
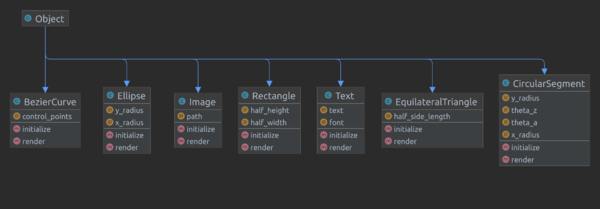
Each of the renderable components has its own file in the src/main/ruby/drawings/core directory.
Be sure to add accessors for all constructor parameters.
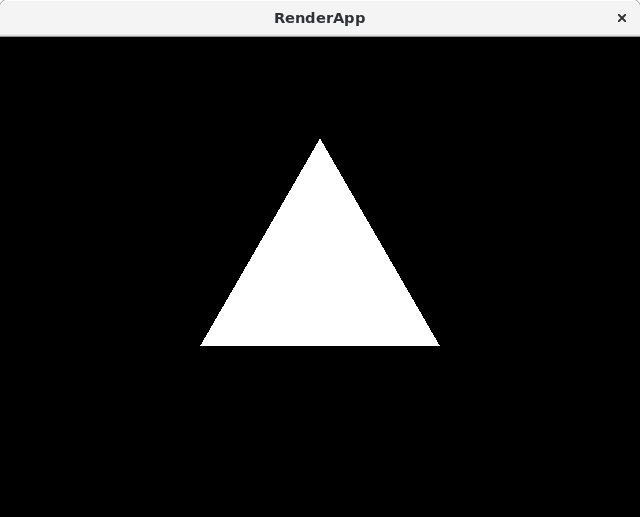
Equilateral Triangle
| file: | src/main/ruby/drawings/core/equilateral_triangle.rb | |
| class: | EquilateralTriangle | |
| superclass: | Object | |
| methods: | initialize(half_side_length) half_side_length() half_side_length=() render() |
WARNING: Ruby division of two integers results in an integer. For example: 1/3 == 0
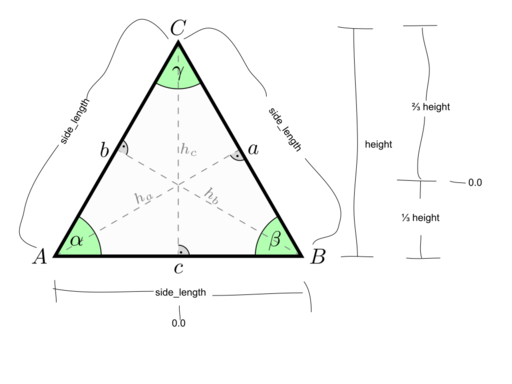
The triangle should be equilateral, rendered with its the origin at the center of mass.
Your constructor should accept a half_side_length parameter.
Add an accessor for half_side_length.
The height of the triangle should be side_length * sqrt(3)/2
The center of mass is one third from the bottom.
So, the bottom left point A's x coordinate should be -half_side_length and its y coordinate should be -1/3 height.
| file to run: | src/main/ruby/drawings/core/equilateral_triangle.rb |
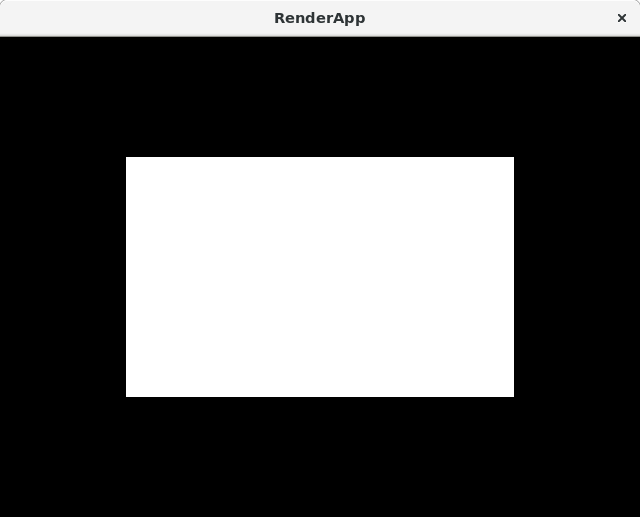
Rectangle
| file: | src/main/ruby/drawings/core/rectangle.rb | |
| class: | Rectangle | |
| superclass: | Object | |
| methods: | initialize(half_width, half_height) half_width() half_width=() half_height() half_height=() render() |
Add an accessors for half_width and half_height.
| file to run: | src/main/ruby/drawings/core/rectangle.rb |
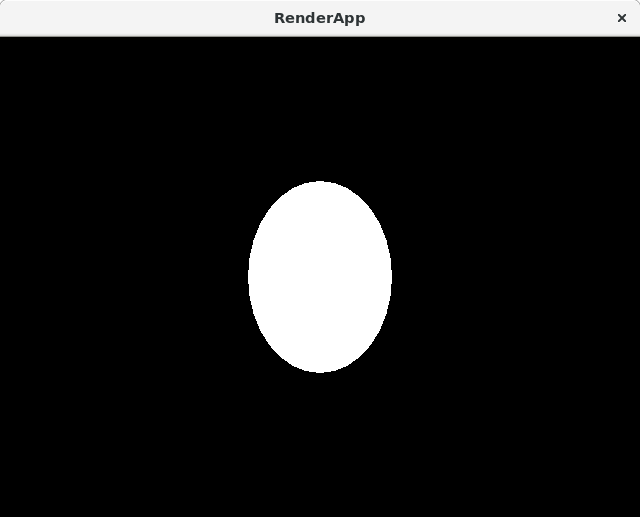
Ellipse
| file: | src/main/ruby/drawings/core/ellipse.rb | |
| class: | Ellipse | |
| superclass: | Object | |
| methods: | initialize(x_radius, y_radius) x_radius() x_radius=() y_radius() y_radius=() render() |
Add an accessors for x_radius and y_radius.
Note: to produce the reference image the code below was used:
slice_count = 32
delta_theta = (2*Math::PI) /slice_count
| file to run: | src/main/ruby/drawings/core/ellipse.rb |
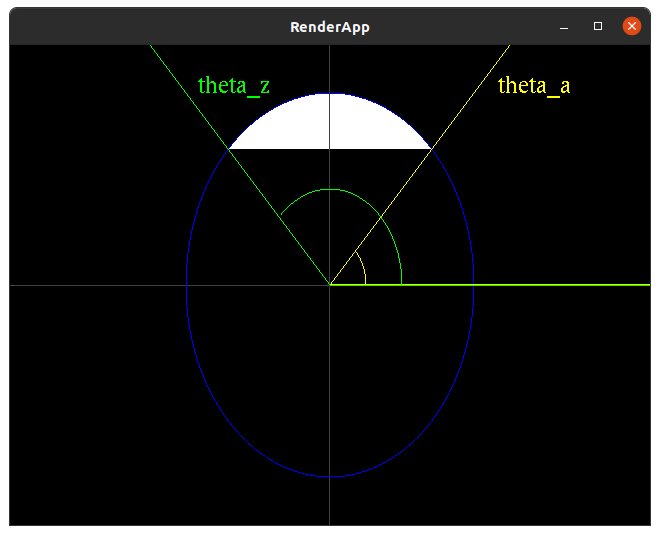
CircularSegment
| file: | src/main/ruby/drawings/core/circular_segment.rb | |
| class: | CircularSegment | |
| superclass: | Object | |
| methods: | initialize(x_radius, y_radius, theta_a, theta_z) render() |
In geometry a chord is a line segment which joins two points on a curve. We will define a class CircularSegment which renders a filled shape of an ellipse cut at the chord between theta_a and theta_z.
Note: to produce the reference image the code below was used:
slice_count = 32
delta_theta = (@theta_z-@theta_a) / slice_count
Note: a Chord with 32 slices will have 33 points.
| file to run: | src/main/ruby/drawings/core/circular_segment.rb |
Image
| file: | src/main/ruby/drawings/core/image.rb | |
| class: | Image | |
| superclass: | Object | |
| methods: | initialize(path) render() |
should draw the pixels from (0,0)
| file to run: | src/main/ruby/drawings/core/image.rb |
Text
| file: | src/main/ruby/drawings/core/text.rb | |
| class: | Text | |
| superclass: | Object | |
| methods: | initialize(text, font) render() |
| file to run: | src/main/ruby/drawings/core/text.rb |
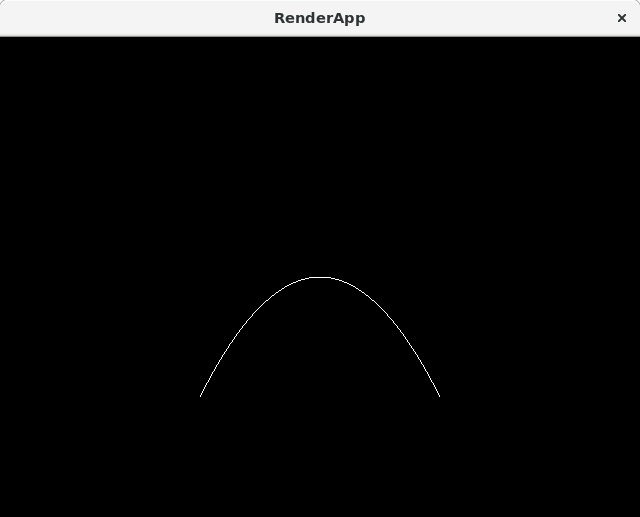
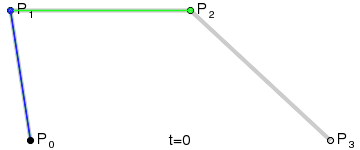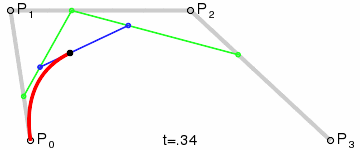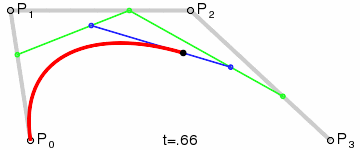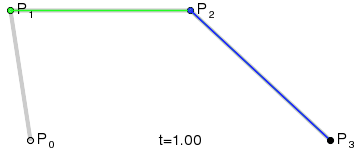
Bézier Curve
| file: | src/main/ruby/drawings/core/bezier_curve.rb | |
| class: | BezierCurve | |
| superclass: | Object | |
| methods: | initialize(control_points) render() |
NOTE: you need not implement the interpolation yourself. Use the draw_curve method on Graphics.
| Quadratic (Second Order) Curve: | 
|

|
| Quadratic (Third Order) Curve: | 
|
|
| Fourth Order Curve: | 
|
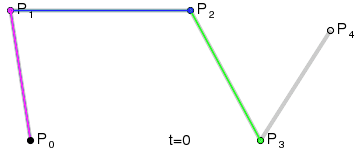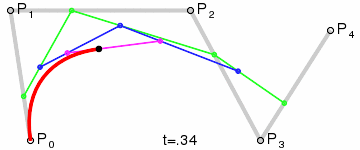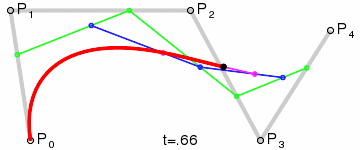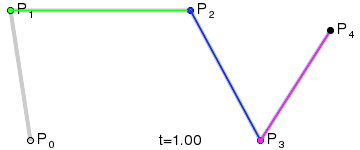
|
| file to run: | src/main/ruby/drawings/core/bezier_curve.rb |
Testing Your Solution
Unit Test
| file: | src/test/ruby/drawings/core/relatively_fast/part_a/*.rb |
note: ensure that you have removed all printing to receive credit for any assignment.
| file: | src/test/ruby/drawings/core/relatively_slow/part_a/*.rb |
note: ensure that you have removed all printing to receive credit for any assignment.
Visual Comparison
| file to run: | src/test/ruby/drawings/core/snapshots/part_a_snapshots_web_page_generator.rb |
Somewhat Outdated Testing Demo