Difference between revisions of "Binary Search Tree Assignment"
| (49 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | We will implement a binary search tree data structure as well as | + | We will implement a binary search tree data structure as well as Higher Order Function Hall of Fame inductees: find and fold. |
=Background= | =Background= | ||
| + | ==student record example== | ||
| + | <youtube>dxqoq8R3k34</youtube> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <nowiki>type course = (string*int) | ||
| + | type student = {first_name: string, last_name: string, wustl_key: string, bear_bucks: real, courses: course list} | ||
| + | |||
| + | val bst = BinarySearchTree.create_empty(String.compare, (fn(s:student) => (#wustl_key s))) | ||
| + | val (bst, _) = BinarySearchTree.insert(bst, {first_name="Bruce", last_name="Wayne", wustl_key="wayne.b", bear_bucks=999999.99, courses=[("Business", 101)]}) | ||
| + | val (bst, _) = BinarySearchTree.insert(bst, {first_name="Peter", last_name="Parker", wustl_key="webslinger", bear_bucks=12.34, courses=[("Biology", 101)]}) | ||
| + | val (bst, _) = BinarySearchTree.insert(bst, {first_name="Diana", last_name="Prince", wustl_key="amazon_diana", bear_bucks=234.56, courses=[("Anthropology", 101)]}) | ||
| + | val (bst, _) = BinarySearchTree.insert(bst, {first_name="Clark", last_name="Kent", wustl_key="i.m.superman", bear_bucks=34.56, courses=[("Journalism", 101)]}) | ||
| + | val (bst, _) = BinarySearchTree.insert(bst, {first_name="Bruce", last_name="Banner", wustl_key="gamma.ray", bear_bucks=456.78, courses=[("Physics", 101)]})</nowiki> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Bst example supers.svg]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==student record example with int as key== | ||
| + | |||
| + | <nowiki>datatype department = COMPUTER_SCIENCE | ENGLISH | ARCHITECTURE | BIOCHEMISTRY | ||
| + | type student = {id: int, name: string, major: department} | ||
| + | |||
| + | val bst = BinarySearchTree.create_empty(Int.compare, fn(s:student) => #id s) | ||
| + | val (bst,_) = BinarySearchTree.insert(bst, {id=401936, name="Tennessee Williams", major=ENGLISH}) | ||
| + | val (bst,_) = BinarySearchTree.insert(bst, {id=401927, name="Charles Eams", major=ARCHITECTURE}) | ||
| + | val (bst,_) = BinarySearchTree.insert(bst, {id=401991, name="Rochelle Walensky", major=BIOCHEMISTRY})</nowiki> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Bst example students.svg]] | ||
| + | |||
==order== | ==order== | ||
| − | SML's General structure's [ | + | SML's General structure's [https://smlfamily.github.io/Basis/general.html#SIG:GENERAL.order:TY order] |
| − | + | <syntaxhighlight lang="sml"> | |
| + | datatype order = LESS | EQUAL | GREATER | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
Values of type order are used when comparing elements of a type that has a linear ordering. | Values of type order are used when comparing elements of a type that has a linear ordering. | ||
| − | Functions which take ((' | + | Functions which take (('k * 'k) -> order) functions behave as [https://smlfamily.github.io/Basis/integer.html#SIG:INTEGER.compare:VAL Int.compare] does: |
: compare (i, j) | : compare (i, j) | ||
:: returns LESS, EQUAL, or GREATER when i is less than, equal to, or greater than j, respectively. | :: returns LESS, EQUAL, or GREATER when i is less than, equal to, or greater than j, respectively. | ||
==list== | ==list== | ||
| − | We will implement some of the higher ordered functions [ | + | We will implement some of the higher ordered functions [https://smlfamily.github.io/Basis/list.html list] provides on our binary tree. |
==traversal order== | ==traversal order== | ||
| − | + | * [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tree_traversal#In-order_(LNR) In-order LNR] | |
| − | [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tree_traversal#In-order_(LNR) In-order LNR | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | * [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tree_traversal#In-order_(RNL) Reverse in-order RNL] | |
=Code to Implement= | =Code to Implement= | ||
| − | {{SMLToImplement|binary_tree|insert<br/>remove<br/> | + | {{SMLToImplement|binary_tree|create_empty<br/>find<br/>insert<br/>remove<br/>fold_lnr<br/>fold_rnl<br/>debug_message<br/>to_graphviz_dot|binary_tree}} |
| − | + | <syntaxhighlight lang="sml"> | |
| + | signature BINARY_SEARCH_TREE = sig | ||
type 'k compare_function = (('k * 'k) -> order) | type 'k compare_function = (('k * 'k) -> order) | ||
| − | type (' | + | type ('e,'k) to_key_function = 'e -> 'k |
| − | type (' | + | type ('e,'k) tree; |
| − | val | + | val create_empty : ('k compare_function * ('e,'k) to_key_function) -> ('e,'k) tree |
| − | |||
| − | val | + | val find : (('e,'k) tree * 'k) -> 'e option |
| − | val | + | val insert : (('e,'k) tree * 'e) -> (('e,'k) tree * 'e option) |
| − | val | + | val remove : (('e,'k) tree * 'k) -> (('e,'k) tree * 'e option) |
| − | val fold_lnr : ((' | + | val fold_lnr : ((('e * 'b) -> 'b) * ('b) * (('e,'k) tree)) -> 'b |
| − | val fold_rnl : ((' | + | val fold_rnl : ((('e * 'b) -> 'b) * ('b) * (('e,'k) tree)) -> 'b |
| − | val | + | val debug_message : (('e -> string) * (('e,'k) tree)) -> string |
| − | end</ | + | val to_graphviz_dot : (('e -> string) * ('k -> string) * (('e,'k) tree)) -> string |
| + | end | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==type== | ||
| + | ===provided compare_function and to_key_function type synonyms=== | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="sml"> | ||
| + | type 'k compare_function = (('k * 'k) -> order) | ||
| + | type ('e,'k) to_key_function = 'e -> 'k | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===required (at minimum) tree=== | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="sml"> | ||
| + | |||
| + | (* TODO: replace unit with the datatype(s) and/or type synonym(s) you decide upon *) | ||
| + | type ('a,'k) tree = unit | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==create_empty== | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="sml"> | ||
| + | fun create_empty(cmp : 'k compare_function, to_key : ('e,'k) to_key_function) : ('e,'k) tree = | ||
| + | raise Fail("NotYetImplemented") | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==find== | ||
| + | reference: [https://smlfamily.github.io/Basis/list.html#SIG:LIST.find:VAL List.find] | ||
| + | |||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="sml"> | ||
| + | fun find(t : ('e,'k) tree, key : 'k) : 'e option = | ||
| + | raise Fail("NotYetImplemented") | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
==insert== | ==insert== | ||
| − | + | <syntaxhighlight lang="sml"> | |
| − | + | fun insert(t : ('e,'k) tree, element : 'e) : (('e,'k) tree * 'e option) = | |
| + | raise Fail("NotYetImplemented") | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | |||
| + | NOTE: if the key for the specified item matches a key already in the tree, the previous item is replaced. | ||
| + | |||
| + | NOTE: it is critical to build the tree "on the way out" of the recursion. This is much like one must build the list "on the way out" in the [[Remove_First_Assignment| Remove First]] and [[Eliminate_Unsorted_Assignment|Eliminate Unsorted]] assignments. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <code>insert</code> returns a pair containing the new tree and the (optional) replaced value. | ||
==remove== | ==remove== | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="sml"> | ||
| + | fun remove(t : ('e,'k) tree, key : 'k) : (('e,'k) tree * 'e option) = | ||
| + | raise Fail("NotYetImplemented")</syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <code>remove</code> the item whose key matches <code>item_key</code>, if it is found. | ||
| + | |||
| + | returns a pair of the modified tree and the (optional) removed item. | ||
| + | |||
Remove contains the most challenging aspect of this studio. When instructed to remove a node from a tree, there are several cases: | Remove contains the most challenging aspect of this studio. When instructed to remove a node from a tree, there are several cases: | ||
| Line 57: | Line 129: | ||
===no child in the right tree=== | ===no child in the right tree=== | ||
how will you detect this pattern?<br>note: this has a trivial solution. | how will you detect this pattern?<br>note: this has a trivial solution. | ||
| − | === | + | ===both children are present=== |
If you need to remove a node and it has both children, now you have a legit problem. You must maintain a correct binary search tree. | If you need to remove a node and it has both children, now you have a legit problem. You must maintain a correct binary search tree. | ||
| + | ====standard approach==== | ||
A common approach is to choose one of the following: | A common approach is to choose one of the following: | ||
* remove the right most descendant in the left child, and promote it to be the node at the current level, or | * remove the right most descendant in the left child, and promote it to be the node at the current level, or | ||
| − | * remove the left most descendant in right | + | * remove the left most descendant in the right child, and promote it to be the node at the current level |
The image below shows finding the left most child in the right subtree for promotion: | The image below shows finding the left most child in the right subtree for promotion: | ||
| Line 72: | Line 145: | ||
[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Binary_search_tree#Deletion Wikipedia BST Deletion] | [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Binary_search_tree#Deletion Wikipedia BST Deletion] | ||
| − | + | ====alternate approach?==== | |
| − | + | Can you come up with a different approach that produces a clean solution while still providing O(lg(N)) expected performance? | |
| − | == | + | ==fold== |
| − | reference: [ | + | reference: [https://smlfamily.github.io/Basis/list.html#SIG:LIST.foldl:VAL List.foldl] [https://smlfamily.github.io/Basis/list.html#SIG:LIST.foldr:VAL foldr] |
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Sorted binary tree inorder.svg|Sorted binary tree inorder|frame|LNR would produce: ABCDEFGHI<br>RNL would produce: IHGFEDCBA]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===fold_lnr=== | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="sml"> | ||
| + | (* | ||
| + | * depth-first, in-order traversal | ||
| + | * https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tree_traversal#In-order_(LNR) | ||
| + | *) | ||
| + | fun fold_lnr(f, init, t) = | ||
| + | raise Fail("NotYetImplemented") | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | ===fold_rnl=== | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="sml"> | ||
| + | (* | ||
| + | * depth-first, reverse in-order traversal | ||
| + | * https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tree_traversal#Reverse_in-order_(RNL) | ||
| + | *) | ||
| + | fun fold_rnl(f, init, t) = | ||
| + | raise Fail("NotYetImplemented") | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | |||
| + | =Debugging= | ||
| + | Visualizing the state of the tree often helps with debugging. We have provided a skeleton which can be adapted to your particular type declaration(s). | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==BinarySearchTree== | ||
| + | ===to_graphviz_dot=== | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang=java> | ||
| + | fun to_graphviz_dot(element_to_string, key_to_string, t) = | ||
| + | let | ||
| + | |||
| + | (* TODO: bind root *) | ||
| + | val root = raise Fail("NotYetImplemented") | ||
| + | (* TODO: bind to_key *) | ||
| + | val to_key = raise Fail("NotYetImplemented") | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | fun nodes_to_dot(bst) = | ||
| + | let | ||
| + | fun empty_to_string() = | ||
| + | "" | ||
| + | fun present_to_string(left, element, right) = | ||
| + | let | ||
| + | fun node_to_dot(element) = | ||
| + | "\t" ^ key_to_string(to_key(element)) ^ " [label= \"{ " ^ element_to_string(element) ^ " | { <child_left> | <child_right> } }\"]" | ||
| + | in | ||
| + | node_to_dot(element) ^ "\n" ^ nodes_to_dot(left) ^ nodes_to_dot(right) | ||
| + | end | ||
| + | in | ||
| + | raise Fail("NotYetImplemented") | ||
| + | end | ||
| − | + | fun edges_to_dot(bst, parent_element_opt, tag) = | |
| − | + | let | |
| + | fun empty_to_string() = | ||
| + | "" | ||
| + | fun present_to_string(left, element, right) = | ||
| + | let | ||
| + | fun edge_to_dot(parent_element_opt, tag, element) = | ||
| + | case parent_element_opt of | ||
| + | NONE => "" | ||
| + | | SOME(parent_element) => "\t" ^ key_to_string(to_key(parent_element)) ^ tag ^ " -> " ^ key_to_string(to_key(element)) | ||
| + | in | ||
| + | edge_to_dot(parent_element_opt, tag, element) ^ "\n" ^ edges_to_dot(left, SOME(element), ":child_left:center") ^ edges_to_dot(right, SOME(element), ":child_right:center") | ||
| + | end | ||
| + | in | ||
| + | raise Fail("NotYetImplemented") | ||
| + | end | ||
| + | in | ||
| + | "digraph g {\n\n\tnode [\n\t\tshape = record\n\t]\n\n\tedge [\n\t\ttailclip=false,\n\t\tarrowhead=vee,\n\t\tarrowtail=dot,\n\t\tdir=both\n\t]\n\n" ^ nodes_to_dot(root) ^ edges_to_dot(root, NONE, "") ^ "\n}\n" | ||
| + | end | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | == | + | ==debug_binary_search_tree== |
| − | + | file: <code>debug_binary_search_tree.sml</code> | |
| − | + | in folder: <code>src/test/sml/run_binary_search_tree_testing</code> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ==graphviz dot extenstion in visual studio code== | |
| − | + | search for "graphviz dot" in vs code extensions marketplace | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
=Testing= | =Testing= | ||
| − | {{ | + | ==Complete== |
| + | {{SMLUnitTesting|run_bst_testing|binary_search_tree}} | ||
| + | ==Without Remove== | ||
| + | sml -Ccm.verbose=false run_bst_testing.sml --remove=false | ||
| + | |||
| + | sml run_bst_testing.sml --remove=false | ||
=Pledge, Acknowledgments, Citations= | =Pledge, Acknowledgments, Citations= | ||
{{Pledge|studio-binary-search-tree}} | {{Pledge|studio-binary-search-tree}} | ||
Latest revision as of 17:18, 26 October 2023
We will implement a binary search tree data structure as well as Higher Order Function Hall of Fame inductees: find and fold.
Contents
Background
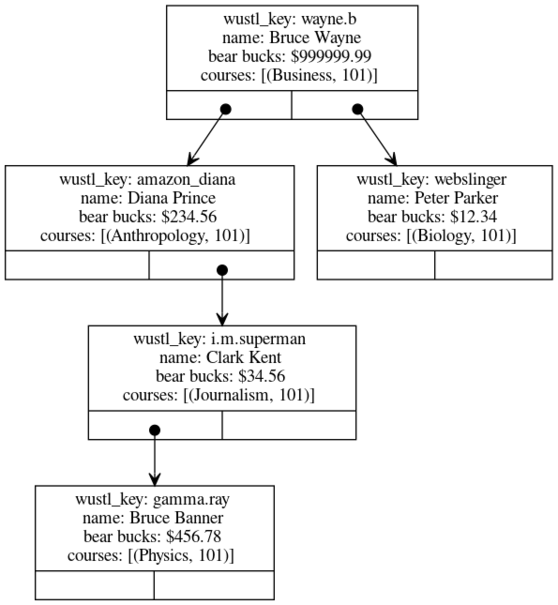
student record example
type course = (string*int)
type student = {first_name: string, last_name: string, wustl_key: string, bear_bucks: real, courses: course list}
val bst = BinarySearchTree.create_empty(String.compare, (fn(s:student) => (#wustl_key s)))
val (bst, _) = BinarySearchTree.insert(bst, {first_name="Bruce", last_name="Wayne", wustl_key="wayne.b", bear_bucks=999999.99, courses=[("Business", 101)]})
val (bst, _) = BinarySearchTree.insert(bst, {first_name="Peter", last_name="Parker", wustl_key="webslinger", bear_bucks=12.34, courses=[("Biology", 101)]})
val (bst, _) = BinarySearchTree.insert(bst, {first_name="Diana", last_name="Prince", wustl_key="amazon_diana", bear_bucks=234.56, courses=[("Anthropology", 101)]})
val (bst, _) = BinarySearchTree.insert(bst, {first_name="Clark", last_name="Kent", wustl_key="i.m.superman", bear_bucks=34.56, courses=[("Journalism", 101)]})
val (bst, _) = BinarySearchTree.insert(bst, {first_name="Bruce", last_name="Banner", wustl_key="gamma.ray", bear_bucks=456.78, courses=[("Physics", 101)]})
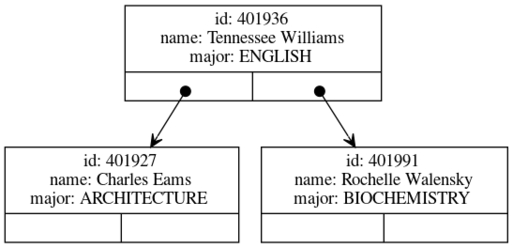
student record example with int as key
datatype department = COMPUTER_SCIENCE | ENGLISH | ARCHITECTURE | BIOCHEMISTRY
type student = {id: int, name: string, major: department}
val bst = BinarySearchTree.create_empty(Int.compare, fn(s:student) => #id s)
val (bst,_) = BinarySearchTree.insert(bst, {id=401936, name="Tennessee Williams", major=ENGLISH})
val (bst,_) = BinarySearchTree.insert(bst, {id=401927, name="Charles Eams", major=ARCHITECTURE})
val (bst,_) = BinarySearchTree.insert(bst, {id=401991, name="Rochelle Walensky", major=BIOCHEMISTRY})
order
SML's General structure's order
datatype order = LESS | EQUAL | GREATER
Values of type order are used when comparing elements of a type that has a linear ordering.
Functions which take (('k * 'k) -> order) functions behave as Int.compare does:
- compare (i, j)
- returns LESS, EQUAL, or GREATER when i is less than, equal to, or greater than j, respectively.
list
We will implement some of the higher ordered functions list provides on our binary tree.
traversal order
Code to Implement
| file: | src/main/sml/binary_tree/binary_tree.sml | |
| functions: | create_empty find insert remove fold_lnr fold_rnl debug_message to_graphviz_dot |
signature BINARY_SEARCH_TREE = sig
type 'k compare_function = (('k * 'k) -> order)
type ('e,'k) to_key_function = 'e -> 'k
type ('e,'k) tree;
val create_empty : ('k compare_function * ('e,'k) to_key_function) -> ('e,'k) tree
val find : (('e,'k) tree * 'k) -> 'e option
val insert : (('e,'k) tree * 'e) -> (('e,'k) tree * 'e option)
val remove : (('e,'k) tree * 'k) -> (('e,'k) tree * 'e option)
val fold_lnr : ((('e * 'b) -> 'b) * ('b) * (('e,'k) tree)) -> 'b
val fold_rnl : ((('e * 'b) -> 'b) * ('b) * (('e,'k) tree)) -> 'b
val debug_message : (('e -> string) * (('e,'k) tree)) -> string
val to_graphviz_dot : (('e -> string) * ('k -> string) * (('e,'k) tree)) -> string
end
type
provided compare_function and to_key_function type synonyms
type 'k compare_function = (('k * 'k) -> order)
type ('e,'k) to_key_function = 'e -> 'k
required (at minimum) tree
(* TODO: replace unit with the datatype(s) and/or type synonym(s) you decide upon *)
type ('a,'k) tree = unit
create_empty
fun create_empty(cmp : 'k compare_function, to_key : ('e,'k) to_key_function) : ('e,'k) tree =
raise Fail("NotYetImplemented")
find
reference: List.find
fun find(t : ('e,'k) tree, key : 'k) : 'e option =
raise Fail("NotYetImplemented")
insert
fun insert(t : ('e,'k) tree, element : 'e) : (('e,'k) tree * 'e option) =
raise Fail("NotYetImplemented")
NOTE: if the key for the specified item matches a key already in the tree, the previous item is replaced.
NOTE: it is critical to build the tree "on the way out" of the recursion. This is much like one must build the list "on the way out" in the Remove First and Eliminate Unsorted assignments.
insert returns a pair containing the new tree and the (optional) replaced value.
remove
fun remove(t : ('e,'k) tree, key : 'k) : (('e,'k) tree * 'e option) =
raise Fail("NotYetImplemented")
remove the item whose key matches item_key, if it is found.
returns a pair of the modified tree and the (optional) removed item.
Remove contains the most challenging aspect of this studio. When instructed to remove a node from a tree, there are several cases:
not found
What will indicate that you reached the point where you know the node is not found in the tree?
note: this has a trivial solution.
no child in the left tree
How will you detect this pattern?
note: this has a trivial solution.
no child in the right tree
how will you detect this pattern?
note: this has a trivial solution.
both children are present
If you need to remove a node and it has both children, now you have a legit problem. You must maintain a correct binary search tree.
standard approach
A common approach is to choose one of the following:
- remove the right most descendant in the left child, and promote it to be the node at the current level, or
- remove the left most descendant in the right child, and promote it to be the node at the current level
The image below shows finding the left most child in the right subtree for promotion:
Building a helper function will likely be helpful.
alternate approach?
Can you come up with a different approach that produces a clean solution while still providing O(lg(N)) expected performance?
fold
reference: List.foldl foldr
fold_lnr
(*
* depth-first, in-order traversal
* https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tree_traversal#In-order_(LNR)
*)
fun fold_lnr(f, init, t) =
raise Fail("NotYetImplemented")
fold_rnl
(*
* depth-first, reverse in-order traversal
* https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tree_traversal#Reverse_in-order_(RNL)
*)
fun fold_rnl(f, init, t) =
raise Fail("NotYetImplemented")
Debugging
Visualizing the state of the tree often helps with debugging. We have provided a skeleton which can be adapted to your particular type declaration(s).
BinarySearchTree
to_graphviz_dot
fun to_graphviz_dot(element_to_string, key_to_string, t) =
let
(* TODO: bind root *)
val root = raise Fail("NotYetImplemented")
(* TODO: bind to_key *)
val to_key = raise Fail("NotYetImplemented")
fun nodes_to_dot(bst) =
let
fun empty_to_string() =
""
fun present_to_string(left, element, right) =
let
fun node_to_dot(element) =
"\t" ^ key_to_string(to_key(element)) ^ " [label= \"{ " ^ element_to_string(element) ^ " | { <child_left> | <child_right> } }\"]"
in
node_to_dot(element) ^ "\n" ^ nodes_to_dot(left) ^ nodes_to_dot(right)
end
in
raise Fail("NotYetImplemented")
end
fun edges_to_dot(bst, parent_element_opt, tag) =
let
fun empty_to_string() =
""
fun present_to_string(left, element, right) =
let
fun edge_to_dot(parent_element_opt, tag, element) =
case parent_element_opt of
NONE => ""
| SOME(parent_element) => "\t" ^ key_to_string(to_key(parent_element)) ^ tag ^ " -> " ^ key_to_string(to_key(element))
in
edge_to_dot(parent_element_opt, tag, element) ^ "\n" ^ edges_to_dot(left, SOME(element), ":child_left:center") ^ edges_to_dot(right, SOME(element), ":child_right:center")
end
in
raise Fail("NotYetImplemented")
end
in
"digraph g {\n\n\tnode [\n\t\tshape = record\n\t]\n\n\tedge [\n\t\ttailclip=false,\n\t\tarrowhead=vee,\n\t\tarrowtail=dot,\n\t\tdir=both\n\t]\n\n" ^ nodes_to_dot(root) ^ edges_to_dot(root, NONE, "") ^ "\n}\n"
end
debug_binary_search_tree
file: debug_binary_search_tree.sml
in folder: src/test/sml/run_binary_search_tree_testing
graphviz dot extenstion in visual studio code
search for "graphviz dot" in vs code extensions marketplace
Testing
Complete
| source folder: | src/test/sml/binary_search_tree |
| how to run with CM.make verbosity off: | sml -Ccm.verbose=false run_bst_testing.sml |
| how to run with CM.make verbosity on: | sml run_bst_testing.sml |
note: ensure that you have removed all printing to receive credit for any assignment.
Without Remove
sml -Ccm.verbose=false run_bst_testing.sml --remove=false
sml run_bst_testing.sml --remove=false
Pledge, Acknowledgments, Citations
| file: | studio-binary-search-tree-pledge-acknowledgments-citations.txt |
More info about the Honor Pledge