Difference between revisions of "Render Part C Assignment"
| (73 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
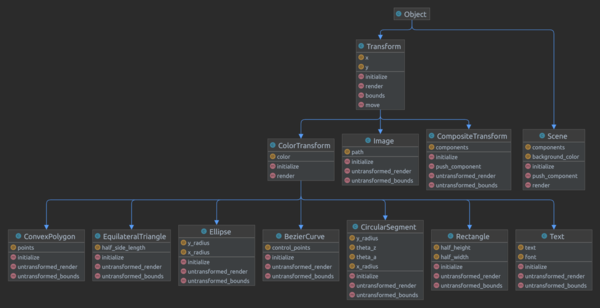
In this studio we will evolve our code from [[Render_Part_B_Assignment]] to add new methods and a new class. | In this studio we will evolve our code from [[Render_Part_B_Assignment]] to add new methods and a new class. | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:Diagram_part_c.png|600px]] |
| − | Continue editing files in the render/ | + | Continue editing files in the drawings directory. |
| + | |||
| + | =Background= | ||
| + | ==Bounds Calculation== | ||
| + | We will add support for calculating a bounding box for each of our drawable objects. | ||
| + | |||
| + | We will implement a BoundingBox class (via [https://ruby-doc.org/core-2.5.0/Struct.html Struct], if desired) to store the min and max points of a box which bounds the object. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Transformable objects will split the responsibility into two methods, untransformed_bounds and bounds. On the subclasses the untransformed_bounds method will return its object's bounds in the same untransformed space that untransformed_render acts: that is, about its origin. On the Transform superclass, the bounds method will transform the untransformed_bounds by the x and y location (akin to how render transforms the affine matrix via glTranslate to transform the space untransformed_render operates in). The bounds method will not be able to rely on glTranslate. It will need to create a new transformed BoundingBox. | ||
| + | |||
| + | For example, an Ellipse created with an x_radius of 0.3, a y_radius of 0.4, an x location of 0.1, and a y location of 0.2 would produce an untransformed_bounds with a min of (-0.3, -0.4) and a max of (0.3, 0.4). The bounds calculation inherited from Transform would transform the untransformed bounds with the x and y locations, producing a bounding box with a min of (-0.2, -0.2) and a max of (0.4, 0.6). | ||
| + | |||
| + | =Code To Use= | ||
| + | ==[https://www.cse.wustl.edu/~dennis.cosgrove/courses/cse425s/current/doc/Graphics.html Graphics]== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Point2== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==[https://www.cse.wustl.edu/~dennis.cosgrove/courses/cse425s/current/doc/BoundingBox.html BoundingBox]== | ||
| + | : [https://www.cse.wustl.edu/~dennis.cosgrove/courses/cse425s/current/doc/BoundingBox.html#max-instance_method max] | ||
| + | : [https://www.cse.wustl.edu/~dennis.cosgrove/courses/cse425s/current/doc/BoundingBox.html#min-instance_method min] | ||
=Code to Implement= | =Code to Implement= | ||
| + | <!-- | ||
| + | ==BoundingBox== | ||
| + | {{RubyToImplement|bounding_box|drawings|BoundingBox|Object|initialize(min,max)<br/>min()<br/>min=(min)<br/>max()<br/>max=(max)}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | Note: be sure to require_relative 'point2'. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Note: min and max should be instances of <code>Point2</code>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Note: You may wish to use Ruby's convenient [https://ruby-doc.org/core-2.4.2/Struct.html Struct] construct. | ||
| + | |||
| + | --> | ||
| + | |||
==Transform== | ==Transform== | ||
| + | {{RubyToEvolve|transform|drawings|Transform|Object|Ø|move(direction,amount)<br/>bounds()|Ø}} | ||
===move=== | ===move=== | ||
| − | + | the move method will accept two parameters: direction and amount and change the x,y position as appropriate. | |
| + | |||
| + | direction can be one of four [https://ruby-doc.org/core-2.5.0/Symbol.html symbols] | ||
| + | <nowiki>:left | ||
| + | :right | ||
| + | :up | ||
| + | :down</nowiki> | ||
| + | |||
| + | :left corresponds to translating along the negative x axis | ||
| + | |||
| + | :right corresponds to translating along the positive x axis | ||
| + | |||
| + | :down corresponds to translating along the negative y axis | ||
| + | |||
| + | :up corresponds to translating along the positive y axis | ||
| + | |||
| + | any other value for direction should raise an [https://ruby-doc.org/core-2.5.0/ArgumentError.html ArgumentError]. | ||
| − | == | + | Note: do NOT call glTranslate here. simply update your instance fields so that later when you are rendering, you will glTranslate the updated amounts. |
| − | + | ||
| + | ===bounds=== | ||
| + | invoke <code>untransformed_bounds</code> and transform the returned bounds by x and y. | ||
| + | |||
| + | NOTE: <code>untransformed_bounds</code> is abstract. it must be defined by the subclasses. | ||
==Rectangle== | ==Rectangle== | ||
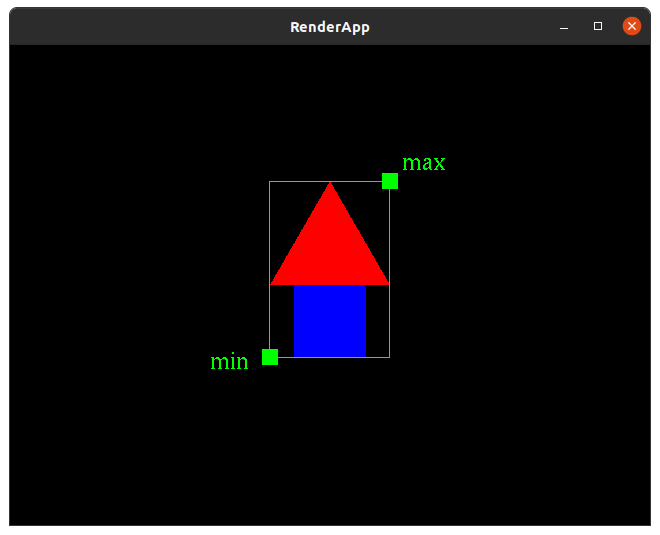
| − | === | + | {{RubyToEvolve|rectangle|drawings|Rectangle|ColorTransform|Ø|untransformed_bounds|Ø}} |
| + | ===untransformed_bounds=== | ||
| + | Returns an instance of BoundingBox specified by min and max instances of <code>Point2</code>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | NOTE: this method must be private. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{BoundingBoxRendering|Rectangle_bounds}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Ellipse== | ||
| + | {{RubyToEvolve|ellipse|drawings|Ellipse|ColorTransform|Ø|untransformed_bounds|Ø}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===untransformed_bounds=== | ||
| + | Returns an instance of BoundingBox specified by min and max instances of <code>Point2</code>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | NOTE: this method must be private. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{BoundingBoxRendering|Ellipse bounds}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==EquilateralTriangle== | ||
| + | {{RubyToEvolve|equilateral_triangle|drawings|EquilateralTriangle|ColorTransform|Ø|untransformed_bounds|Ø}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===untransformed_bounds=== | ||
| + | Returns an instance of BoundingBox specified by min and max instances of <code>Point2</code>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | NOTE: this method must be private. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{BoundingBoxRendering|Equilateral triangle bounds}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==BezierCurve== | ||
| + | {{RubyToEvolve|bezier_curve|drawings|BezierCurve|ColorTransform|Ø|untransformed_bounds|Ø}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===untransformed_bounds=== | ||
| + | Contemplate for a moment how you would build this method and then raise an error and move on. | ||
| + | |||
| + | NOTE: this method must be private. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <nowiki> def untransformed_bounds | ||
| + | raise StandardError.new("not yet implemented") | ||
| + | end</nowiki> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Text== | ||
| + | {{RubyToEvolve|text|drawings|Text|ColorTransform|Ø|untransformed_bounds|Ø}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===untransformed_bounds=== | ||
| + | Contemplate for a moment how you would build this method and then raise an error and move on. | ||
| + | |||
| + | NOTE: this method must be private. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <nowiki> def untransformed_bounds | ||
| + | raise StandardError.new("not yet implemented") | ||
| + | end</nowiki> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==CircularSegment== | ||
| + | {{RubyToEvolve|circular_segment|drawings|CircularSegment|ColorTransform|Ø|untransformed_bounds|Ø}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===untransformed_bounds=== | ||
| + | Contemplate for a moment how you would build this method and then raise an error and move on. | ||
| + | |||
| + | NOTE: this method must be private. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <nowiki> def untransformed_bounds | ||
| + | raise StandardError.new("not yet implemented") | ||
| + | end</nowiki> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Image== | ||
| + | {{RubyToEvolve|image|drawings|Image|Transform|Ø|untransformed_bounds|Ø}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===untransformed_bounds=== | ||
| + | Contemplate for a moment how you would build this method and then raise an error and move on. | ||
| + | |||
| + | NOTE: this method must be private. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <nowiki> def untransformed_bounds | ||
| + | raise StandardError.new("not yet implemented") | ||
| + | end</nowiki> | ||
| + | |||
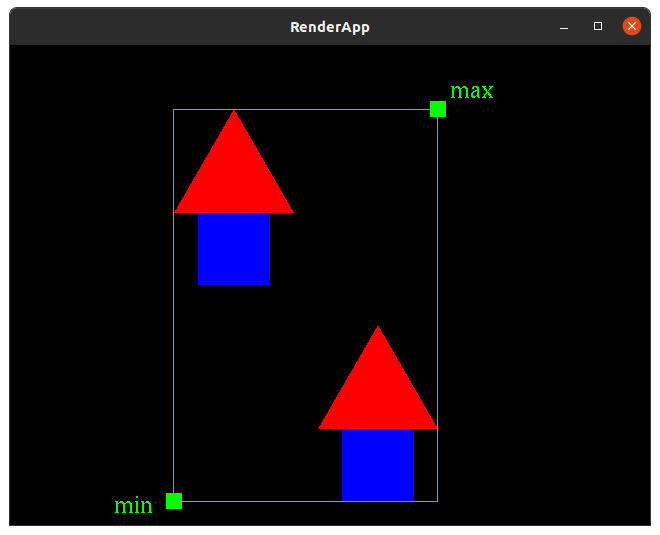
==CompositeTransform== | ==CompositeTransform== | ||
| − | === | + | {{RubyToEvolve|composite_transform|drawings|CompositeTransform|Transform|Ø|untransformed_bounds|Ø}} |
| + | |||
| + | ===untransformed_bounds=== | ||
| + | Returns an instance of Bounds specified by min and max instances of <code>Point2</code>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | NOTE: this method must be private. | ||
| + | |||
| + | NOTE: when computing the bounds of multiple objects, recall that the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Identity_element#Examples identity element of minimum and the maximum] is not 0. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{BoundingBoxRendering|Composite transform bounds}} | ||
| + | |||
==Scene== | ==Scene== | ||
| − | === | + | {{RubyToEvolve|scene|drawings|Scene|Object|bounds()|Ø|Ø}} |
| + | ===bounds=== | ||
| + | NOTE: this method must be public. | ||
| + | |||
| + | NOTE: when computing the bounds of multiple objects, recall that the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Identity_element#Examples identity element of minimum and the maximum] is not 0. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{BoundingBoxRendering|Scene bounds}} | ||
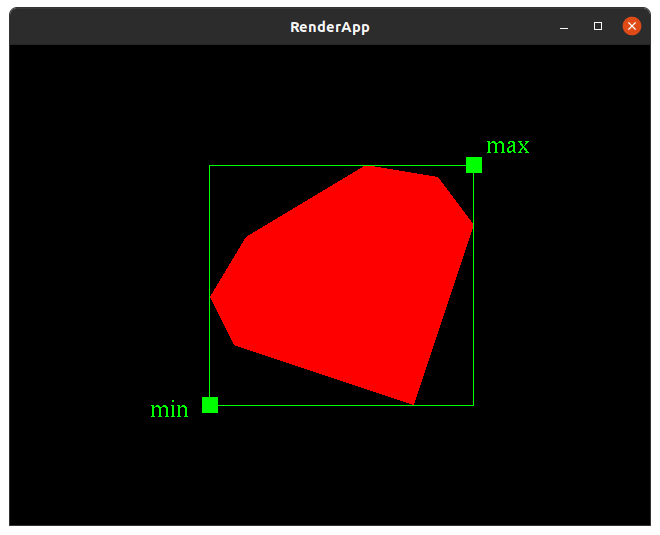
==ConvexPolygon== | ==ConvexPolygon== | ||
| − | ===render_transformed=== | + | {{RubyToImplement|convex_polygon|drawings|ConvexPolygon|ColorTransform|initialize(points, x: 0, y: 0, color: nil)<br/>untransformed_render()<br/>untransformed_bounds()}} |
| − | === | + | |
| + | ===initialize=== | ||
| + | Accept a required parameter points which is an array of Point2s. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Accept keyword parameters for x: 0, y: 0, and color: nil to the constructor and pass them to the superclass. | ||
| + | |||
| + | NOTE: Be sure to not override render. Implement the render_transformed method instead. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===untransformed_render=== | ||
| + | NOTE: this method must be private. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===untransformed_bounds=== | ||
| + | NOTE: this method must be private. | ||
| + | |||
| + | NOTE: when computing the bounds of multiple objects, recall that the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Identity_element#Examples identity element of minimum and the maximum] is not 0. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{BoundingBoxRendering|Convex polygon bounds}} | ||
| + | |||
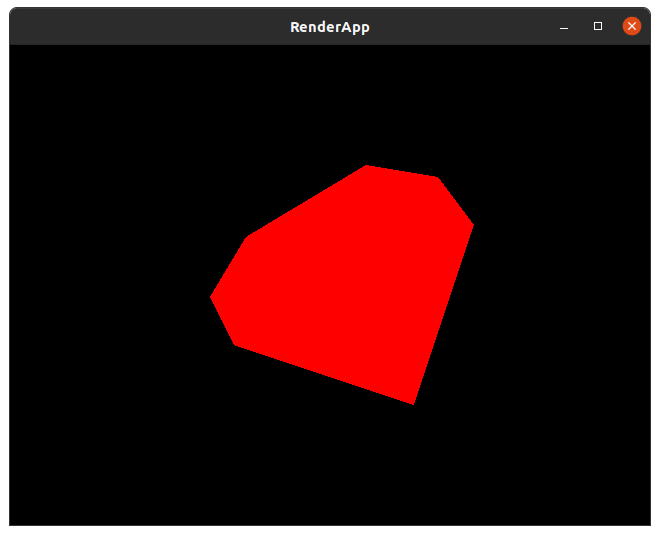
| + | {{RubyToRun|convex_polygon|drawings|main}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Render convex polygon.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | =Testing Your Solution= | ||
| + | ==Unit Test== | ||
| + | {{RubyUnitTest|*|drawings/core/relatively_fast/part_c}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{RubyUnitTest|*|drawings/core/relatively_slow/part_c}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Backwards Compatibility=== | ||
| + | {{RubyUnitTest|*|drawings/core/relatively_fast/part_a}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{RubyUnitTest|*|drawings/core/relatively_fast/part_b}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Visual Comparison== | ||
| + | {{RubyToRun|part_c_snapshots_web_page_generator|drawings/core/snapshots|test}} | ||
Latest revision as of 02:09, 15 December 2023
In this studio we will evolve our code from Render_Part_B_Assignment to add new methods and a new class.
Continue editing files in the drawings directory.
Contents
Background
Bounds Calculation
We will add support for calculating a bounding box for each of our drawable objects.
We will implement a BoundingBox class (via Struct, if desired) to store the min and max points of a box which bounds the object.
Transformable objects will split the responsibility into two methods, untransformed_bounds and bounds. On the subclasses the untransformed_bounds method will return its object's bounds in the same untransformed space that untransformed_render acts: that is, about its origin. On the Transform superclass, the bounds method will transform the untransformed_bounds by the x and y location (akin to how render transforms the affine matrix via glTranslate to transform the space untransformed_render operates in). The bounds method will not be able to rely on glTranslate. It will need to create a new transformed BoundingBox.
For example, an Ellipse created with an x_radius of 0.3, a y_radius of 0.4, an x location of 0.1, and a y location of 0.2 would produce an untransformed_bounds with a min of (-0.3, -0.4) and a max of (0.3, 0.4). The bounds calculation inherited from Transform would transform the untransformed bounds with the x and y locations, producing a bounding box with a min of (-0.2, -0.2) and a max of (0.4, 0.6).
Code To Use
Graphics
Point2
BoundingBox
Code to Implement
Transform
| file: | src/main/ruby/drawings/transform.rb | |
| class: | Transform | |
| superclass: | Object | |
| methods to evolve: | Ø | |
| methods to add: | move(direction,amount) bounds() |
|
| methods to remove: | Ø |
move
the move method will accept two parameters: direction and amount and change the x,y position as appropriate.
direction can be one of four symbols
:left :right :up :down
- left corresponds to translating along the negative x axis
- right corresponds to translating along the positive x axis
- down corresponds to translating along the negative y axis
- up corresponds to translating along the positive y axis
any other value for direction should raise an ArgumentError.
Note: do NOT call glTranslate here. simply update your instance fields so that later when you are rendering, you will glTranslate the updated amounts.
bounds
invoke untransformed_bounds and transform the returned bounds by x and y.
NOTE: untransformed_bounds is abstract. it must be defined by the subclasses.
Rectangle
| file: | src/main/ruby/drawings/rectangle.rb | |
| class: | Rectangle | |
| superclass: | ColorTransform | |
| methods to evolve: | Ø | |
| methods to add: | untransformed_bounds | |
| methods to remove: | Ø |
untransformed_bounds
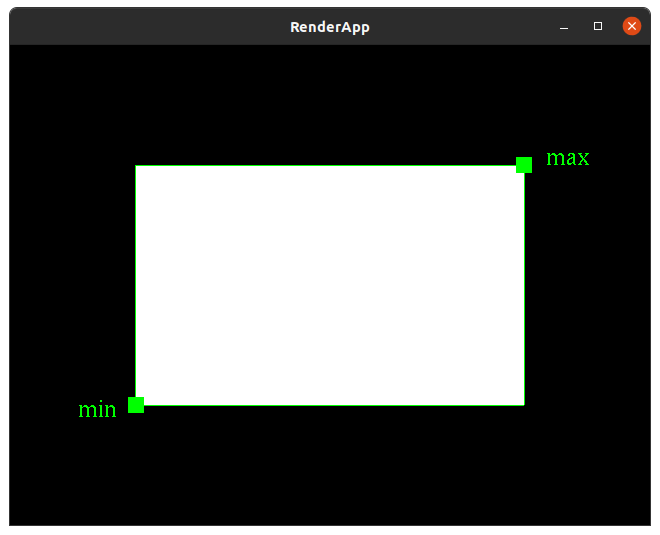
Returns an instance of BoundingBox specified by min and max instances of Point2.
NOTE: this method must be private.
bounding box decoration rendering
Note: the bounding box and minimum and maximum points are only for demonstration here. The should not be drawn in your solution.
Ellipse
| file: | src/main/ruby/drawings/ellipse.rb | |
| class: | Ellipse | |
| superclass: | ColorTransform | |
| methods to evolve: | Ø | |
| methods to add: | untransformed_bounds | |
| methods to remove: | Ø |
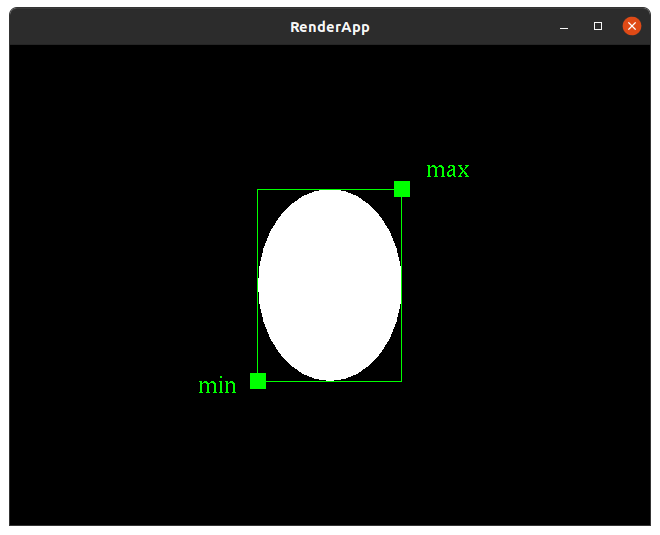
untransformed_bounds
Returns an instance of BoundingBox specified by min and max instances of Point2.
NOTE: this method must be private.
bounding box decoration rendering
Note: the bounding box and minimum and maximum points are only for demonstration here. The should not be drawn in your solution.
EquilateralTriangle
| file: | src/main/ruby/drawings/equilateral_triangle.rb | |
| class: | EquilateralTriangle | |
| superclass: | ColorTransform | |
| methods to evolve: | Ø | |
| methods to add: | untransformed_bounds | |
| methods to remove: | Ø |
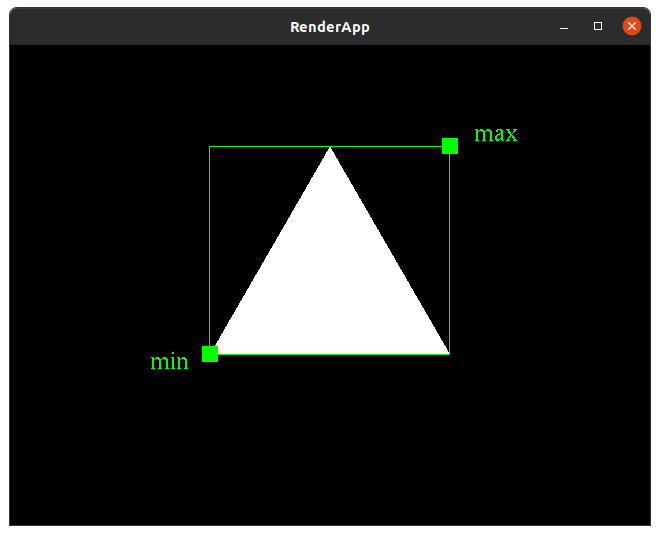
untransformed_bounds
Returns an instance of BoundingBox specified by min and max instances of Point2.
NOTE: this method must be private.
bounding box decoration rendering
Note: the bounding box and minimum and maximum points are only for demonstration here. The should not be drawn in your solution.
BezierCurve
| file: | src/main/ruby/drawings/bezier_curve.rb | |
| class: | BezierCurve | |
| superclass: | ColorTransform | |
| methods to evolve: | Ø | |
| methods to add: | untransformed_bounds | |
| methods to remove: | Ø |
untransformed_bounds
Contemplate for a moment how you would build this method and then raise an error and move on.
NOTE: this method must be private.
def untransformed_bounds
raise StandardError.new("not yet implemented")
end
Text
| file: | src/main/ruby/drawings/text.rb | |
| class: | Text | |
| superclass: | ColorTransform | |
| methods to evolve: | Ø | |
| methods to add: | untransformed_bounds | |
| methods to remove: | Ø |
untransformed_bounds
Contemplate for a moment how you would build this method and then raise an error and move on.
NOTE: this method must be private.
def untransformed_bounds
raise StandardError.new("not yet implemented")
end
CircularSegment
| file: | src/main/ruby/drawings/circular_segment.rb | |
| class: | CircularSegment | |
| superclass: | ColorTransform | |
| methods to evolve: | Ø | |
| methods to add: | untransformed_bounds | |
| methods to remove: | Ø |
untransformed_bounds
Contemplate for a moment how you would build this method and then raise an error and move on.
NOTE: this method must be private.
def untransformed_bounds
raise StandardError.new("not yet implemented")
end
Image
| file: | src/main/ruby/drawings/image.rb | |
| class: | Image | |
| superclass: | Transform | |
| methods to evolve: | Ø | |
| methods to add: | untransformed_bounds | |
| methods to remove: | Ø |
untransformed_bounds
Contemplate for a moment how you would build this method and then raise an error and move on.
NOTE: this method must be private.
def untransformed_bounds
raise StandardError.new("not yet implemented")
end
CompositeTransform
| file: | src/main/ruby/drawings/composite_transform.rb | |
| class: | CompositeTransform | |
| superclass: | Transform | |
| methods to evolve: | Ø | |
| methods to add: | untransformed_bounds | |
| methods to remove: | Ø |
untransformed_bounds
Returns an instance of Bounds specified by min and max instances of Point2.
NOTE: this method must be private.
NOTE: when computing the bounds of multiple objects, recall that the identity element of minimum and the maximum is not 0.
bounding box decoration rendering
Note: the bounding box and minimum and maximum points are only for demonstration here. The should not be drawn in your solution.
Scene
| file: | src/main/ruby/drawings/scene.rb | |
| class: | Scene | |
| superclass: | Object | |
| methods to evolve: | bounds() | |
| methods to add: | Ø | |
| methods to remove: | Ø |
bounds
NOTE: this method must be public.
NOTE: when computing the bounds of multiple objects, recall that the identity element of minimum and the maximum is not 0.
bounding box decoration rendering
Note: the bounding box and minimum and maximum points are only for demonstration here. The should not be drawn in your solution.
ConvexPolygon
| file: | src/main/ruby/drawings/convex_polygon.rb | |
| class: | ConvexPolygon | |
| superclass: | ColorTransform | |
| methods: | initialize(points, x: 0, y: 0, color: nil) untransformed_render() untransformed_bounds() |
initialize
Accept a required parameter points which is an array of Point2s.
Accept keyword parameters for x: 0, y: 0, and color: nil to the constructor and pass them to the superclass.
NOTE: Be sure to not override render. Implement the render_transformed method instead.
untransformed_render
NOTE: this method must be private.
untransformed_bounds
NOTE: this method must be private.
NOTE: when computing the bounds of multiple objects, recall that the identity element of minimum and the maximum is not 0.
bounding box decoration rendering
Note: the bounding box and minimum and maximum points are only for demonstration here. The should not be drawn in your solution.
| file to run: | src/main/ruby/drawings/convex_polygon.rb |
Testing Your Solution
Unit Test
| file: | src/test/ruby/drawings/core/relatively_fast/part_c/*.rb |
note: ensure that you have removed all printing to receive credit for any assignment.
| file: | src/test/ruby/drawings/core/relatively_slow/part_c/*.rb |
note: ensure that you have removed all printing to receive credit for any assignment.
Backwards Compatibility
| file: | src/test/ruby/drawings/core/relatively_fast/part_a/*.rb |
note: ensure that you have removed all printing to receive credit for any assignment.
| file: | src/test/ruby/drawings/core/relatively_fast/part_b/*.rb |
note: ensure that you have removed all printing to receive credit for any assignment.
Visual Comparison
| file to run: | src/test/ruby/drawings/core/snapshots/part_c_snapshots_web_page_generator.rb |