Difference between revisions of "Iterable Immutable List Assignment"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| (34 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | = | + | =Exercise To Revisit= |
| − | + | In this studio we will complete the <code>EmptyImmutableList</code> and <code>NonEmptyImmutableList</code> implementations from the [[ImmutableList_Assignment|ImmutableList exercise]]. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | == | + | ==ImmutableList== |
| − | + | The [https://www.cse.wustl.edu/~cosgroved/courses/cse425s/spring20/apidocs/immutable/list/core/ImmutableList.html ImmutableList] interface extends [https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/lang/Iterable.html Iterable] which has one method: [https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/lang/Iterable.html#iterator-- iterator()]. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
<nowiki>public interface ImmutableList<E> extends Iterable<E> { | <nowiki>public interface ImmutableList<E> extends Iterable<E> { | ||
E head(); | E head(); | ||
| Line 16: | Line 11: | ||
}</nowiki> | }</nowiki> | ||
| − | = | + | ==Iterable== |
| − | + | [https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/lang/Iterable.html interface java.lang.Iterable<T>] | |
| − | + | #[https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/lang/Iterable.html#iterator-- Iterator<T> iterator()] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ==Iterator== | |
| + | [https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/util/Iterator.html interface java.util.Iterator<T>] | ||
| + | #[https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/util/Iterator.html#hasNext-- boolean hasNext()] | ||
| + | #[https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/util/Iterator.html#next-- T next()] | ||
| − | === | + | =Examples= |
| − | + | ==Using Iterable== | |
| + | <youtube>A-rTJTHq5B4</youtube> | ||
| + | ==Implementing Iterable: DOM NodeList== | ||
| + | <youtube>4ycpqdJ4yb4</youtube> | ||
| − | + | =Example= | |
| + | {{Example|IterableImmutableListExample|immutable.list.example}} | ||
| − | + | The code: | |
| − | <nowiki> | + | <nowiki>ImmutableList<Integer> numbers = Lists.brackets(4, 66, 99); |
| + | for (Integer i : numbers) { | ||
| + | System.out.println(i); | ||
| + | }</nowiki> | ||
| − | + | produces: | |
| − | === | + | <nowiki>4 |
| − | <nowiki> | + | 66 |
| + | 99</nowiki> | ||
| + | |||
| + | =Diagrams= | ||
| + | ==ImmutableList== | ||
| + | <nowiki>ImList<Char> letters = Lists.brackets('A', 'B', 'C'); </nowiki> | ||
| − | + | [[File:ImmutableList_letters.svg|600px]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ==Initial Iterator State== | |
| − | == | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | <nowiki>ImList<Char> letters = Lists.brackets('A', 'B', 'C'); | |
| − | < | + | Iterator<Char> iter = letters.iterator(); </nowiki> |
| − | + | [[File:ImmutableList_iterator.svg|600px]] | |
| − | + | ==Iterator State after next()== | |
| − | == | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | <nowiki>ImList<Char> letters = Lists.brackets('A', 'B', 'C'); | |
| + | Iterator<Char> iter = letters.iterator(); | ||
| + | if(iter.hasNext()) { | ||
| + | char a = iter.next(); | ||
| + | } </nowiki> | ||
| − | + | [[File:ImmutableList_iterator_next.svg|600px]] | |
| − | == | + | ==Iterator State after next() next()== |
| − | <nowiki> | + | <nowiki>ImList<Char> letters = Lists.brackets('A', 'B', 'C'); |
| + | Iterator<Char> iter = letters.iterator(); | ||
| + | if(iter.hasNext()) { | ||
| + | char a = iter.next(); | ||
| + | if(iter.hasNext()) { | ||
| + | char b = iter.next(); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | } </nowiki> | ||
| − | + | [[File:ImmutableList_iterator_next_next.svg|600px]] | |
| + | ==Iterator State after next() next() next()== | ||
| + | <nowiki>ImList<Char> letters = Lists.brackets('A', 'B', 'C'); | ||
| + | Iterator<Char> iter = letters.iterator(); | ||
| + | if(iter.hasNext()) { | ||
| + | char a = iter.next(); | ||
| + | if(iter.hasNext()) { | ||
| + | char b = iter.next(); | ||
| + | if(iter.hasNext()) { | ||
| + | char c = iter.next(); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | } </nowiki> | ||
| − | + | [[File:ImmutableList_iterator_next_next_next.svg|600px]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | =Code To Implement= | |
| + | ==enum EmptyImmutableList== | ||
| + | {{JavaToImplement|EmptyImmutableList|iterator|immutable.list.assignment}} | ||
| + | ===iterator()=== | ||
| + | return an [https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/util/Iterator.html Iterator] for the EmptyImmutableList. | ||
| − | + | Question to ask yourself: Does an iterator for an EmptyImmutableList ever have a next? | |
| − | = | + | ==class NonEmptyImmutableList== |
| − | {{ | + | {{JavaToImplement|NonEmptyImmutableList|iterator|immutable.list.assignment}} |
| + | ===iterator()=== | ||
| + | return an [https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/util/Iterator.html Iterator] for this instance of NonEmptyImmutableList. | ||
| − | + | Note: If you are within an anonymous inner class, the way to get the outer class's this instance is to qualify it with the out class identifier. For example: | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | <nowiki>NonEmptyImmutableList.this</nowiki> | |
| − | <nowiki> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
=Test= | =Test= | ||
| − | {{TestSuite| | + | {{TestSuite|IterableAssignmentTestSuite|immutable.list.util.exercise}} |
| + | |||
| + | :{{TestSuite|ImmutableListIteratorMethodTestSuite|immutable.list.util.exercise}} | ||
Latest revision as of 19:05, 24 April 2022
Exercise To Revisit
In this studio we will complete the EmptyImmutableList and NonEmptyImmutableList implementations from the ImmutableList exercise.
ImmutableList
The ImmutableList interface extends Iterable which has one method: iterator().
public interface ImmutableList<E> extends Iterable<E> {
E head();
ImmutableList<E> tail();
boolean isEmpty();
}
Iterable
interface java.lang.Iterable<T>
Iterator
interface java.util.Iterator<T>
Examples
Using Iterable
Implementing Iterable: DOM NodeList
Example
| class: | IterableImmutableListExample.java | |
| package: | immutable.list.example | |
| source folder: | src/main/java |
The code:
ImmutableList<Integer> numbers = Lists.brackets(4, 66, 99);
for (Integer i : numbers) {
System.out.println(i);
}
produces:
4 66 99
Diagrams
ImmutableList
ImList<Char> letters = Lists.brackets('A', 'B', 'C');
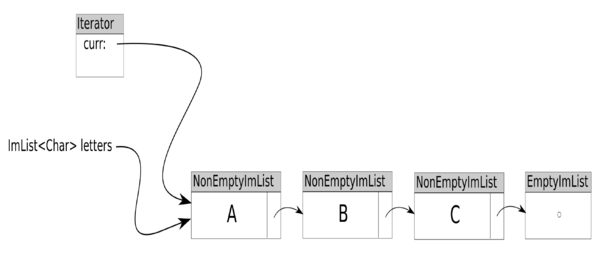
Initial Iterator State
ImList<Char> letters = Lists.brackets('A', 'B', 'C');
Iterator<Char> iter = letters.iterator();
Iterator State after next()
ImList<Char> letters = Lists.brackets('A', 'B', 'C');
Iterator<Char> iter = letters.iterator();
if(iter.hasNext()) {
char a = iter.next();
}
Iterator State after next() next()
ImList<Char> letters = Lists.brackets('A', 'B', 'C');
Iterator<Char> iter = letters.iterator();
if(iter.hasNext()) {
char a = iter.next();
if(iter.hasNext()) {
char b = iter.next();
}
}
Iterator State after next() next() next()
ImList<Char> letters = Lists.brackets('A', 'B', 'C');
Iterator<Char> iter = letters.iterator();
if(iter.hasNext()) {
char a = iter.next();
if(iter.hasNext()) {
char b = iter.next();
if(iter.hasNext()) {
char c = iter.next();
}
}
}
Code To Implement
enum EmptyImmutableList
| class: | EmptyImmutableList.java | |
| methods: | iterator | |
| package: | immutable.list.assignment | |
| source folder: | src/main/java |
iterator()
return an Iterator for the EmptyImmutableList.
Question to ask yourself: Does an iterator for an EmptyImmutableList ever have a next?
class NonEmptyImmutableList
| class: | NonEmptyImmutableList.java | |
| methods: | iterator | |
| package: | immutable.list.assignment | |
| source folder: | src/main/java |
iterator()
return an Iterator for this instance of NonEmptyImmutableList.
Note: If you are within an anonymous inner class, the way to get the outer class's this instance is to qualify it with the out class identifier. For example:
NonEmptyImmutableList.this
Test
| class: | IterableAssignmentTestSuite.java | |
| package: | immutable.list.util.exercise | |
| source folder: | src/test/java |