
Product: ABAQUS/Explicit

This verification test consists of a list of single-element models that use either C3D8R or CPE4R elements and are run under simple loading conditions (uniaxial tension, uniaxial compression, and simple shear). The purpose of this example is to test the equation of state material model and its combination with the Mises and Johnson-Cook plasticity models. Two parallel sets of models are studied. The first set uses the linear elastic, linear elastic with Mises plastic, and linear elastic with Johnson-Cook plastic materials. The second set uses the linear ![]() type of EOS, linear
type of EOS, linear ![]() type of EOS with Mises plastic, and linear
type of EOS with Mises plastic, and linear ![]() type of EOS with Johnson-Cook plastic materials.
type of EOS with Johnson-Cook plastic materials.
For linear elasticity the volumetric response is defined by
![]()
![]()
The elastic material properties are Young's modulus = 207 GPa and Poisson's ratio = 0.29. The initial material density, ![]() , is 7890 kg/m3. The equivalent properties for the linear
, is 7890 kg/m3. The equivalent properties for the linear ![]() type of equation of state material model are
type of equation of state material model are ![]() = 4563.115 m/s and shear modulus = 80.233 GPa. For models in which plasticity (including both Mises and Johnson-Cook plasticity models) is used, the plastic hardening is chosen to be
= 4563.115 m/s and shear modulus = 80.233 GPa. For models in which plasticity (including both Mises and Johnson-Cook plasticity models) is used, the plastic hardening is chosen to be
![]()
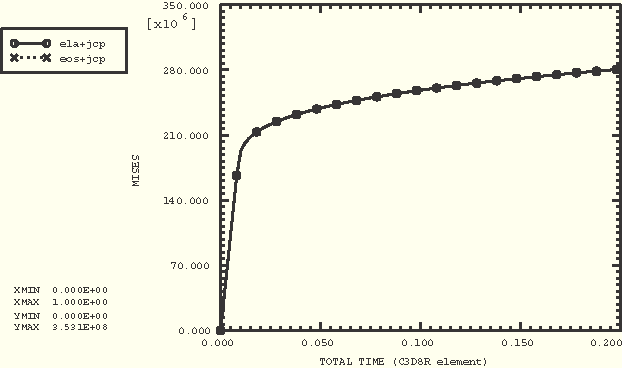
The results obtained from the analyses that use the EOS material model match the corresponding results obtained from the analyses that use the linear elasticity model. The comparison of the pressure and Mises stresses obtained with the EOS material model (with Johnson-Cook plastic shear response) and the linear elasticity model (with the same Johnson-Cook plastic shear response) using the C3D8R element under uniaxial tension loading are shown in Figure 2.2.19–1 and Figure 2.2.19–2, respectively. The uniaxial compression comparisons are shown in Figure 2.2.19–3 and Figure 2.2.19–4.
Uniaxial tension test.
Uniaxial compression test.
Simple shear test.
Simple shear test with nonzero initial conditions for ![]() .
.

Figure 2.2.19–1 Pressure stress in uniaxial tension: elastic response versus linear ![]() type of equation of state response.
type of equation of state response.
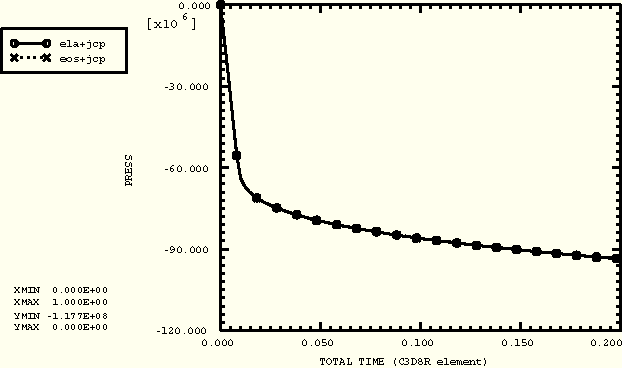
Figure 2.2.19–2 Mises stress in uniaxial tension: elastic response versus linear ![]() type of equation of state response.
type of equation of state response.

This verification test consists of a list of single-element models that use either C3D8R or CPE4R elements and are run under simple loading conditions (uniaxial, hydrostatic, and simple shear). The purpose of this example is to test the ![]() equation of state material model and its combination with different models for the deviatoric behavior: linear elastic, Newtonian viscous shear, and Mises and Johnson-Cook plasticity.
equation of state material model and its combination with different models for the deviatoric behavior: linear elastic, Newtonian viscous shear, and Mises and Johnson-Cook plasticity.
The material properties used for the tests are representative of partially saturated sand. They are summarized below:
Material:Solid phase
Compaction properties
Compaction properties are specified with the *EOS COMPACTION option:
Plasticity
For models with plastic shear behavior (either Mises or Johnson-Cook plasticity), the plastic hardening is chosen to be
![]()
The results obtained from the analyses agree well with exact analytical or approximate solutions. The evolution of the distension ![]() with hydrostatic pressure during a cyclic volumetric test is shown in Figure 2.2.19–5.
with hydrostatic pressure during a cyclic volumetric test is shown in Figure 2.2.19–5.
Uniaxial test.
Cyclic hydrostatic test.
Simple shear test.
Simple shear test with nonzero initial conditions for ![]() .
.