
Product: ABAQUS/Standard
The initial starting geometry for each test is shown in Figure 1.10.3–1. In the linear tests each coupling node is connected by a spring to ground (SPRING1) in each direction. In the geometrically nonlinear tests each coupling node is connected by a dashpot to ground (DASHPOT1) in each direction, and an axial spring element (SPRINGA) connects each pair of coupling nodes.
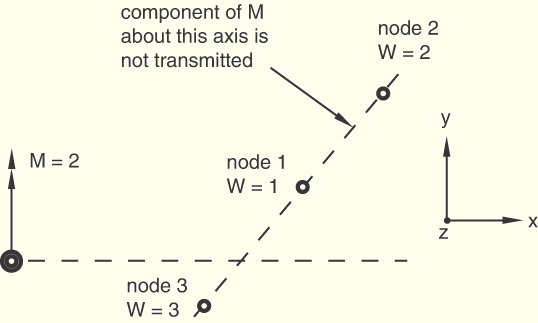
Distributing coupling elements connect a single reference node that has translational and rotational degrees of freedom to a collection of coupling nodes that have only translational degrees of freedom. Thus, when the coupling nodes are colinear, a situation can arise where the moments applied to the reference node are not transmitted by the element. This condition is relevant only for the three-dimensional version of the element. The third problem in this section tests the behavior of the element in this pathological situation.
Properties:
The spring stiffnesses are 100, 200, and 300 for degrees of freedom 1, 2, and 3, respectively, for the springs connected to all coupling nodes. The mass of the distributing coupling is 10. The weight factors are 1, 2, and 3 for nodes 1, 2, and 3, respectively.
Loading:
Step 1: The force at node 10 is 1.0 in the x-direction. The moment at node 10 is 2.0 about the z-axis.
Step 2: (DCOUP3D only) The force at node 10 is 1.0 in the y-direction. The moment at node 10 is 2.0 about the x-axis.
Step 3: (DCOUP3D only) The force at node 10 is 1.0 in the z-direction. The moment at node 10 is 2.0 about the y-axis.
Step 4: Frequency extraction. (Step 2 for DCOUP2D)
Step 5: Transient modal dynamic step with a load, ![]() 1.0
1.0![]() , applied to node 10. (Step 3 for DCOUP2D)
, applied to node 10. (Step 3 for DCOUP2D)
Step 6: Mode-based steady-state dynamic step with a load, ![]() 1.0, applied to node 10. (Step 4 for DCOUP2D)
1.0, applied to node 10. (Step 4 for DCOUP2D)
Properties:
The dashpot damping coefficients are 100, 200, and 300 for degrees of freedom 1, 2, and 3, respectively, for the dashpots connected to all coupling nodes. The axial springs connecting the coupling nodes each have a spring constant of 1.0 × 108. The mass of the distributing coupling is 10.
Prescribed reference node motion:
Step 1: Total rotation of ![]() about the z-axis. Translation
about the z-axis. Translation ![]() .
.
Step 2: (DCOUP3D only) Total rotation of ![]() about the y-axis. Translation
about the y-axis. Translation ![]() .
.
Step 3: (DCOUP3D only) Total rotation of ![]() about the x-axis. Translation
about the x-axis. Translation ![]() .
.
Step 4: Direct-integration dynamic step with a total rotation of ![]() about the x-axis. Translation
about the x-axis. Translation ![]() . (Step 2 for DCOUP2D)
. (Step 2 for DCOUP2D)
Properties:
The spring stiffnesses are 100, 200, and 300 for degrees of freedom 1, 2, and 3, respectively, for the springs connected to all coupling nodes. The mass of the distributing coupling is 10. The weight factors are 1, 2, and 3 for nodes 1, 2, and 3, respectively.
Loading:
Step 1: The moment at node 10 is 2.0 about the z-axis.
Step 2: The moment at node 10 is 2.0 about the x-axis.
Step 3: The moment at node 10 is 2.0 about the y-axis.
Step 4: The moment at node 10 has a magnitude of 2.0 and is parallel to the coupling node colinear axis.
Step 5: Frequency extraction.
In all tests the load distribution among coupling nodes adheres to the relation
![]()
The results for each problem are discussed below.
Table 1.10.3–1 Displacements at node 10.
| Step | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 6.67 × 10–3 | –1.67 × 10–2 | 0.0 |
| 2 | –2.06 × 10–3 | 1.35 × 10–2 | –2.67 × 10–2 |
| 3 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 8.50 × 10–2 |
Table 1.10.3–2 Rotations at node 10.
| Step | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.05 × 10–2 |
| 2 | 1.33 × 10–2 | –1.33 × 10–2 | –7.33 × 10–3 |
| 3 | –2.67 × 10–2 | 4.50 × 10–2 | 0.0 |
Table 1.10.3–3 Displacements at node 1.
| Step | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.19 × 10–3 | 1.44 × 10–3 | 0.0 |
| 2 | 2.97 × 10–4 | –5.78 × 10–5 | 6.67 × 10–3 |
| 3 | 0.0 | 0.0 | –1.83 × 10–2 |
Table 1.10.3–4 NFORC output at node 2.
| Step | NFORC1 | NFORC2 | NFORC3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.39 | 0.574 | 0.0 |
| 2 | –0.653 | –2.31 × 10–2 | –2.00 |
| 3 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 2.50 |
All results correspond to the increment when the rotation is 3![]() 4.
4.
Table 1.10.3–7 Displacements at node 1.
| Step | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | –3.06 | 0.561 | 0.0 |
| 2 | –3.41 | –2.22 × 10–4 | –0.706 |
| 3 | 9.30410 × 10–5 | –0.1451 | 0.353 |
| 4 | –3.06 | 0.561 | 5.51 × 10–5 |
Table 1.10.3–8 NFORC output at node 1.
| Step | NFORC1 | NFORC2 | NFORC3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | –679 | –1080 | 0.0 |
| 2 | –1090 | –47.7 | 1120 |
| 3 | –8.46 | –1190 | –757 |
| 4 | –623 | –1270 | 4.44 × 10–2 |
Table 1.10.3–11 Displacements at node 10.
| Step | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.59 × 10–3 | –7.69 × 10–3 | 0.0 |
| 2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | –2.06 × 10–3 |
| 3 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 2.06 × 10–3 |
| 4 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
Table 1.10.3–12 Rotations at node 10.
| Step | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 3.76 × 10–3 |
| 2 | 8.36 × 10–4 | –8.36 × 10–4 | 0.0 |
| 3 | –8.36 × 10–4 | 8.36 × 10–4 | 0.0 |
| 4 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
Table 1.10.3–13 Displacements at node 1.
| Step | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3.45 × 10–4 | –1.72 × 10–4 | 0.0 |
| 2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | –1.15 × 10–4 |
| 3 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.15 × 10–4 |
| 4 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
Table 1.10.3–14 NFORC output at node 2.
| Step | NFORC1 | NFORC2 | NFORC3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.483 | –0.483 | 0.0 |
| 2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | –0.483 |
| 3 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.483 |
| 4 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
Linear behavior of DCOUP2D elements with *LOAD CASE.
Linear behavior of DCOUP3D elements.
Geometrically nonlinear behavior of DCOUP2D elements.
Geometrically nonlinear behavior of DCOUP3D elements.
Test of DCOUP3D elements with colinear coupling nodes.