
ABAQUS/CAE can apply the swept meshing technique to solid regions that can be replicated by sweeping a source side along an edge to the target side. For a three-dimensional solid the sweep path is an edge, but the source and target sides are faces. Figure 17–75 illustrates an extruded swept mesh—ABAQUS/CAE meshes the source side and extrudes that mesh along an edge to the target side. Figure 17–76 illustrates a revolved swept mesh—ABAQUS/CAE meshes the source side and revolves that mesh about the axis of the circular edge to the target side.
Figure 17–76 The revolved swept meshing technique sweeps the mesh on the source side along a circular edge.

If a region is swept meshable, ABAQUS/CAE can generate the swept mesh on a region that has been assigned the Hex, Hex-dominated, or Wedge element shape option. To generate the preliminary two-dimensional mesh on the source side, ABAQUS/CAE uses the free meshing technique with the Quad, Quad-dominated, or Tri element shape option, respectively.
You can choose between the medial axis and advancing front meshing algorithms when you mesh a solid region with hexahedral or hexahedral-dominated elements using the swept meshing technique. (ABAQUS/CAE generates hexahedral and hexahedral-dominated meshes by sweeping the quadrilateral and quadrilateral-dominated elements generated by the two algorithms from the source side to the target side.) However, if the region to be meshed contains virtual topology, you can use only the advancing front algorithm to generate the swept mesh. For more information, see “What is the difference between the medial axis algorithm and the advancing front algorithm?,” Section 17.7.6, and “Free meshing with quadrilateral and quadrilateral-dominated elements,” Section 17.9.2.
If you select the advancing front algorithm, you can allow ABAQUS/CAE to decide whether mapped meshing is appropriate. (Mapped meshing is the same as structured meshing but applies only to four-sided regions.) If you choose this option, ABAQUS/CAE determines whether it is appropriate to replace the advancing front algorithm with mapped meshing on any of the faces that belong to the source side. For more information, see “What is mapped meshing?,” Section 17.8.2, and “When can ABAQUS/CAE apply mapped meshing?,” Section 17.8.6.
ABAQUS/CAE uses mapped meshing to create quadrilateral and quadrilateral-dominated elements on the boundary faces and then sweeps the elements from the source side to the target side to create the hexahedral and hexahedral-dominated elements.
A three-dimensional region can be meshed using the swept meshing technique if it has the following characteristics:
Every side that connects the source side to the target side must contain only a single face without isolated edges or isolated vertices. For example, the model in Figure 17–77 cannot be meshed using the swept meshing technique because one of the connecting sides is partitioned into two faces.
Similarly, Figure 17–78 shows a part that cannot be swept meshed with hexahedral elements because the connecting side contains six rings. To make the part swept meshable, you can create partitions at these rings using the N-sided patch partition tool. The part now consists of seven separate swept cells, and the connecting side of each cell contains only a single face. As a result, the part is now swept meshable. Alternatively, you may be able to use virtual topology to remove edges or vertices from a connecting side to make a part swept meshable.The target side must contain only a single face without isolated edges or isolated vertices. For example, the region on the left in Figure 17–79 can be meshed using the swept meshing technique because all of the isolated edges are on the source side; the region on the right, however, cannot be meshed using this technique because the target side contains two faces.
Figure 17–80 illustrates a part that has been swept meshed along a varying cross-section. The part appears to be relatively complex; for example, the source side is non-planar, and the cross-section of the part varies along the sweep path. However, the rules for generating a swept mesh still apply.
Every side that connects the source side to the target side contains only a single face.
Although the source side contains two faces, the target side contains only a single face.
You may be able to use virtual topology to combine faces on the target side to make a part swept meshable. Figure 17–81 illustrates a part that was swept mesh after the five faces on the target side were combined into a single face using virtual topology. However, because the part now contains virtual topology, it can be swept meshed with only the advancing front algorithm.
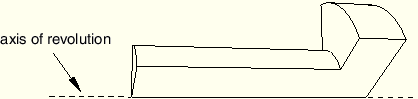
For a revolved region, the profile that was revolved to create the region must not touch the axis of revolution at one or more isolated points, as shown in Figure 17–82.
Similarly, ABAQUS/CAE cannot mesh a region with hexahedral or wedge elements if one or more edges lie along the axis of revolution, as shown in Figure 17–83.
Figure 17–83 ABAQUS/CAE cannot mesh a region with hexahedral elements if one or more edges lie along the axis of revolution.
A fully revolved region that does not touch the axis of revolution is meshable only if all the edges that are associated with the profile being revolved exist. However, the edges that bound the profile must not create a face. Figure 17–85 shows a meshable part instance where all of the edges of the revolved profile exist.
In this example the user sketched the profile, and ABAQUS/CAE revolved the profile to create the part; however, the edges that bound the profile do not form a face. In contrast, Figure 17–86 shows a part instance that is not meshable because some of the edges of the revolved profile are missing.A fully revolved region that touches the axis of revolution is meshable only if all of the edges that are associated with the profile being revolved exist except the edges along the axis of revolution. Figure 17–87 shows a part instance that is meshable because all of the edges of the revolved profile exist except for the edge along the axis of revolution. If the profile included the edge along the axis of revolution, the part instance would not be meshable.
If a revolved region was created by revolving a sketch that contains a spline, the region is meshable only if the vertices at each end of the spline are not on the axis of revolution.
If a part was created by sweeping a cross-section along a sweep path that is composed of a closed spline, the resulting part is meshable only if it is split into two or more regions.