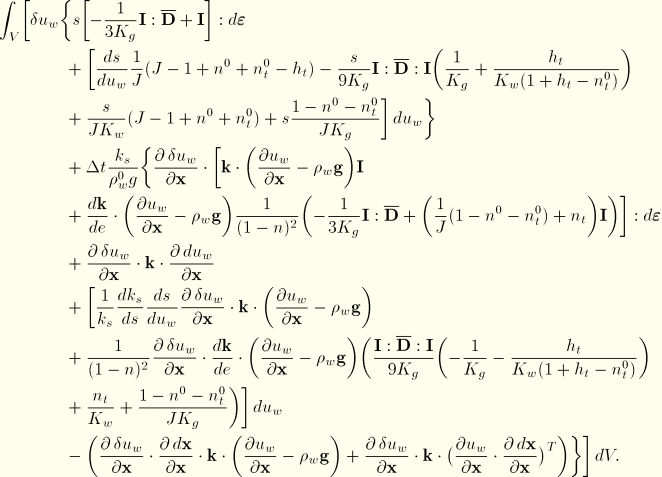Product: ABAQUS/Standard
ABAQUS/Standard provides capabilities for particular cases of fluid flow through a porous medium. These cases are associated with having a relatively incompressible wetting liquid present in the medium. The medium may be wholly or partially saturated, with this liquid. When the medium is only partially saturated the remainder of the voids is filled with another fluid. An example is a geotechnical problem, with soil containing water and air: continuity is written for the water phase.
The wetting liquid can attach to and, thus, be trapped by certain solid particles in the medium: this volume of trapped liquid attached to solid particles forms a “gel.”
A porous medium is modeled approximately in ABAQUS by attaching the finite element mesh to the solid phase. Liquid can flow through this mesh. A continuity equation is, therefore, required for the liquid, equating the rate of increase in liquid mass stored at a point to the rate of mass of liquid flowing into the point within the time increment. This continuity statement is defined in this section. It is written in a variational form as a basis for finite element approximation. The liquid flow is described by introducing Darcy's law or, alternatively, Forchheimer's law. The continuity equation is satisfied approximately in the finite element model by using excess wetting liquid pressure as the nodal variable (degree of freedom 8), interpolated over the elements. The equation is integrated in time by using the backward Euler approximation. The total derivative of this integrated variational statement of continuity with respect to the nodal variables is required for the Newton iterations used to solve the nonlinear, coupled, equilibrium and continuity equations. This expression is also derived in this section.
Consider a volume containing a fixed amount of solid matter. In the current configuration this volume occupies space ![]() with surface
with surface ![]() . In the reference configuration it occupied space
. In the reference configuration it occupied space ![]() . Wetting liquid can flow through this volume: at any time the volume of such “free” liquid (liquid that can flow if driven by pressure) is written
. Wetting liquid can flow through this volume: at any time the volume of such “free” liquid (liquid that can flow if driven by pressure) is written ![]() . Wetting liquid can also become trapped in the volume, by absorption into the gel. The volume of such trapped liquid is written
. Wetting liquid can also become trapped in the volume, by absorption into the gel. The volume of such trapped liquid is written ![]() .
.
The total mass of wetting liquid in the control volume is
![]()
The time rate of change of this mass of wetting liquid is
![]()
The mass of wetting liquid crossing the surface and entering the volume per unit time is
![]()
Equating the addition of liquid mass across the surface ![]() to the rate of change of liquid mass within the volume
to the rate of change of liquid mass within the volume ![]() gives the wetting liquid mass continuity equation
gives the wetting liquid mass continuity equation
![]()
![]()
The equivalent weak form is
![]()
![]()
In ABAQUS/Standard this continuity statement is integrated approximately in time by the backward Euler formula, giving
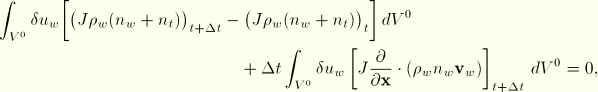

The divergence theorem allows the equation to be rewritten as
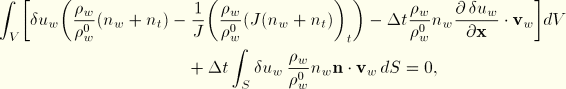
Since ![]() , this is the same as
, this is the same as

The constitutive behavior for pore fluid flow is governed either by Darcy's law or by Forchheimer's law. Darcy's law is generally applicable to low fluid flow velocities, whereas Forchheimer's law is commonly used for situations involving higher flow velocities. Darcy's law can be thought of as a linearized version of Forchheimer's law. Darcy's law states that, under uniform conditions, the volumetric flow rate of the wetting liquid through a unit area of the medium, ![]() , is proportional to the negative of the gradient of the piezometric head (Bear, 1972):
, is proportional to the negative of the gradient of the piezometric head (Bear, 1972):
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() can be anisotropic and is a function of the saturation and void ratio of the material.
can be anisotropic and is a function of the saturation and void ratio of the material. ![]() has units of velocity (length/time). [Some authors refer to
has units of velocity (length/time). [Some authors refer to ![]() as the hydraulic conductivity (Bear, 1972) and define the permeability as
as the hydraulic conductivity (Bear, 1972) and define the permeability as
![]()
We assume that ![]() is constant in magnitude and direction, so
is constant in magnitude and direction, so
![]()
The permeability of a particular fluid in a multiphase flow system depends on the saturation of the phase being considered and on the porosity of the medium. We assume these dependencies are separable, so
![]()
The function ![]() can be defined by the user. Nguyen and Durso (1983) observe that, in steady flow through a partially saturated medium, the permeability varies with
can be defined by the user. Nguyen and Durso (1983) observe that, in steady flow through a partially saturated medium, the permeability varies with ![]() . We, therefore, take
. We, therefore, take ![]() by default.
by default.
Introducing the flow constitutive law allows the mass continuity equation (Equation 2.8.4–1) to be written

The bulk behavior of the grains was discussed in “Constitutive behavior in a porous medium,” Section 2.8.3. From Equation 2.8.3–2,
![]()
![]()
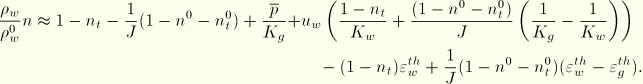

Because ![]() measures pressure in the wetting liquid and we neglect the pressure in the other fluid phase in the medium (see “Effective stress principle for porous media,” Section 2.8.1), the medium is fully saturated for
measures pressure in the wetting liquid and we neglect the pressure in the other fluid phase in the medium (see “Effective stress principle for porous media,” Section 2.8.1), the medium is fully saturated for ![]() . Negative values of
. Negative values of ![]() represent capillary effects in the medium. For
represent capillary effects in the medium. For ![]() it is known (see, for example, Nguyen and Durso, 1983) that, at a given value of capillary pressure,
it is known (see, for example, Nguyen and Durso, 1983) that, at a given value of capillary pressure, ![]() , the saturation lies within certain limits. Typical forms of these limits are shown in Figure 2.8.4–1.
, the saturation lies within certain limits. Typical forms of these limits are shown in Figure 2.8.4–1.
Bear (1972) suggests that the transition between absorption and exsorption and vice versa takes place along “scanning” curves. We approximate these with a straight line, as shown in Figure 2.8.4–1.
Saturation is treated as a state variable that may have to change if the wetting liquid pressure is outside the range for which its value is admissible according to that actual data corresponding to Figure 2.8.4–1. The evolution of saturation as a state variable is defined as follows. Assume that the saturation at time ![]() ,
, ![]() , is known. It must satisfy the constraints
, is known. It must satisfy the constraints
![]()
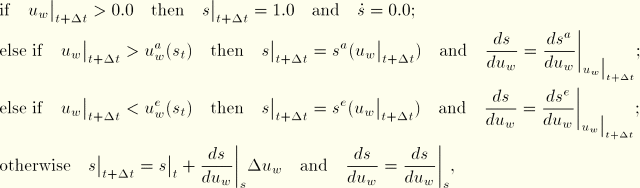

The Jacobian contribution from the continuity equation is obtained from the variation of Equation 2.8.4–2 with respect to ![]() and
and ![]() at time
at time ![]() .
.
Consider first the surface integral. The surface divides into that part across which the liquid mass flow rate, ![]() , is prescribed and that part where the wetting liquid pressure,
, is prescribed and that part where the wetting liquid pressure, ![]() , is prescribed. Thus, the only contribution of this term to the Jacobian is the variation in the integral caused by change in surface area in that part where the mass flow is prescribed. We neglect this contribution.
, is prescribed. Thus, the only contribution of this term to the Jacobian is the variation in the integral caused by change in surface area in that part where the mass flow is prescribed. We neglect this contribution.
The remaining part of the variation of Equation 2.8.4–2 is
![]()
Using Equation 2.8.4–3 we have
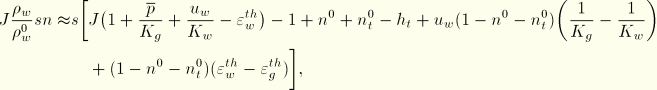

Equation 2.8.3–5 shows that ![]() , which is defined by the evolution equation given in “Constitutive behavior in a porous medium,” Section 2.8.3, and so makes no contribution to the Jacobian.
, which is defined by the evolution equation given in “Constitutive behavior in a porous medium,” Section 2.8.3, and so makes no contribution to the Jacobian.
Finally, the Jacobian contribution from the permeability term is rather complex in the general case of the nonlinear Forchheimer flow law. Although we include it in the software, here we only write the linearized flow version reflecting Darcy's law (![]() ):
):
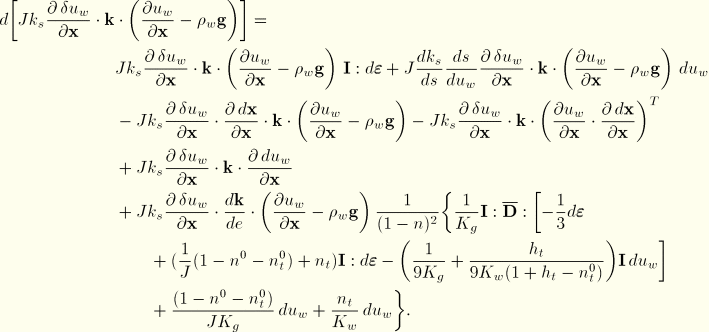
Using these results provides the Jacobian of the continuity equation as