The Future of Networking: The Green Movement
Tim Johnson, tjj3@wustl.edu (A project report written under the guidance of Prof. Raj Jain)
Abstract:
This paper will discuss the green movement in the telecommunications field to develop new energy efficient hardware. First I will examine the work being done by telecommunications companies to go green. Then I will explain ways different countries are trying to green there telecommunications to expand service to remote areas. Finally, I will talk about Power over Ethernet and its effects on power consumption in the office.
1.0 Introduction: What is Green Networking?
Green is a giant buzz word in the electronics field that has finally made its way into the everyday business of telecommunications companies. There are no guidelines for what makes something green however the main focus is on power management and cooling systems. Green networking is an initiative begun by many telecommunication companies to reduce the carbon dioxide emissions from base stations. Base station emissions are expected to peak at 22 megatons this year and with green initiatives drop 30% to 15.6 megatons by 2014. If these measures are not instituted carbon emissions are expected to rise to 35 megatons in 5 years. Surveys of consumers show that they would be more likely to buy a product from a vendor if it was labeled as green or energy efficient [HARRISON09]. Reducing energy consumption allows developing countries with limited access to reliable electricity to continue on as "high-growth markets for telecommunications" [PIKER09].
Back to Table of Contents
2.0 Companies Going Green
With all the talks about global warming and energy efficient appliances and vehicles it is no wonder that the going green phenomenon has spread into the field of telecommunications. As companies battle it out to develop new technology that can function on as little power as possible, mobile services are able to expand to areas of the world that no one could have expected. As companies put time and money into research and development of green technologies, they stand to make that money back by leading the way in offering green mobile equipment. As electric bills continue to rise the market for green equipment is waiting eagerly for the first products to roll off the assembly line.
2.1 Alcatel-Lucent
Alcatel-Lucent was founded in 2006 with the merger of the France based Alcatel and the United States based Lucent technologies. By the end of this year Alcatel-Lucent hopes to have its products using 20% less energy than they did in 2008. Alcatel-Lucent believes in a holistic line of attack when it comes to reducing the carbon footprint associated with telecommunications focusing on both ends to the communication used in "access, transport and core networks." In 2009, Alcatel-Lucent unveiled the Dynamic Power Save feature for its GSM/EDGE mobile networks. This allows for power consumption to drop when traffic is low, reducing average power consumption by 30%. This technology can be installed on all of the 500,000 Alcatel-Lucent base stations deployed since 1999, thus protecting mobile operators" investments and making existing networks more energy efficient." The company was also the first to combine different technologies at a single base station requiring less energy to support different types of users. They also were the first to develop a 100 Gigabit Ethernet interface which uses only 4 watts per gigabit. Alternative energy base stations run by wind, solar and bio-fuel cells have been developed by their Alternative Energy Programme to help spread wireless access to areas without electricity. Alcatel-Lucent is spearheading a new project Energy Aware Radio and neTwork tecHnologies (EARTH). The project hopes to develop technology which will cut energy consumption in half. The project is primarily focused on the future 3rd Generation Partnership Project's (3GPP) mobile cellular systems Long Term Evolution (LTE), and Long Term Evolution-Advanced (LTE-A) [BARTH09].
2.2 Cisco Systems
In 2007, Cisco Systems brought in their resident �green guru� Paul Marcoux. Mr. Marcoux is in charge of the Green Engineering team and has started work studying all of Cisco�s products and determining if any changes need to be made to restore them to the company's new green initiative. Network management products are in the works that will allow users to see the current power consumption statistics of any device connected to the network. Mr. Marcoux expects green products from Cisco to be ready for deployment in the next couple of years. Cisco realizes that the green movement needs to happen at the social level. Companies have the ability to create products that use less power, but people must first begin to support the green state of mind before these products can be used successfully [HICKEY07].
These are only a few of the companies that are making strides to green their technologies. Everyone is working around the clock to get these technologies consumer ready. Whatever company can roll out their green products first will stand to have an enormous advantage over the rest of the field. Once one company earns the support of the public for its energy saving products all other vendors will be forced to follow suit successfully completing the green revolution. It is important to get in on the action sooner rather than later. Being know as the "green" company can help a business continue to gain customers even after every vendor has energy efficient products.
Back to Table of Contents
3.0 Efforts around the World
The green movement is not just something going on in America. It is a worldwide phenomenon that is changing the way people think about consumer goods. As developing nations work to catch up with more technologically advanced areas they are vendors� biggest customers. They stand together as a large market looking for cheap and energy efficient products. Green networks are not just about using less power it also helps areas provide wireless services to citizens that would otherwise be without.
3.1 Sri Lanka
Last year Sri Lanka�s main telecommunication company Dialog Telkom began tests in rural areas of the country to determine which forms of alternate energies can be used to power base stations in hopes of increasing mobile phone coverage. The company is looking into wind turbines and solar panels to decide if one option or a combination of the two can be used throughout the country. Developing countries pose the last great market for telecommunication companies and by finding a way to expand into new areas to create larger access areas around the world [ANDERSON09]. With many people giving up their land lines for cellular phones, it becomes even more important for coverage areas to increase and be able to accommodate larger user bases without the need to increase prices.
3.2 China
In February, 100 internet service providers in China signed a proposal to create a green mobile internet for the country. 60.8% of internet users in China use their phones to access information. With this extra demand on 3G networks it is important for China to have a reliable and energy efficient system. With all of the providers working together it will make the internet more cohesive and allow service throughout the country for all users [CHINA10]. The popularity of the Iphone and BlackBerry have progressed phones from the voice market and well into the data market. This is forcing vendors to develop new technologies with higher speeds while at the same time using less energy than the existing equipment.
As countries continue to develop it is important that technology advances with them. With a growing amount of people having internet access either in their homes or on their phones it is important that service providers can handle the added bandwidth without having to pass additional costs onto the user or having to accept it as a sunk cost. A green network allows for more users at a cheaper price, this way everyone wins.
Back to Table of Contents
4.0 Power over Ethernet
With the rising power consumption associated with high density computing equipment the going green movement couldn't come sooner for some businesses. According to the EPA, servers and their related equipment were responsible for 1.5% of the electricity used in America in 2006. The most power hungry piece of equipment is the switch. With the growing fascination with Power over Ethernet (PoE), many IT managers are being held responsible to find equipment that will help relieve the high electric bills [FODALE08].
PoE delivers electrical power as well as data over the twisted pair from the switch to the equipment at the other end, usually an IP phone. The convenience associated with powering equipment in this way has led to a dramatic increase in the number of PoE units shipped. The downside is that these types of switches use 10x more energy than standard switches. Also, PoE switches are used to power critical equipment and therefore require battery backups in case the power were to go out as well as fans to keep the units cool. A new standard is in development for these units which would supply 56 watts per port(see Figure 1 to see how this will affect power consumption and ultimately the electric bill) [FODALE08].
Figure 1: PoE power consumption
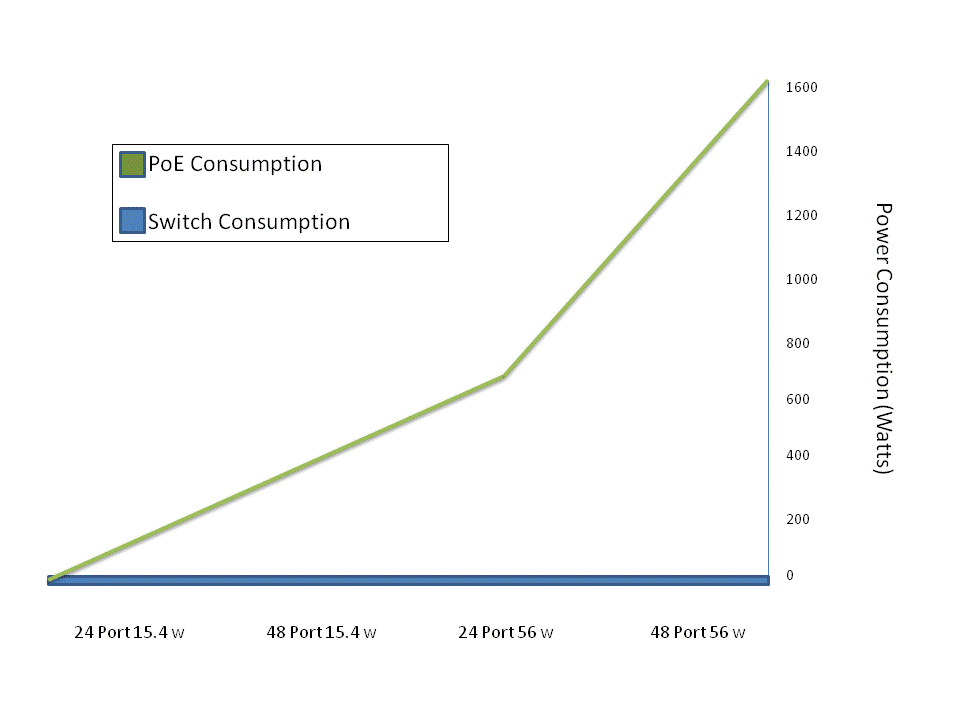
As switches expand to contain more and more ports, the cost to power them has jumped through the roof. Not only does PoE require electricity but with the added heat, it becomes even more important to have cooling systems in place to prevent overheating. At the same time the only way to power the cooling systems is with more electricity. At this time vendors are looking to programmers to write software that will be able to power down switches when not in use hoping to lower average power consumption and most importantly electric bills for the consumers.
Back to Table of Contents
5.0 Summary
This paper has shown the steps taken by telecommunication companies and countries to green their hardware and expand coverage to citizens in rural areas. It also discussed the power hungry and widely popular Power over Ethernet switch and how it has affected decisions made in the workplace. As more people demand energy efficient products vendors will roll out new equipment capable of keeping using less energy while supporting more users. As we move into the future the green buzz word will disappear as it becomes the norm as opposed to a dream.
Back to Table of Contents
6.0 References
[HARRISON09] Erin Harrison, "Green Technology- Green Mobile Networks Poised to Radically Reduce CO2 Emissions," http://green.tmcnet.com/topics/green/articles/60430-green-mobile-networks-poised-radically-reduce-co2-emissions.htm 7-22-2009
[PIKER09] Piker Research, "Green Telecom Networks," http://www.pikeresearch.com/research/green-telecom-networks 2009
[BARTH09] Ulrich Barth, Patty Wong, Didier Bourse, "Key Challenges for Green Networking," http://ercim-news.ercim.eu/en79/special/key-challenges-for-green-networking 10-2009
[HICKEY07] Andrew Hickey, "Cisco Urges Going Green," http://www.crn.com/networking/205101470 12-20-2007
[ANDERSON09] Tatum Anderson, "Green mobile network for rural Sri Lanka under trial," http://www.scidev.net/en/news/green-mobile-network-for-rural-sri-lanka-under-tri.html 3-18-2009
[CHINA10] China Tech News, "Chinese Wireless Providers Work Towards Green Mobile Internet," http://www.chinatechnews.com/2010/02/22/11608-chinese-wireless-providers-work-towards-green-mobile-internet 2-22-2010
[FODALE08] Victoria Fodale, Scott Scherer, "Green Networking Equipment: Who Leads and Who Lags," In-Stat, 2-2008
Back to Table of Contents
7.0 Acronyms
| 3GPP | 3rd Generation Partnership Project |
| EARTH | Energy Aware Radio and neTwork tecHnologies |
| LTE | Long Term Evolution |
| LTE-A | Long Term Evolution-Advanced |
| PoE | Power over Ethernet |
Back to Table of Contents
Last Modified: April 21, 2010.
This paper is available on line at http://www.cse.wustl.edu/~jain/cse574-10/index.html

