The
ExcessFairShareterm is defined as follows:
This divides the excess available bandwidth (
![]() ) proportional to the weights w(i).
) proportional to the weights w(i).
The activity level for a given VC is defined as follows:
The activity level can be used to accurately estimate the effective number of VCs [ 3]. We extend this notion to the weighted case by multiplying the weight function with the activity level of the ExcessFairShareterm. Therefore the ExcessFairShareis:
In Algorithm A, the Excess_ERis calculated based on the VCShareand the ExcessFairShareterms.
End_of_Interval_Accounting():
foreach VC i
| AL(i) |
|
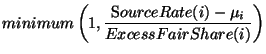 |
(20) |
| ExcessFairShare(i) |
|
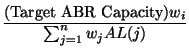 |
(21) |
Calculate_Excess_ER():
|
|
|
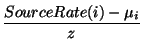 |
(22) |
|
|
|
|
(23) |