Trilateration in Robotic Sensing using Acoustic Sensors Errors
<sidebar>Trilateration_in_Robotic_Sensing_using_Acoustic_Sensors_Nav</sidebar>
Error
Reducing error in our algorithm is one of the primary goals of this project. Accountable error can be attributed to two causes; quantization and noise.
Quantization
When our microphone hears the chirps it takes discrete samples. When we're estimating range, then, we can only place the source of each chirp at set intervals. More than likely the point we want to locate is not at one of those intervals but our algorithm will say it is. We are left with a quantization error which might be as large as half the distance between samples.
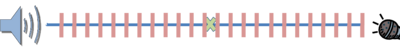
The following image illustrates this problem. The red lines represent the possible distances cross-correlation can report to us. Anything which falls between those lines has to be rounded to the nearest one. The green X, for instance, is a position we cannot calculate, and if our speaker were there we would have to say it was positioned either at the red line to the left or the one to the right, creating an error.
Reducing this Error:
Increasing the sample rate reduces the space between these intervals, increasing or resolution and decreasing quantization error.
Noise
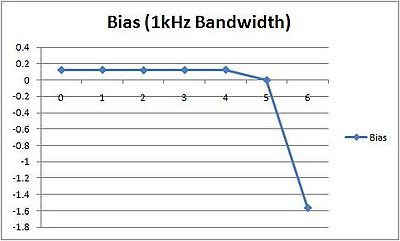
While our filters help isolate each signal, there will still be noise at any given frequency. Depending on how loud that noise is compared to the chirp, it can impact the results of cross-correlation and create an error. We ran a series of simulations to determine how large this effect was.
Reducing this Error: ...