
Product: ABAQUS/Standard
The tests in this section verify crack propagation between two surfaces that are initially partially bonded. They test the crack propagation capability from a single crack tip as well as multiple crack tips. All three fracture criteria (the critical stress criterion, the crack length versus time criterion, and the COD criterion) are verified.

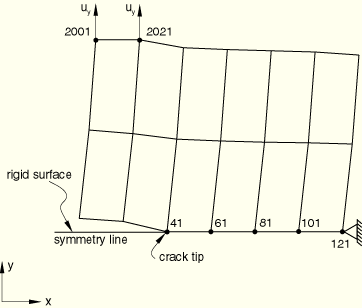
In the symmetry model the top half of a single-edge notch plate is modeled with a mesh of 2 × 6 CPE4 elements. The lower surface of the bottom row of elements defines the slave surface of the partially bonded contact pair, and the master surface is defined by an analytical rigid surface. The master surface also lies along the symmetry plane. Nonzero displacement boundary conditions are applied at two nodes remote from the symmetry plane. The time for bond failure and the position of the node at which the bond failure occurs (obtained from pdebnods.inp) are used to give the crack length versus time data in pdebcrgr.inp. The crack opening displacement at a distance behind the crack tip (obtained from pdebnods.inp) is used to specify the data for the COD criterion in pdebcods.inp. The stresses at a distance ahead of the crack tip (obtained from pdebnods.inp) are used to specify the data in pdebnodsd.inp. The time from pdebnods.inp is also used to set the time period for each step in pdebchck.inp.
The complete mesh is analyzed in pdebnods2.inp, pdebcrgr2.inp, and pdebcods2.inp.
Input files pdebnodnlg.inp, pdebcrgnlg.inp, and pdebcodnlg.inp consider finite deformation and finite sliding. The crack length versus time data for pdebcrgnlg.inp and the COD data for pdebcodnlg.inp are obtained from pdebnodnlg.inp.
The time at bond failure, the remaining fraction of the stress at debonding, the remaining debond stress, and all element stresses and strains must be the same for corresponding increments of tests pdebnods.inp, pdebcrgr.inp, and pdebcods.inp. At the total time corresponding to the end of each step in pdebchck.inp, the stresses and strains in the continuum elements are the same for all three tests. The same results are obtained for the models analyzed in pdebnods2.inp, pdebcrgr2.inp, and pdebcods2.inp.
The results obtained from pdebnodnlg.inp are compared with that of pdebcodnlg.inp and pdebcrgnlg.inp. The time at bond failure, the debond stress at failure, and the element stresses and strains are the same at the corresponding times.
The following problems test the crack propagation capability for an edge crack notch plate with symmetry conditions taken into account:
Tests crack propagation using a critical stress criterion. The distance ahead of the crack tip at which the critical stress is evaluated is set to zero.
Tests crack propagation capability by using the crack length versus time criterion.
Tests crack propagation capability by using the COD criterion.
Checks this procedure without using any contact surface definitions by simulating the debonding by *BOUNDARY, OP=NEW with multiple steps.
Tests crack propagation capability by considering the critical stress at a distance ahead of the crack tip. The distance ahead of the crack tip at which the critical stress is evaluated is varied from step to step.
The following problems simulate the complete model:
Tests crack propagation capability by using a critical stress criterion. The distance ahead of the crack tip at which the critical stress is evaluated is set to zero.
Tests crack propagation capability by using the crack length versus time criterion.
Tests crack propagation capability by using the COD criterion.
The following verification tests involve finite deformation and finite sliding:
Tests crack propagation capability by using a critical stress criterion. The distance ahead of the crack tip at which the critical stress is evaluated is set to zero.
Tests crack propagation capability by using the crack length versus time criterion.
Tests crack propagation capability by using the COD criterion.
The following files simulate crack propagation in the symmetry model using 8-node elements:
Tests crack propagation capability by using a critical stress criterion. The distance ahead of the crack tip at which the critical stress is evaluated is set to zero.
Tests crack propagation capability by using the crack length versus time criterion.
Tests crack propagation capability by using the COD criterion.

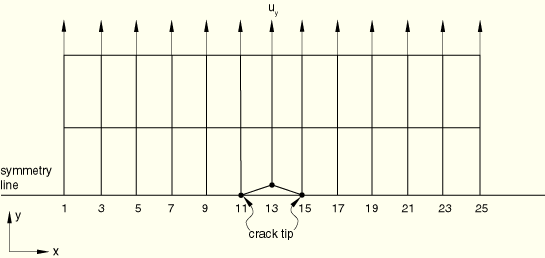
The top half of a center cracked plate is modeled with a mesh of 2 × 12 CPE4 elements. The lower surface of the bottom row of elements is used to define the slave surface of the partially bonded contact pair, and the master surface is defined by an analytical rigid surface. The master surface also lies on the symmetry plane. Nonzero displacement boundary conditions are applied on the top row of nodes.
The time for bond failure and the position of the node at which the bond failure occurs (obtained from pdebnodcc1.inp) are used to give the crack length versus time data in pdebcrgcc1.inp. The reference point for the crack length versus time criterion is defined such that the crack propagation occurs simultaneously from both the crack tips.
The crack opening displacement at a distance behind the crack tip (obtained from pdebcodcc1.inp) is used to specify the data for the COD criterion in pdebcodcc1.inp.
The complete mesh is analyzed in pdebnodcc2.inp, pdebcodcc2.inp, and pdebcrgcc2.inp.
The time to bond failure and the debond stress at the time of bond failure are the same in all the tests. The stresses and strains in the elements are the same at a given time in all the tests.
Tests crack propagation using a critical stress criterion. The distance ahead of the crack tip at which the critical stress is evaluated is set to zero.
Tests crack propagation capability by using the crack length versus time criterion.
Tests crack propagation capability by using the COD criterion.
The following input files simulate the complete model:
Tests crack propagation using a critical stress criterion. The distance ahead of the crack tip at which the critical stress is evaluated is set to zero.
Tests crack propagation capability by using the crack length versus time criterion.
Tests crack propagation capability by using the COD criterion.

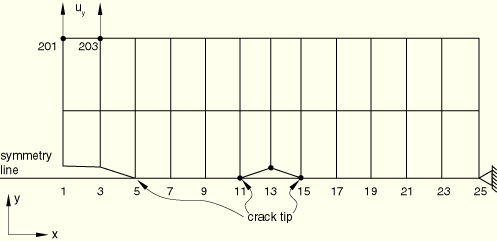
The top half of a plate that consists of an edge crack and a center crack is modeled with a mesh consisting of 2 × 12 CPE4 elements. The bottom surface of the lower row of elements is used to define the slave surface of the initially partially bonded contact pair. The master surface of the contact pair is defined by an analytical rigid surface and also lies along the symmetry plane. Nonzero displacement boundary conditions are applied at two nodes remote from the bonded plane, as shown in the figure.
The complete mesh is analyzed in pdebcrgco2.inp and pdebcodco2.inp.
The time to bond failure and the debond stress at the time of bond failure are the same in all the tests. The stresses and strains in the elements are the same at a given time in all the tests.
The following series of tests is used to demonstrate crack propagation and coalescence of two cracks:
Tests crack coalescence by using the crack length versus time criterion.
Tests crack coalescence by using the COD criterion.
The following input files simulate the complete model:
Tests crack coalescence by using the crack length versus time criterion.
Tests crack coalescence by using the COD criterion.

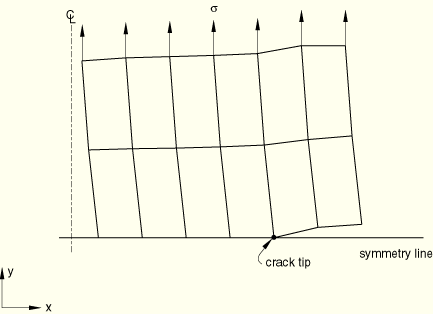
The problem of a round bar with an external notch (crack) subjected to tensile loading is analyzed as an axisymmetric case. Only the top half is modeled in pdebnodax1.inp, pdebcrgax1.inp, and pdebcodax1.inp. The mesh consists of 2 × 6 CAX4 elements. The lower surface of the bottom row of elements is used to define the slave surface, while the master surface is defined by an analytical rigid surface. A far-field load ![]() is applied.
is applied.
Input file pdebnodax1.inp uses the critical stress criterion for crack propagation analysis. The crack length versus time data for pdebcrgax1.inp and the crack opening displacement versus cumulative incremental crack length for pdebcodax1.inp are obtained from pdebnodax1.inp.
The complete mesh is analyzed in pdebnodax2.inp, pdebcrgax2.inp, and pdebcodax2.inp.
The time to bond failure and the debond stress at the time of bond failure are the same in all the tests. The stresses and strains in the elements are the same at a given time in all the tests.
The following tests are used to verify the crack propagation capability for axisymmetric elements:
Tests crack propagation using a critical stress criterion. The distance ahead of the crack tip at which the critical stress is evaluated is set to zero.
Tests crack propagation by using the crack length versus time criterion.
Tests crack propagation by using the COD criterion.
The following input files simulate the complete model:
Tests crack propagation using a critical stress criterion. The distance ahead of the crack tip at which the critical stress is evaluated is set to zero.
Tests crack propagation by using the crack length versus time criterion.
Tests crack propagation by using the COD criterion.

The debond variables are identical to those obtained in the original analysis.
Tests the *POST OUTPUT option. The restart file from pdebnods.inp is needed to run this input file.