14.2.2 Infinite element library

Products: ABAQUS/Standard ABAQUS/Explicit
References
Element types

Plane strain solid continuum infinite elements
| CINPE4 | 4-node linear, one-way infinite |
|
| CINPE5R(S) | 5-node quadratic, one-way infinite |
|
Active degrees of freedom
1, 2
Additional solution variables
None.
Plane stress solid continuum infinite elements
| CINPS4 | 4-node linear, one-way infinite |
|
| CINPS5R(S) | 5-node quadratic, one-way infinite |
|
Active degrees of freedom
1, 2
Additional solution variables
None.
3-D solid continuum infinite elements
| CIN3D8 | 8-node linear, one-way infinite |
|
| CIN3D12R(S) | 12-node quadratic, one-way infinite |
|
| CIN3D18R(S) | 18-node quadratic, one-way infinite |
|
Active degrees of freedom
1, 2, 3
Additional solution variables
None.
Axisymmetric solid continuum infinite elements
| CINAX4 | 4-node linear, one-way infinite |
|
| CINAX5R(S) | 5-node quadratic, one-way infinite |
|
Active degrees of freedom
1, 2
Additional solution variables
None.
2-D acoustic infinite elements
| ACIN2D2 | 2-node linear, acoustic infinite |
|
| ACIN2D3(S) | 3-node quadratic, acoustic infinite |
|
Active degree of freedom
8
3-D acoustic infinite elements
| ACIN3D3 | 3-node linear, acoustic infinite triangular element |
|
| ACIN3D4 | 4-node linear, acoustic infinite quadrilateral element |
|
| ACIN3D6(S) | 6-node quadratic, acoustic infinite triangular element |
|
| ACIN3D8(S) | 8-node quadratic, acoustic infinite quadrilateral element |
|
Active degree of freedom
8
Axisymmetric acoustic infinite elements
| ACINAX2 | 2-node linear, acoustic infinite |
|
| ACINAX3(S) | 3-node quadratic, acoustic infinite |
|
Active degree of freedom
8
Element property definition

For two-dimensional, plane strain, and plane stress elements, you must provide the thickness of the elements; by default, unit thickness is assumed.
For three-dimensional and axisymmetric solid elements, you do not need to specify a thickness.
For acoustic elements, you must specify the coordinates of the reference point in addition to the thickness.
Element-based loading

None.
Element output

Stress, strain, and other tensor components
No output is available from ABAQUS/Explicit for infinite elements. Stress and other tensors (including strain tensors) are available from ABAQUS/Standard for infinite elements with displacement degrees of freedom. All tensors have the same components. For example, the stress components are as follows:
S11 | 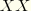 direct stress or radial stress for axisymmetric elements. direct stress or radial stress for axisymmetric elements.
|
S22 | 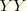 direct stress or axial stress for axisymmetric elements. direct stress or axial stress for axisymmetric elements.
|
S33 | 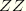 direct stress (not available for plane stress elements) or hoop stress for axisymmetric elements. direct stress (not available for plane stress elements) or hoop stress for axisymmetric elements.
|
S12 | 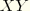 shear stress or shear stress for axisymmetric elements. shear stress or shear stress for axisymmetric elements.
|
S13 | 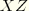 shear stress (not available for plane stress, plane strain, and axisymmetric elements). shear stress (not available for plane stress, plane strain, and axisymmetric elements).
|
S23 | 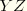 shear stress (not available for plane stress, plane strain, and axisymmetric elements). shear stress (not available for plane stress, plane strain, and axisymmetric elements).
|
Node ordering and face numbering on elements

Plane stress and plane strain solid continuum elements
Axisymmetric solid continuum elements
Three-dimensional solid continuum elements
Two-dimensional and axisymmetric acoustic infinite elements
Three-dimensional acoustic infinite elements
Numbering of integration points for output

Plane stress and plane strain solid continuum elements
Axisymmetric solid continuum elements
Three-dimensional solid continuum elements
This shows the scheme in the layer closest to the 1–2–3–4 face. The integration points in the second layer are numbered consecutively.



![]() ,
, ![]()
![]() ,
, ![]()
![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]()
![]() ,
, ![]()

