
Products: ABAQUS/Standard ABAQUS/CAE

The hypoelastic material model:
is valid for small elastic strains—the stresses should not be large compared to the elastic modulus of the material;
is used when the load path is monotonic; and
must be defined by user subroutine UHYPEL if temperature dependence is to be included.

In a hypoelastic material the rate of change of stress is defined as a tangent modulus matrix multiplying the rate of change of the elastic strain:
![]()

The entries in ![]() are provided by giving Young's modulus,
are provided by giving Young's modulus, ![]() , and Poisson's ratio,
, and Poisson's ratio, ![]() , as functions of strain invariants. The strain invariants are defined for this purpose as
, as functions of strain invariants. The strain invariants are defined for this purpose as
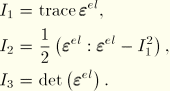
You can define the variation of Young's modulus and Poisson's ratio directly by specifying ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() .
.
| Input File Usage: | *HYPOELASTIC |
| ABAQUS/CAE Usage: | Property module: material editor: Mechanical |
If specifying ![]() and
and ![]() as functions of the strain invariants directly does not allow sufficient flexibility, you can define the hypoelastic material by user subroutine UHYPEL (“UHYPEL,” Section 25.2.26).
as functions of the strain invariants directly does not allow sufficient flexibility, you can define the hypoelastic material by user subroutine UHYPEL (“UHYPEL,” Section 25.2.26).
| Input File Usage: | *HYPOELASTIC, USER |
| ABAQUS/CAE Usage: | Property module: material editor: Mechanical |

For plane stress and uniaxial stress states ABAQUS/Standard does not compute the out-of-plane strain components. For the purpose of defining the above invariants, it is assumed that ![]() ; that is, the material is assumed to be incompressible. For example, in a uniaxial stress case (such as a truss element) this assumption implies that
; that is, the material is assumed to be incompressible. For example, in a uniaxial stress case (such as a truss element) this assumption implies that
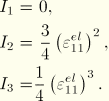

For large-displacement analysis the strain measure in ABAQUS is the integration of the rate of deformation. This strain measure corresponds to log strain if the principal directions do not rotate relative to the material. The strain invariant definitions should be interpreted in this way.

The hypoelastic material model can be used only by itself in the material definition. It cannot be combined with viscoelasticity or with any inelastic response model. See “Combining material behaviors,” Section 9.1.3, for more details.