3.5.4 Hybrid beam elements

The hybrid beam elements in ABAQUS/Standard are designed to handle very slender situations, where the axial stiffness of the beam is very large compared to the bending stiffness; and so a mixed method, where axial force is treated as an independent unknown, is required. For the shear beams mixed elements are provided where the transverse shear forces are also treated as independent unknowns. This section discusses the basis of these mixed methods.
Axial and bending behavior

The internal virtual work of the beam can be written
Alternatively, we can introduce an independent axial force variable,
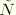
, and write
where
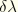
is a Lagrange multiplier introduced to impose the constraint
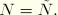
A linear combination of these expressions is
Then
The contribution of this term to the Newton scheme is then
where
The tangent stiffness of the section behavior gives
If
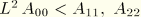
(where
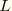
is the element length), then the beam is flexible axially and the mixed formulation is unnecessary. Otherwise, we assume that an inverse of the first equation above defines
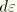
from
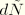
:
and so
Now using the first tangent section stiffness multiplied by

and the second multiplied by
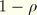
, the Newton contribution of the element becomes
where
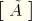
is
The variable
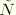
is taken as an independent value at each integration point in the element. We choose

as
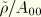
, where
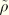
is a small value. With this choice, by ensuring that the variables
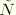
are eliminated after the displacement variables of each element, the Gaussian elimination scheme has no difficulty with solving the equations.
Transverse shear

In the mixed elements that allow transverse shear (B21H, B22H, B31H, B32H), the transverse shear constraints are imposed by treating the shear forces as independent variables, using the following formulation. The internal virtual work associated with transverse shear is
where
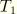
and
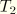
are shear forces on the section, and
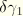
and
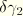
are variations of transverse shear strain. The virtual work can also be written by introducing independent shear force variables
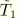
and
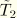
, as
where the
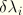
are Lagrange multipliers. As in the axial case, we take a linear combination of these two forms,
where

will be defined later. This gives
where
The contribution of this term to the Newton scheme is
ABAQUS treats transverse shear elastically, so 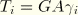 , where
, where 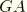 is constant. Then the Newton contribution is
is constant. Then the Newton contribution is
We now define 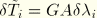 and choose
and choose 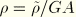 , where
, where 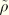 is a small value compared to
is a small value compared to 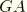 , to give
, to give


![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
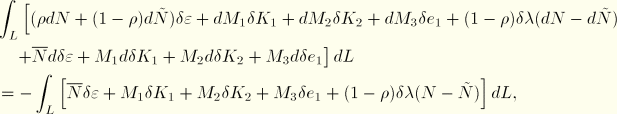
![]()
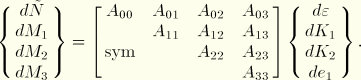
![]()
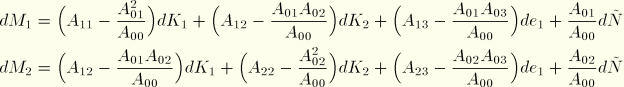
![]()
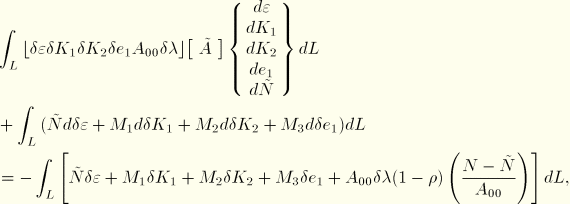
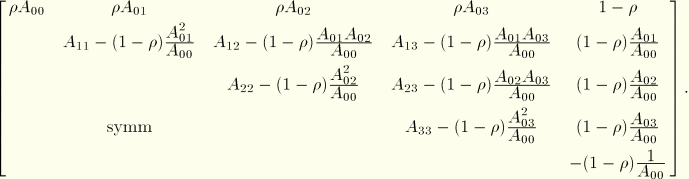

![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() , where
, where ![]() is constant. Then the Newton contribution is
is constant. Then the Newton contribution is ![]()
![]()
![]() and choose
and choose ![]() , where
, where ![]() is a small value compared to
is a small value compared to ![]() , to give
, to give ![]()
![]()